- Title
-
Vegfc acts through ERK to induce sprouting and differentiation of trunk lymphatic progenitors
- Authors
- Shin, M., Male, I., Beane, T.J., Villefranc, J.A., Kok, F.O., Zhu, L.J., Lawson, N.D.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
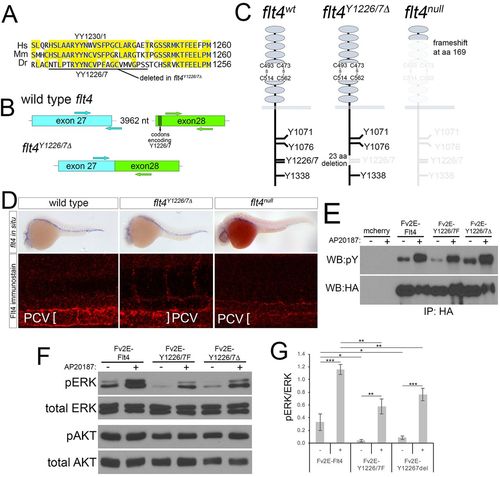
Targeted deletion of Flt4 Y1226/7. (A) Flt4 cytoplasmic domains from human (Hs), mouse (Mm), and zebrafish (Dr). YY1226/7 and 23 amino acid deletion in flt4Y1226/7? mutants are shown. (B) Schematic of wild-type flt4 and flt4Y1226/7? genomic loci. Positions of TALEN pairs in exon 27 and exon 28 are indicated by arrows and codons encoding Y1226/7 are noted. (C) Schematics of wild-type, Flt4Y1226/7? and Flt4null receptors. Residues eliminated by targeted deletions are grayed out. (D) Top: whole-mount in situ hybridization using a digoxigenin-labeled antisense flt4 riboprobe on embryos of the indicated genotype at 25?hpf. Bottom: whole-mount immunostaining using a polyclonal antibody against zebrafish Flt4 at 30?hpf. (E) Immunoprecipitates from human embryonic kidney cells transfected with the indicated constructs and treated with AP20187 to dimerize Fv2E (+), or left untreated (?). Antibodies used for immunoprecipitation (IP) or western blot are indicated. pY, phophotyrosine; HA, hemagglutinin. (F) Western blot analysis of lysates from cells transfected with the indicated construct and treated with AP20187 (+), or left untreated (?). (G) Quantification of pERK/ERK ratio from triplicate western blots (as in F). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001; error bars are ħs.d. |
|
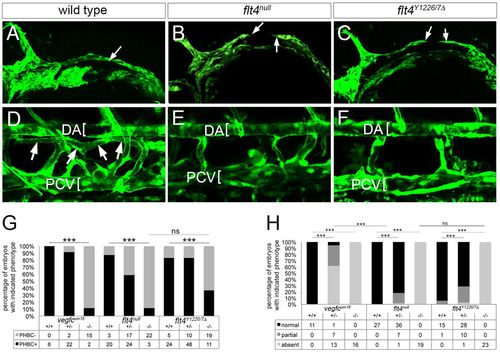
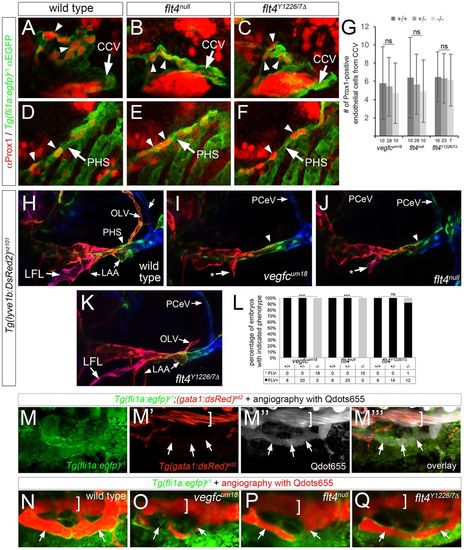
Signaling through Flt4 Y1226/7 is required for vein and lymphatic development. (A-C) Two-photon microscopy of GFP immunostaining in Tg(fli1a:egfp)y1 embryos of the indicated genotype at 26?hpf; arrows denote fully or partially formed primordial hindbrain channel (PHBC). (D-F) Confocal microscopy of live Tg(fli1a:egfp)y1 larvae of the indicated genotype at 5?dpf. DA and PCV are denoted by brackets. Thoracic duct (TD) is indicated by arrows in D. (G) Percentage of embryos with the indicated genotype and PHBC formation at 26?hpf. (H) Percentage of embryos of the indicated genotype with TD formation. In G,H, numbers of embryos scored in each category are indicated; ***P<0.001; ns, not significant. In A-F, lateral views, anterior to the left, dorsal is up. |
|
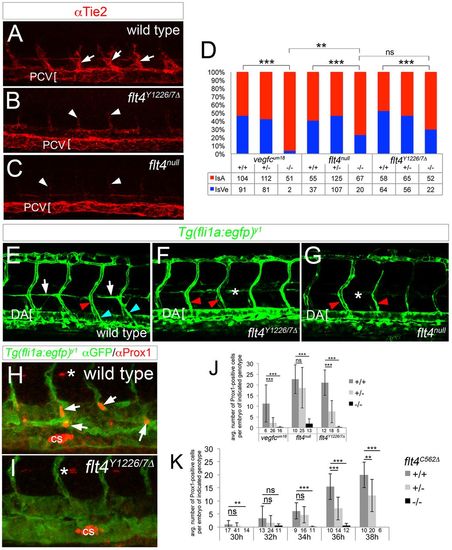
