- Title
-
Rhombomere boundaries are Wnt signaling centers that regulate metameric patterning in the zebrafish hindbrain
- Authors
- Riley, B.B., Chiang, M.Y., Storch, E.M., Heck, R., Buckles, G.R., and Lekven, A.C.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
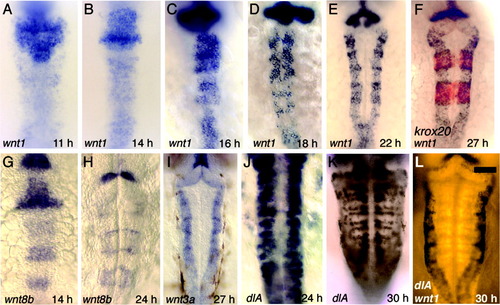
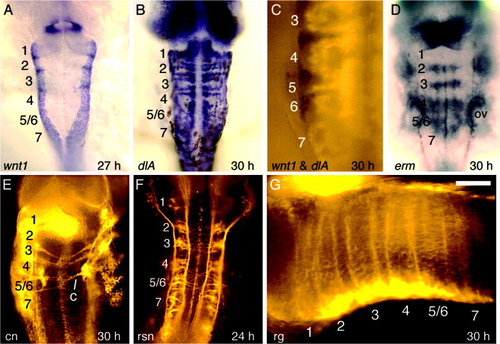
Progressive refinement of wnt expression. All figures show dorsal views of wild-type embryos with anterior to the top. A-F: Expression of wnt1 at 11 hours postfertilization (hpf, A), 14 hpf (B), 16 hpf (C), 18 hpf (D), 22 hpf (E), and 27 hpf (F). Also shown at 27 hpf is expression of krox20 (red), confirming that expression of wnt1 does indeed mark rhombomere boundaries. G,H: Expression of wnt8b at 14 hpf (G) and 24 hpf (H). I: Expression of wnt3a at 27 hpf. J,K: Expression of dlA at 24 hpf (J) and 30 hpf (K). L: Double staining, showing expression of wnt1 (black) and dlA (Fast Red fluorescence) at 30 hpf. Scale bar = 65 μm in L (applies to A-L). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
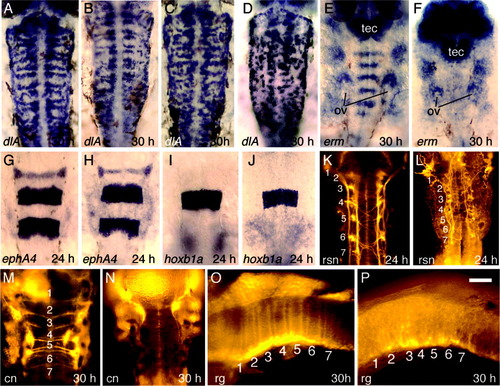
Hindbrain development in wnt-deficient embryos. A-D: Expression of dlA at 30 hours postfertilization (hpf) in a Dfw5 mutant (A), a Dfw5 mutant injected with wnt3a-morpholino oligomers (MOs) (B), a wild-type embryo coinjected with wnt3a-MO and wnt8b-MO (C), and a Dfw5 mutant coinjected with wnt3a-MO and wnt8b-MO (D). E,F: Expression of erm at 30 hpf in a wild-type embryo (E) and a Dfw5 mutant coinjected with wnt3a-MO and wnt8b-MO (F). The otic vesicles (ov) and optic tectum (tec) are indicated to serve as landmarks. G,H: Expression of ephA4 at 24 hpf in a wild-type embryo (G) and a Dfw5 mutant coinjected with wnt3a-MO and wnt8b-MO (H). I,J: Expression of hoxb1a at 30 hpf in a wild-type embryo (I) and a Dfw5 mutant coinjected with wnt3a-MO and wnt8b-MO (J). K,L: Anti-acetylated tubulin staining of reticulospinal neurons (rsn) at 24 hpf in a wild-type embryo (K) and a Dfw5 mutant coinjected with wnt3a-MO and wnt8b-MO (L). M,N: Immunostaining with zn8 antibody at 30 hpf in a wild-type embryo (M) and a Dfw5 mutant coinjected with wnt3a-MO and wnt8b-MO (N). The zn8 antibody recognizes a cell adhesion molecule related to DM-Grasp (Fashena and Westerfield, [1999]) and normally labels commissural neurons (cn), some cranial ganglia, pharyngeal arches, floor plate, and heart (Trevarrow et al., [1990]). Commissural neurons are not produced in the wnt-deficient embryo. O,P: