- Title
-
The Polycomb group protein Ring1b is essential for pectoral fin development
- Authors
- van der Velden, Y.U., Wang, L., van Lohuizen, M., and Haramis, A.P.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
Generation of ring1b mutants. (A) Schematic representation of the zebrafish ring1b gene depicting the location of the ZFN target site. (B) Wild-type ring1b sequence is shown at the top; the ZFN target sites are highlighted in yellow. ZFN-induced bp insertions are highlighted in red, and deletions in gray. (C,C′) ring1b mRNA staining in brain and pectoral fins in wild-type larvae. (D,D′) Expression is absent in ring1b mutants. (E,F) Ring1b (E) and mono-ubiquitylated histone H2A (F) are not detected in 72 hpf ring1b mutants by western blot analysis. (G,H) Dorsal view of wild-type (G) and ring1b (H) larvae at 72 hpf. Asterisks indicate the lack of pectoral fins in ring1b mutants. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Injection of ring1b mRNA rescues pectoral fin outgrowth and restores hoxd9a and tbx5 expression in ring1b mutants. (A-J) Lateral views of 32 hpf embryos stained for hoxd9a (A-E) and 48 hpf fin buds stained for tbx5 (F-J). Anterior expansion of axial hoxd9a expression in ring1b mutants is suppressed by exogenous wild-type ring1b mRNA in a dose-dependent manner (C-E, arrowheads). (K,L) Fin-bud hoxd9a (A-E, arrows) and tbx5 expression (F-J) is restored (arrows) in injected ring1b mutants and fin bud outgrowth is partially rescued at 72 hpf (compare K with L). (M) Western-blot analysis for myc-tagged Ring1b shows dose-dependent expression in 24 hpf embryos. (N) Exogenous Ring1b protein is markedly reduced in 48 hpf embryos. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Gene expression defects in the ring1b pectoral fin mesenchyme. (A-DD) Dorsal views of embryos at the indicated stages stained for tbx5 (A-J), hand2 (K-T) and aldh1a2 (U-DD). Migration and compaction of tbx5-positive pectoral fin precursors is slightly delayed in ring1b mutants (A-F), whereas hand2 expression is identical to wild-type siblings up to 24 hpf (K-P). Expression of tbx5 (G-J) and hand2 (Q-T) is not maintained in the ring1b fin mesenchyme. aldh1a2 is overexpressed and not restricted to the posterior LPM in ring1b mutants (U-BB, brackets). Arrowheads indicate staining at the fin bud region. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
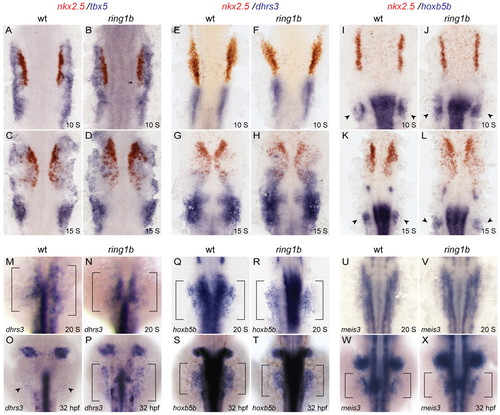
LPM patterning and the RA-signaling response in ring1b mutants. (A-L) Double in situ hybridization for nkx2.5 in red and tbx5 (A-D), dhrs3 (E-H) and hoxb5b (I-L) in blue at 10 ss and 15 ss shows similar staining patterns in wild-type and ring1b mutants. Arrowheads indicate staining at the pectoral fin mesenchyme. (M-X) Dorsal views of embryos stained for the RA targets dhrs3 (M-P), hoxb5b (Q-T) and meis3 (U-X) at 20 ss and 32 hpf. Expression of hoxb5b and meis3 is normal in the ring1b LPM at 20 ss and 32 hpf, whereas dhrs3 expression is upregulated in the ring1b LPM at 32 hpf (P). Arrowheads indicate staining at the fin bud region. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
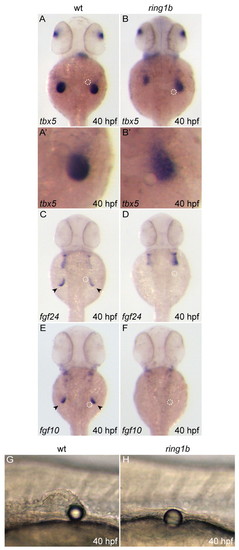