Signaling through Y1226/7 is essential for initial lympho-venous sprouting and lymphatic differentiation. (A-C) Confocal microscopy of Tie2 immunostaining at 36?hpf. Arrows denote lympho-venous sprouts which give rise to trunk lymphatic and intersomitic vein (ISV) in wild-type embryos; arrowheads indicate intersomitic arteries (ISAs), which display Tie2 faint immunostaining in all embryos. Bracket indicates PCV. (D) Percentage of ISA or ISV connections at 72?hpf in embryos of the indicated genotype as determined by angiography. Total numbers of vessels counted for analysis are indicated. (E-G) Confocal microscopy of live Tg(fli1a:egfp)y1 embryos of the indicated genotype at 48?hpf. White arrows denote parachordal cells (PACs) in wild-type embryos. Blue and red arrowheads indicate ISVs and ISAs, respectively. Asterisks denote normal position of PACs; occasional fluorescence is observed in non-endothelial cells at the horizontal myoseptum (e.g. panel F). (H,I) Confocal images of Prox1 (red) and GFP (green) immunostaining in Tg(fli1a:egfp)y1 embryos of the indicated genotype at 36?hpf. Arrows denote Prox1-expressing endothelial cells in lymphatic sprouts; Corpuscle of Stannius (cs) is indicated and asterisk denotes Prox1-positive muscle pioneer. (J,K) Average number of Prox1-positive venous endothelial cells and lymphatic sprouts per embryo of the indicated genotype and at 36 hpf (J) or the indicated stage (K). Total number of embryos scored in each category is indicated on the x-axis. (D,J,K) **P<0.01, ***P<0.001; ns, not significant. Error bars are ħs.d. (A-C,E-I) Lateral views, anterior to the left, dorsal is up. Genotype is indicated for each panel. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
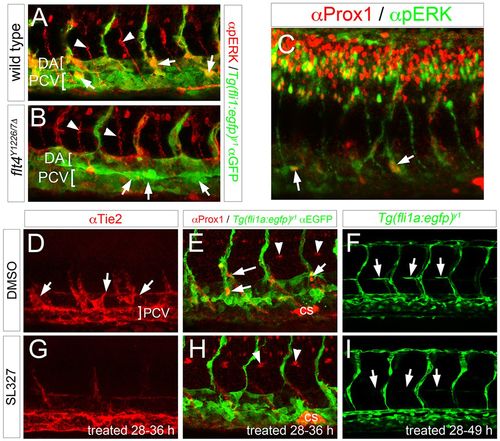
ERK signaling is essential for trunk lymphatic morphogenesis and differentiation. (A-I) Confocal images; lateral views, anterior to the left, dorsal is up. (A,B) pERK (red) and GFP (green) immunostaining in Tg(fli1a:egfp)y1 embryos of the indicated genotype at 34?hpf. Arrows denote pERK-positive lympho-venous sprouts, arrowheads indicate pERK staining in motor neurons. Brackets indicate DA and PCV. (C) Prox1 (red) and pERK (green) immunostaining in a wild-type embryo at 38?hpf. Arrows denote endothelial cells that are positive for Prox1 and pERK in lymphatic sprouts or dorsal wall of PCV. (D-I) Embryos treated with DMSO (D-F) or 15?µM SL327 (G-I). Treatment time is indicated. (D,G) Tie2 immunostaining; arrows denote lympho-venous sprouts, PCV indicated by bracket. (E,H) Prox1 (red) and GFP (green) immunostaining of Tg(fli1a:egfp)y1 embryos at 36?hpf; arrows denote Prox1-positive lymphatic sprouts, arrowheads indicate muscle pioneers and Corpuscle of Stannius (cs) is indicated. (F,I) Live Tg(fli1a:egfp)y1 embryos at 49?hpf. Arrows indicate parachordal cells, or absence thereof. |