Immunostaining with a combination of four antibodies, zrf1-zrf4 (Trevarrow et al., [1990]), was used to label radial glia (rg) at 30 hpf in a wild-type (O) and a Dfw5 mutant coinjected with wnt3a-MO and wnt8b-MO (P). Images show dorsal views with anterior to the top (A-N) or lateral views with anterior to the left (O,P). Numbers mark locations of the corresponding rhombomeres. Scale bar in P = 60 μm in O,P, 70 μm in A-D,G-N, 85 μm in E,F. |
|
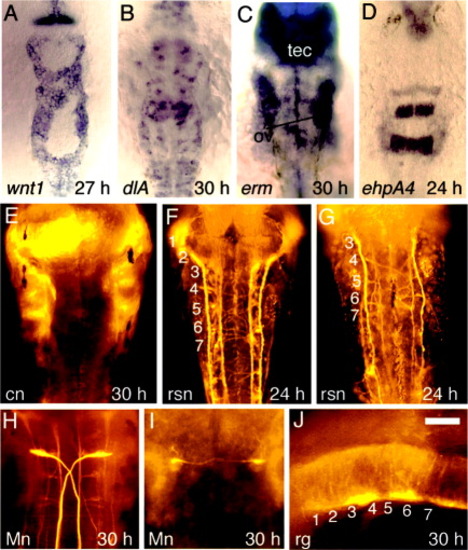
Hindbrain development in tcf3b morphants. All embryos are tcf3b morphants except in H, which depicts a wild-type embryo. A: Expression of wnt1 at 27 hours postfertilization (hpf). B: Expression of dlA at 30 hpf. C: Expression of erm at 30 hpf. The otic vesicles (ov) and tectum (tec) are indicated. D: Expression of ephA4 at 24 hpf. E: Immunostaining with zn8 antibody at 30 hpf shows that commissural neurons (cn) fail to form. Staining of segmental structures along the lateral edges of the hindbrain marks pharyngeal arches and portions of cranial ganglia just out of the plane of focus. F,G: Immunostaining of reticulospinal neurons (rsn) at 24 hpf with anti-acetylated tubulin shows varying degrees of patterning defects in tcf3b-morphants. H,I: 3A10 antibody staining of Mauthner neurons (Mn) at 30 hpf in a wild-type embryo (H) and a tcf3b morphant (I). J: Immunostaining of radial glia (rg) with zrf1-zrf4. Numbers mark locations of the corresponding rhombomeres. Images show dorsal views with anterior to the top (A-I) or a lateral view with anterior to the left (J). Scale bar in J = 60 μm in E,H,I, 75 μm in D,F,G,J, 120 μm in A-C. |
|
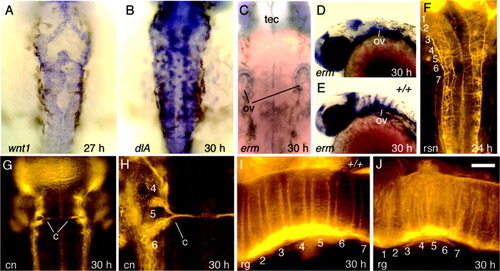
Hindbrain development in spg mutants. All embryos are spg homozygous mutants except for E and I, which show wild-type controls. A: wnt1 expression at 27 hours postfertilization (hpf). B: dlA expression at 30 hpf. C-E: erm expression at 30 hpf in spg mutants (C,D) and a wild-type embryo (E). Spatial patterns are highly variable between spg mutants, but the level of expression is invariably reduced. For landmarks, the otic vesicles (ov) and tectum (tec) are indicated. F: Reticulospinal neurons (rsn) labeled with anti-acetylated tubulin at 24 hpf. G,H: Commissural neurons (cn) labeled with zn8 antibody at 30 hpf. Commissural neurons are absent in anterior rhombomeres and in posterior rhombomeres produce aberrant commissures (c) through the center of the r5 region. H is an enlargement of the left side