Reduced fgf24 and fgf10 expression in ring1b fin mesenchyme. (A-P) Dorsal views of embryos stained for fgf24 (A-H) and fgf10 (I-P). Expression of both genes is initiated at the correct developmental stage, but the levels are reduced in the ring1b pectoral fin mesenchyme. fgf24 and fgf10 expression is restricted to a very small domain in the ring1b fin mesenchyme at 32 hpf (H,P). Arrowheads indicate staining at the pectoral fin mesenchyme and fin bud region. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Loss of Fgf target gene expression in ring1b mutants. (A-L) Expression analysis of the Fgf target genes pea3 (A-D), dusp6 (E-H) and spry4 (I-L) at 24 hpf and 32 hpf. pea3 is greatly reduced and dusp6 and spry4 are undetectable in the ring1b pectoral fin mesenchyme. Arrowheads indicate staining at the fin |
|
FGF4-soaked bead implantation restores tbx5 expression but not fin bud outgrowth. (A-F) Dorsal views of bead-implanted embryos stained for tbx5 (A-B′), fgf24 (C,D) and fgf10 (E,F) at 40 hpf. (G,H) Exogenous FGF4 enhances tbx5 expression maintenance but is not sufficient to initiate fgf24 or fgf10 expression in ring1b mutants. Bead location is indicated by the white dashed circle. Pectoral fin bud outgrowth is not restored in ring1b mutants. Arrowheads indicate staining at the fin bud region. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
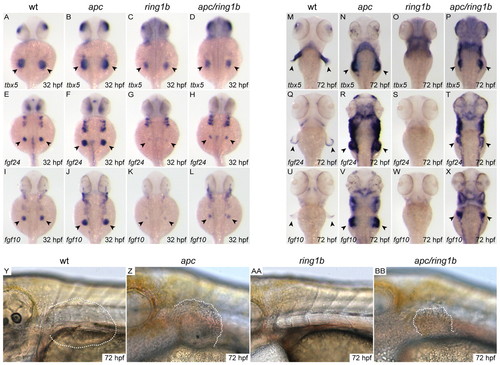
Restoration of mesenchymal gene expression and fin bud outgrowth in apc/ring1b mutants. (A-X) Dorsal views of embryos of the indicated genotypes stained for tbx5, fgf24 and fgf10 at 32 hpf (A-L) and 72 hpf (M-X). tbx5 (B,N), fgf24 (F,R) and fgf10 (J,V) are overexpressed in the apc pectoral fin mesenchyme at both 32 and 72 hpf. Expression of fgf24 (H) and fgf10 (L) is increased in apc/ring1b mutants compared with ring1b mutants (G,K) at 32 hpf. Expression of tbx5 (P), fgf24 (T) and fgf10 (X) is maintained in apc/ring1b mutants at 72 hpf. Arrowheads indicate staining at the fin bud region. (Y-BB) Lateral views of 72 hpf embryos of the indicated genotypes at the level of the pectoral fin. A rudimentary fin bud (outlined) is formed in apc/ring1b mutants at 72 hpf (BB). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
ring1b mRNA and protein are maternally deposited. (A,B) Whole-mount in situ hybridization with a riboprobe against ring1b shows expression at the eight-cell stage, no staining is detected with the sense probe. (C) Western blot analysis of Ring1b protein in wild-type embryos at 24 hpf as control and 2.5 hpf shows maternal Ring1b protein. (D) Ring1b protein is detected in lysates of ring1b mutant embryos at 15 somites but is not or is hardly detectable at 24 hpf (D). Histone H3 is used as a loading control. |
|
Hox gene expression in ring1b mutants. (A-X) Lateral views of in situ hybridization for hoxa9b (A,B,I,J,Q,R), hoxc6a (C,D,K,L,S,T), hoxc8a (E,F,M,N,U,V) and hoxd9a (G,H,O,P,W,X) at 24 hpf (A-H), 48 hpf (I-P) and 72 hpf (Q-X). Axial Hox gene expression is anteriorly restricted in wild-type larvae (A,C,E,G), whereas the anterior border of axial Hox gene expression is slightly less defined in ring1b mutants at 24 hpf (B,D,F,H) (arrowheads). Ectopic Hox gene expression is progressively upregulated in ring1b mutants (B,D,F,H versus J,L,N,P and R,T,V,X). Strong ectopic expression throughout the brain is observed especially for hoxa9b (R), hoxc6a (T) and hoxc8a (V) in ring1b mutants at 72 hpf. Also note that Hox gene expression is absent or severely reduced in the pectoral fin field of ring1b mutants. |