|
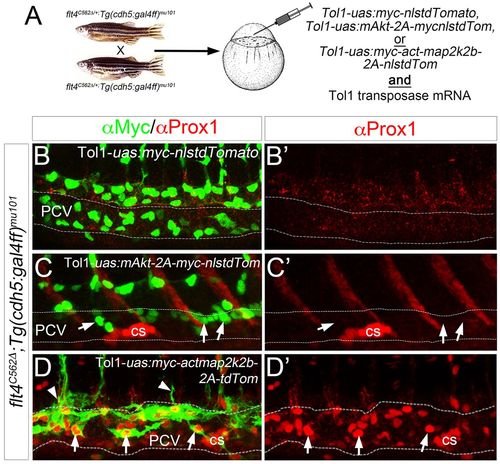
ERK activation rescues early lymphatic morphogenesis and differentiation in the absence of Flt4 signaling. (A) Schematic depicting injection strategy for rescue experiments. (B-D?) Confocal microscopy of Tg(cdh5:gal4ff)mu101;flt4C562? mutant embryos injected with Tol1-uas:myc-nlstdTomato (B), Tol1-uas:mAkt-2a-myc-nlstdTomato (C) or Tol1-uas:myc-actmap2k2b-2a-tdTomato (D) along with mRNA encoding Tol1 Transposase. (B-D) Overlay of Prox1 (red) and Myc (green) immunostaining to visualize transgene expression in injected embryos at 38?hpf. Arrows indicate transgene-expressing cells; arrowheads indicate transgene-expressing cells that are sprouting from the PCV. (B?-D?) Prox1 immunostaining (red) in same injected embryos as in B-D. Corpuscle of Stannius (cs) is indicated. Dashed lines outline the PCV. |
|
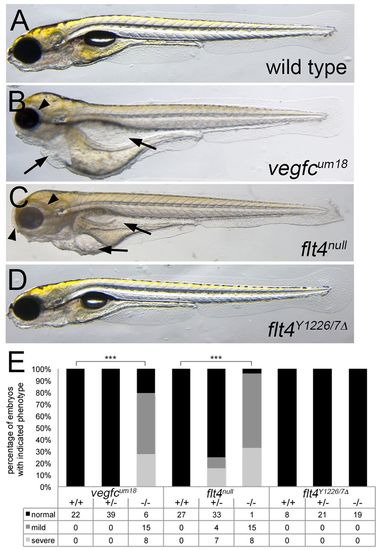
Signaling through Flt4 Y1226/7 is dispensable for normal lymphatic function. (A-D) Transmitted light images of live zebrafish larvae at 10?dpf (A,D) or 5?dpf (B,C). Genotype is indicated in each panel. Lateral views, anterior to the left, dorsal is up. Arrows denote edema surrounding the intestinal tract and heart, arrowheads indicate edema surrounding the eyes. (E) Proportion and numbers of larvae of the indicated genotype exhibiting edema at 5?dpf for vegfcum18 and flt4um131 or 10?dpf for flt4Y1226/7?. ***P<0.001. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Signaling through Flt4 Y1226/7 is dispensable for facial lymphatic formation and function. (A-F) Confocal images of Tg(fli1a:egfp)y1 embryos at 36?hpf of the indicated genotype immunostained with antibodies against Prox1 in red and GFP in green. (A-C) Arrowheads denote Prox1-positive endothelial cells in facial lymphatic sprout (FLS) emerging from the common cardinal vein (CCV, indicated by an arrow). (D-F) Prox1-positive endothelial cells within primary head sinus (PHS, indicated by an arrow) at 36?hpf denoted by arrowheads. (G) Quantification of Prox1-positive cells from the CCV at 36?hpf; ns, not statistically significant; error bars are ħs.d. (H-K) Confocal images of live Tg(lyve1b:dsRed2)nz101 embryos of the indicated genotype at 4?dpf; pseudocoloring is based on depth: red is surface, green and blue are deeper. Lateral facial lymphatic (LFL), otolithic lymphatic vessel (OLV), posterior cerebral vein (PCeV) and forming lymphatic aortic arches (LAA) are indicated. Arrowhead denotes dorsal wall of the primary head sinus (PHS), which is pseudocolored green. Arrows indicated by asterisks denote stunted LFL. (A-F,H-K) Lateral views, anterior to the left, dorsal is up. (L) Percentage of embryos of the indicated genotype with FLV formation. Numbers of embryos scored in each category are indicated; ***P<0.001; ns, not significant. (M-Q) Dorsal views, anterior to the left. (M-M?) Live wild-type Tg(fli1a:egfp)y1;(gata1:dsRed2)sd2 embryo at 4?dpf subjected to microangiography with Qdots655 (gray). Arrows denote Qdot perfusion of FLV, bracket indicates PHS lumen. (N-Q) Confocal images of live Tg(fli1a:egfp)y1 embryos at 4?dpf of the indicated genotype subjected to microangiography with Qdots655 (red). Arrows denote FLV, bracket indicates the lumen of the PHS. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
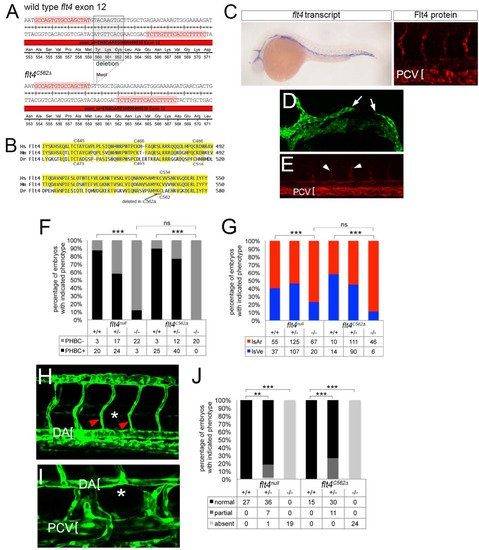
Generation and characterization of flt4C562?. (A) TALEN target sequences (highlighted in pink) in flt4 exon 12 flanking Cysteine 562. Boxed sequence indicates amino acids deleted in flt4C562? mutants. The nine nucleotide deletion creates an MwoI site used for genotyping. (B) Alignment of region of Flt4 extracellular domains from human (Hs), mouse (Mm), and zebrafish (Dr) containing cysteines implicated in disulfide linkage between cleaved extracellular domain and remaining Flt4 protein. Position of amino acids deleted in flt4C562? is indicated. (C) Left, whole mount in situ hybridization using a digoxigenin labeled antisense flt4 riboprobe on flt4C562? mutant embryos at 25 hpf. Right, whole mount immunostaining using a polyclonal antibody against zebrafish Flt4 at 30 hpf; flt4 transcript and Flt4 protein are detectable in flt4C562? mutant embryos. (D) Confocal image of flt4C562? mutant Tg(fli1a:egfp)y1 embryo at 26 hpf; incompletely formed primordial hindbrain channel is indicated by white arrows. (E) Tie2 immunostained flt4C562? mutant embryo showing ISVe loss. White arrowheads denote weak staining in ISAs (F) Percentage of embryos with delayed PHBC formation of indicated genotype. (G) Percentage of ISA and ISVe connections in embryos of indicated genotype at 72 hpf. (F, G) Data from flt4null are same as those shown in main figures. (H) Tg(fli1a:egfp)y1 embryo mutant for flt4C562? at 48 hpf showing lack of parachordal cells (PACs; normal position indicated by asterisk); ISAs indicated by red arrowheads, dorsal