of the specimen shown in G. I,J: Radial glia (rg) labeled with zrf1-4 antibodies at 30 hpf in a wild-type embryo (I) and a spg mutant (J). The wild-type rg pattern is an enlargement of the specimen shown in Figure 2O. Numbers indicate the positions of corresponding rhombomeres. Images show dorsal views with anterior to the top (A-C,F-H) or a lateral view with anterior to the left (D,E,I,J). Scale bar in J = 25 μm in H, 50 μm in I,J, 65 μm in A-C,F,G, 150 μm in D,E. |
|
Hindbrain development in val mutants. All embryos are val homozygous mutants. A: wnt1 expression at 27 hours postfertilization (hpf). B: dlA expression at 30 hpf. C: Two-color in situ hybridization, showing wnt1 (black) and dlA (Fast Red fluorescence) on the left side of the hindbrain at 30 hpf. D: erm expression at 30 hpf. The position of the otic vesicles (ov) is indicated. E: Commissural neurons (cn) labeled with zn8 antibody at 30 hpf. The number and positions of commissural axons is highly variable in the posterior hindbrain. Note that the right side of the r5/6 region has only a single commissure (c), which is not in register with the two commissures on the left. F: Reticulospinal neurons (rsn) labeled with anti-acetylated tubulin at 24 hpf. G: Radial glia labeled with zrf1-4 antibodies at 30 hpf. All images show dorsal views with anterior to the top except for G, which shows a lateral view with anterior to the left. Numbers indicate corresponding rhombomeres. Scale bar in G = 50 μm in C,G, 70 μm in E, 90 μm in F, 120 μm in A,B,D. |
|
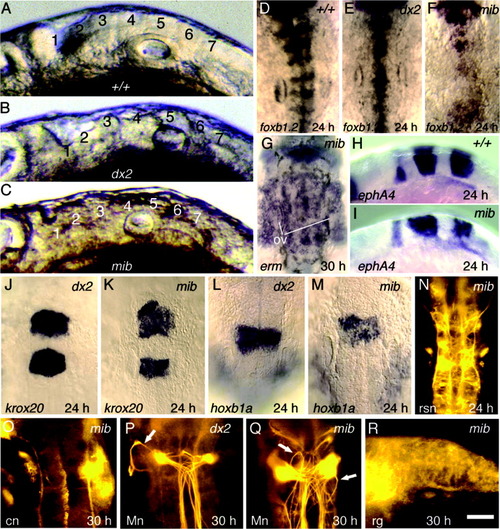
Hindbrain patterning in Delta-Notch mutants. A-C: Hindbrain morphology at 24 hours postfertilization (hpf) in wild-type (A), dlAdx2 (B), and mibta52b (C) embryos. Positions of rhombomeres 1-7 are indicated. D-F: Dorsal views, showing expression of foxb1.2 at 24 hpf in wild-type (D), dlAdx2 (E), and mibta52b (F) embryos. G: erm expression in mibta52b at 30 hpf. The otic vesicles (ov) are indicated to serve as landmarks. H,I: ephA4 expression at 24 hpf in a wild-type embryo (H) and a mibta52b mutant (I). J,K: Expression of krox20 at 24 hpf in dlAdx2 (J) and mibta52b (K) embryos. L,M: Expression of hoxb1a at 24 hpf in dlAdx2 (L) and mibta52b (M) embryos. N: Reticulospinal neurons (rsn) in a mibta52b mutant labeled with anti-acetylated tubulin at 24 hpf. O: zn8 antibody staining of a mibta52b mutant at 30 hpf shows that commissural neurons (cn) are not produced. P,Q: Mauthner neurons (Mn) labeled with 