|
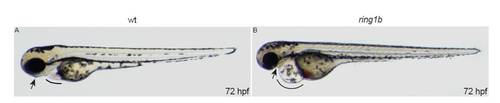
Lateral views of live embryos at 72 hpf. ring1b homozygotes display heart edema (line) and jaw abnormalities (arrow). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
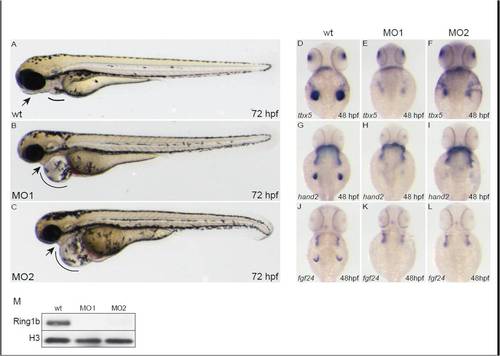
Injection of morpholinos against ring1b phenocopies the ring1b developmental phenotype. Lateral views of embryos at 72 hpf. MO1- and MO2-injected embryos display the heart edema (lines) and jaw abnormalities (arrows) similar to ring1b mutants (A-C). Expression of tbx5 (E,F), hand2 (H,I) and fgf24 (K,L) in ring1b MO-injected embryos at 48 hpf, shows the same pattern as the one in ring1b mutants. No Ring1b protein is detected in lysates from ring1b MO-injected embryos (M). Histone H3 serves as loading control. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
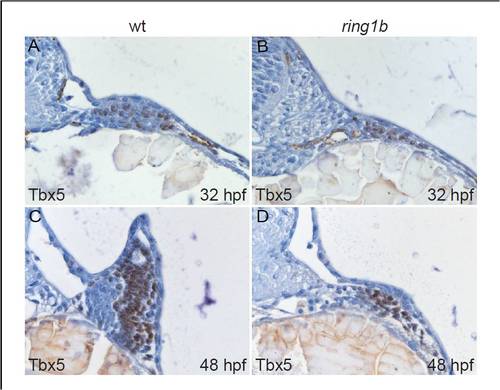
Nuclear Tbx5 localization in the ring1b pectoral fin mesenchyme. Transverse sections of wild type (A,C) and ring1b mutants (B,D) stained with an antibody against Tbx5 at 32 (A,B) and 48 hpf (C,D). Nuclei in the pectoral fin mesenchyme of ring1b mutants stain positive for Tbx5 at 32 and 48 hpf (B,D). |
|
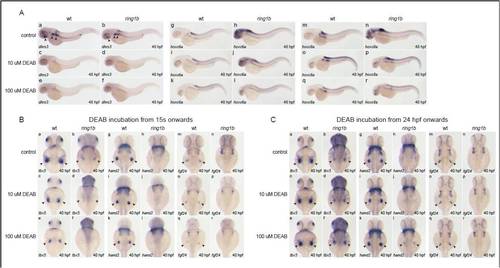
DEAB treatment initiated at 24 hpf leads to partial restoration of mesenchymal gene expression in ring1b fin buds. (A) In situ hybridization for the RA-responsive genes dhrs3 (a-f) hoxc6a (g-l) and hoxc8a (m-r) in wild-type and ring1b embryos at 48 hpf, treated with DEAB from 24 hpf. DEAB (10 μM and 100 μM) potently suppresses expression of dhsr3 in wild-type and ring1b embryos (a-f). While 10 μM DEAB suppresses ectopic overexpression of hoxc6a and hoxc8a in ring1b embryos, 100 ÁM DEAB leads to more potent inhibition (i,k,o,q). (B) In situ hybridization for tbx5 (a-f), hand2 (g-l) and fgf24 (m-r) in wild-type and ring1b embryos at 40 hpf, treated with DEAB from 15 ss. Inhibition of RA signaling by DEAB leads to downregulation of tbx5 (c,e), hand2 (i,k) and fgf24 (o,q) expression in wild-type embryos in a dose-dependent manner. DEAB (10 μM) leads to almost complete downregulation of tbx5 expression in ring1b fin buds (d) and this effect is more pronounced with 100 μM DEAB (f). DEAB treatment initiated at 15 ss in ring1b embryos does not have an effect on the (lack of) expression of hand2 (j,l) and fgf24 (p,r) in ring1b fin buds. (C) In situ hybridization for tbx5 (a-f), hand2 (g-l) and fgf24 (m-r) in wild-type and ring1b embryos at 40 hpf, treated with DEAB from 24 hpf. DEAB treatment initiated at 24 hpf does not have a significant impact in expression of tbx5 (c,e), hand2 (i,k) and fgf24 (o,q) in wild-type fin buds. DEAB treatment of ring1b embryos initiated at 24 hpf leads to partial restoration of tbx5 (d,f) and hand2 (j,l) expression in a dose-dependent manner. However, this treatment does not lead to restoration of fgf24 expression (p,r). |
|
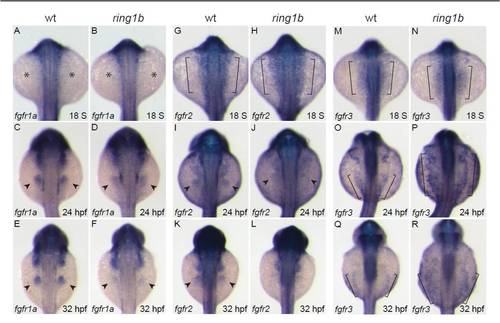