aorta denoted by bracket. (I) Loss of thoracic duct in Tg(fli1a:egfp)y1 embryo mutant for flt4C562? at 5 dpf. Normal position of thoracic duct denoted by asterisk; dorsal aorta (DA) and posterior cardinal vein (PCV) are indicated by brackets. (J) Percentage of embryos of indicated genotype with normal, partial, or absent thoracic duct at 5 dpf. Data from flt4null are the same as those shown in Figure 2 |
|
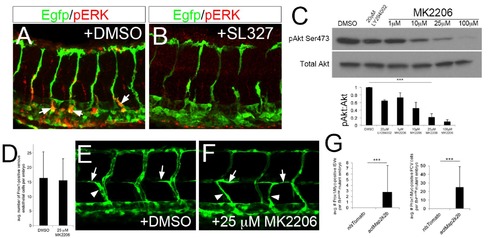
Akt is dispensable for early lymphatic development. (A, B) Wild type Tg(fli1a:egfp)y1 at 36 hpf immuonstained for pERK (red) and EGFP (Green). Embryos were treated with (A) DMSO or (B) 15 ?M SL327 starting at 28 hpf. (C) pAkt and total Akt levels in whole embryo lysates treated with indicate compound at indicated concentration. Graph shows quantification of Akt phosphorylation intensity from Western normalized to total Akt levels. ***p<0.001, error barsħS. D. 25 ?M MK2206 significantly reduce pAkt levels by 80% and was used for subsequent studies. (D) Quantification of Prox1-positive endothelial cells in embryos treated with DMSO or 25 ?M MK2206 between 28 and 38hpf. (E, F) Confocal microscopy of live Tg(fli1a:egfp)y1 at 49 hpf treated with (E) DMSO or (F) 25 ?M MK2206 from 20 hpf. Parachordal cells (arrows) and lymphatic sprouts (arrowheads) are apparent in both DMSO and MK2206-treated embryos. (G) Quantification of lymphatic sprouts and Prox1/Mycpositive posterior cardinal vein (PCV) endothelial cells in flt4C562? mutant embryos injected with indicated transgene. |
|
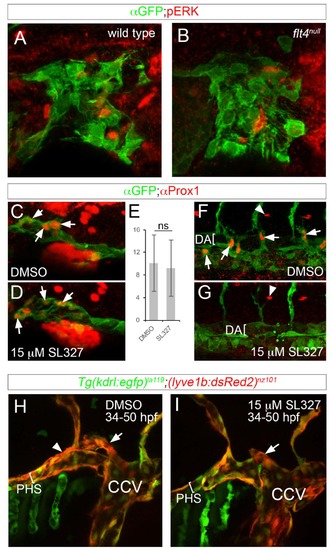
Flt4 and ERK are dispensable for initial facial lymphatic progenitor specification and sprouting. (A-D, F-I) Confocal images, lateral views, dorsal is up, anterior to the left. (A, B) Tg(fli1a:egfp)y1 of the indicated genotypes immunostained with anti-GFP and anti-pERK antibodies at 36hpf (C, D, F, G) Tg(fli1a:egfp)y1 immunostained with anti-GFP and anti-Prox1 antibodies at 36hpf. (C, F) Embryo treated with DMSO; images from same embryo. (F, G) Embryo treated with 15?M SL327starting at 28hpf; images from same embryo. (E) Average number of Prox1-positive CCV endothelial cells per embryo at 36hpf; ns ? not statistically significant, error bars are ħ S.D. (H, I) Live Tg(kdr:egfp)la119;(lyve1b:DsRed2)nz101 at 50hpf treated with (H) DMSO or (I) 15?M SL327 starting at 28hpf. Lumen of primary head sinus denoted by a bracket. Position of facial lymphatic vessel derived from PHS is indicated by arrowhead; brach derived from common cardinal vein (CCV) is denoted by an arrow. |