3A10 antibody at 30 hpf in dlAdx2 (P) and mibta52b (Q) embryos. Abnormal axonal trajectories are indicated (arrows). R: Radial glia (rg) labeled with zrf1-4 antibodies at 30 hpf in a mibta52b mutant. Images show lateral views with anterior to the left (A-C,H,I,R) or dorsal views with anterior to the top (D-G,J-Q). Scale bar in R = 55 μm in A-C, 75 μm in O-Q, 100 μm in R,125 μm in D-N. |
|
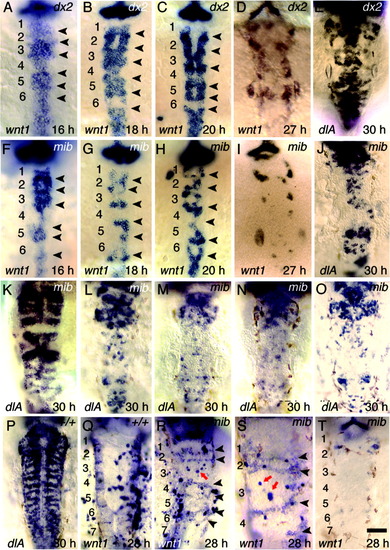
Expression of wnt1 and dlA in Delta-Notch mutants. All images show dorsal views with anterior to the top. A-D: wnt1 expression in dlAdx2 mutants at 16 hours postfertilization (hpf, A), 18 hpf (B), 20 hpf (C), and 27 hpf (D). E: dlA expression in a severely affected dlAdx2 mutant at 30 hpf. F-I: wnt1 expression in mibta52b mutants at 16 hpf (F), 18 hpf (G), 20 hpf (H), and 27 hpf (I). J: Expression of dlA in a mibta52b mutant at 30 hpf. K-N: dlA expression at 30 hpf in mibta52b mutants injected with pHS-wnt1-myc and subjected to serial heat shocks beginning at 16 hpf (K), no heat shock (L), a single heat shock delivered at 24 hpf (M), or serial heat shocks beginning at 24 hpf (N). O: expression of dlA at 30 hpf in a mibta52b mutant injected with pHS-GFP and given serial heat shocks beginning at 16 hpf. P: dlA expression in a wild-type embryo injected with pHS-wnt1-myc and given serial heat shocks beginning at 16 hpf. Q: wnt1 staining in a wild-type embryo injected with pHS-wnt1-myc and given serial heat shocks beginning at 16 hpf. R-T: wnt1 staining in mibta52b mutants injected with pHS-wnt1-myc and given serial heat shocks beginning at 16 hpf. Arrowheads indicate stripes of wnt1 expression at presumptive rhombomere boundaries. Note the close proximity of darkly stained plasmid-containing cells in or near each stripe of endogenous wnt1 (R,S), compared with the absence of endogenous wnt1 stripes when pHS-wnt1-myc is absent (T). Red arrows show groups of cells containing pHS-wnt1-myc in the center of rhombomere 3. This rhombomere is particularly easy to locate and assess, because it is abnormally large at this stage in mibta52b mutants, and its position relative to the anterior edge of the otic vesicle is highly reproducible. Note the absence of stripes of endogenous wnt1 expression in r-center cells surrounding plasmid-containing cells. Scale bar in T = 45 μm in S, 90 μm in A-R,T. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|

Unillustrated author statements EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|