Time-course expression analysis of the FGF receptors. (A-R) Dorsal views of in situ hybridization for fgfr1a (A-F), fgfr2 (G-L) and fgfr3 (M-R). fgfr1a is not expressed in either wild type or ring1b LPM at 18 ss (A,B; asterisks indicate absence of expression). At 24 hpf, fgfr1a is expressed in the fin buds of wild-type embryos and at weaker levels in ring1b fin buds (C,D). At 32 hpf, strong fgfr1 expression is detected in the wild-type fin buds but is greatly reduced in the ring1b fin buds (E,F). fgfr2 is expressed in the LPM of wild-type and ring1b embryos at 18 ss (brackets, G,H). At 24 hpf, fgfr2 expression in ring1b fin buds is weak (I,J) and is hardly detectable in ring1b fin buds at 32 hpf (K,L). fgfr3 is expressed at higher levels in the LPM of ring1b mutants at 18 ss (M,N). At 24 hpf, fgfr3 expression is upregulated and expanded in mutants (O,P). At 32 hpf, fgfr3 remains high and the expression domain is expanded in ring1b embryos (Q,R). Brackets in M-R indicate the LPM. |
|
Impaired AP/DV patterning and loss of AER gene expression in ring1b mutants. (A) Dorsal view of in situ hybridization for the AP markers msxc (a,b) and shh (c,d) and the DV markers eng1a (e,f) and wnt7a (g,h) at 32 hpf. msxc is not restricted to the anterior pectoral fin mesenchyme because shh is not expressed in the zone of polarizing activity (ZPA) of ring1b mutants (b,d). eng1a expression is greatly reduced, whereas wnt7a is not expressed in the ring1b pectoral fin ectoderm (f,h). (B) Dorsal (a-h) and lateral (a′-h′) views of in situ hybridizations for the AER markers dlx2a (a-b′), fgf8 (c-d′), fgf24 (e-f′) and versican (g-h′) at 40 hpf. The examined AER markers are not expressed in the pectoral fin ectoderm of ring1b mutants at 40 hpf and fin bud outgrowth is not initiated (b-h′). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
FGF4-coated bead implantation induces ectopic expression of FGF-target genes. (A-C) Whole-mount in situ hybridization for the FGF-target genes dusp6 (A), pea3 (B), spry4 (C) in embryos at 90% epiboly following FGF4-coated bead implantation at the 1000-cell stage. Arrowheads indicate the position of the bead and ectopic expression of the FGF-target genes induced in the proximity of the bead. |
|
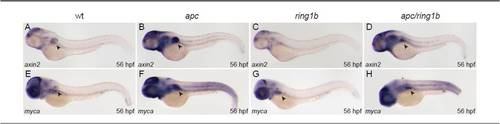
The Wnt-target genes myca and axin2 are overexpressed in apc and downregulated in ring1b fin mesenchyme. (A-H) Embryos of the indicated genotypes were stained at 56 hpf with axin2 (A-D) and myca (E-H). myca and axin2 are overexpressed in apc mutants, including the fin mesenchyme (B,F). In ring1b fin mesenchyme, myca and axin2 expression is very weak (C,G). myca and axin2 expression is restored in the nascent fin bud of apc/ring1b mutants (D,H). |
|
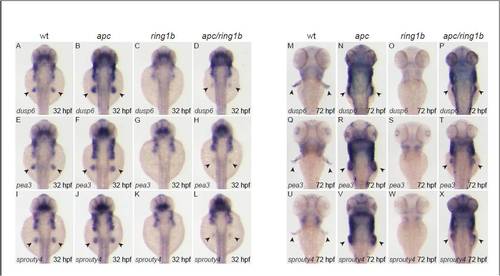
The FGF target genes dusp6, pea3 and spry4 are overexpressed in apc fin mesenchyme. Embryos of the indicated genotypes were stained at 32 hpf (A-L) and 72 hpf (M-X) with the indicated FGF-target genes. dusp6, pea3 and spry4 are expressed in wild-type fin buds at 32 hpf (A,E,I). Expression of all three genes is upregulated in apc fin buds (B,F,J), not detectable in ring1b mutants (C,G,K) and expression is restored, albeit weak, in apc/ring1b mutants (D,H,L). dusp6, pea3 and spry4 are expressed in wild-type growing fins at 72 hpf (M,Q,U). Expression of all three genes is upregulated in the apc fin buds (N,R,V) and not detectable in ring1b fin buds (O,S,W). Expression of the FGF-target genes is restored in the apc/ring1b fin buds (P,T,X). |