- Title
-
Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway Is Strongly Implicated in Cadmium-Induced Developmental Neurotoxicity and Neuroinflammation: Clues from Zebrafish Neurobehavior and In Vivo Neuroimaging
- Authors
- Xu, Y., Liu, J., Tian, Y., Wang, Z., Song, Z., Li, K., Zhang, S., Zhao, H.
- Source
- Full text @ Int. J. Mol. Sci.
|
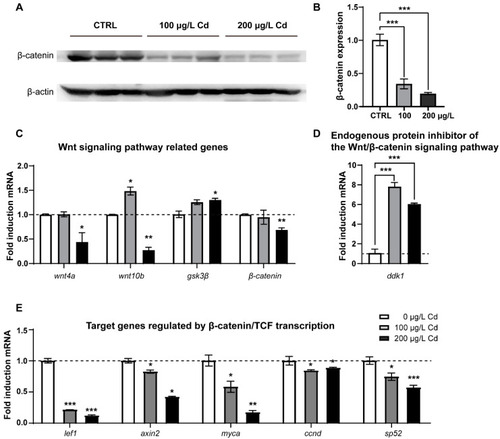
Cd2+ exposure inhibited zebrafish Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. ( |
|
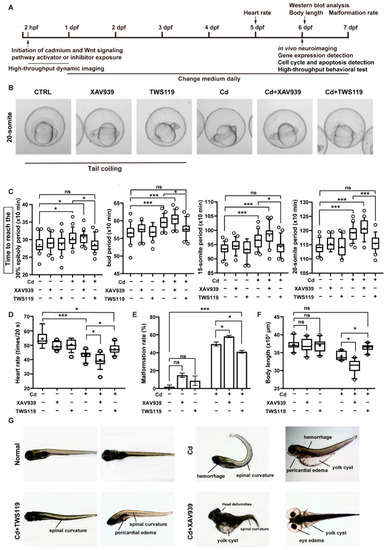
Activation of Wnt signaling pathway attenuated the adverse effects of Cd2+ on zebrafish early development. ( PHENOTYPE:
|
|
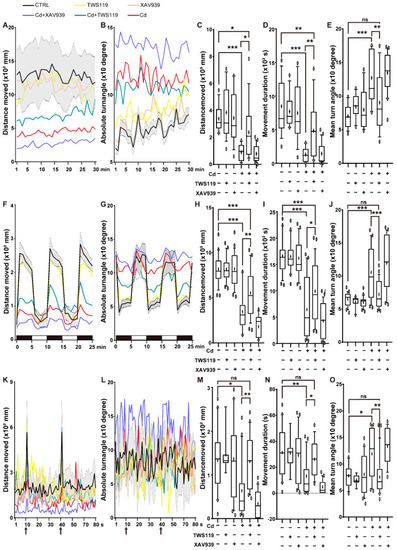
Patterns of zebrafish locomotor activities and reactivity to light–dark/vibration stimulation. Swimming distance, velocity of 6 dpf zebrafish larvae in open field tests ( PHENOTYPE:
|
|
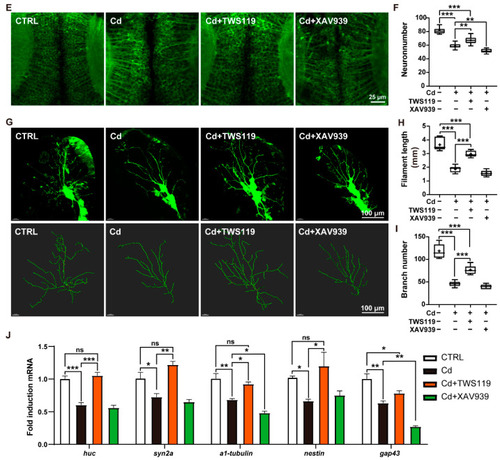
Involvement of zebrafish Wnt signaling pathway in Cd2+-induced neurodevelopmental disorders. ( |
|
Involvement of zebrafish Wnt signaling pathway in Cd2+-induced neurodevelopmental disorders. ( |
|
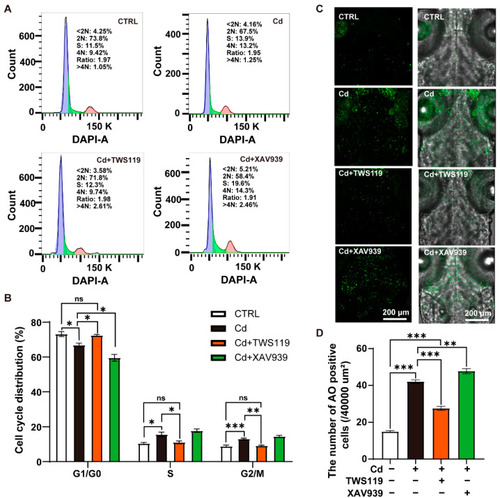
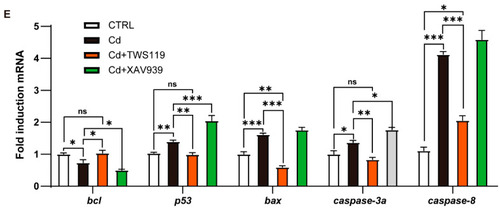
Apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in zebrafish larvae caused by Cd2+ are mediated by Wnt signaling pathway. ( |
|
Apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in zebrafish larvae caused by Cd2+ are mediated by Wnt signaling pathway. ( |
|
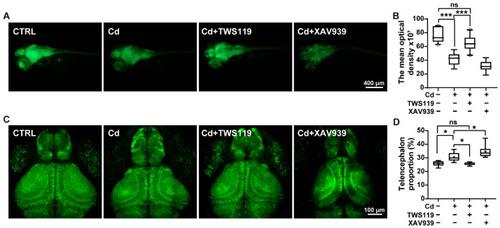
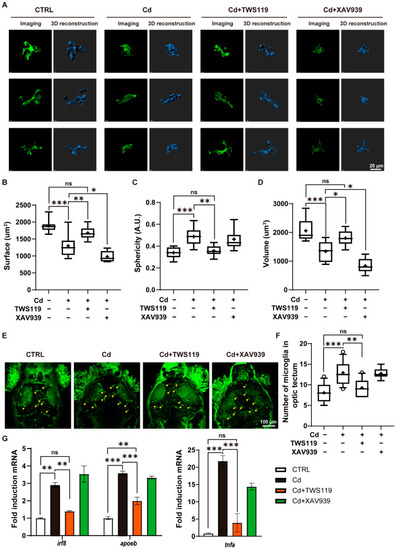
Role of zebrafish Wnt signaling pathway in Cd2+-induced microgliosis and neuroinflammation. ( |