- Title
-
Ribosomal protein gene knockdown causes developmental defects in zebrafish
- Authors
- Uechi, T., Nakajima, Y., Nakao, A., Torihara, H., Chakraborty, A., Inoue, K., and Kenmochi, N.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
Lateral Views of Wild-Type and MO-Injected Embryos The genes targeted by MOs and the observation time are indicated for each image. ?rpl5; MO116? and ?rpl5; MO117? indicate two MOs designed and injected separately for two functional copies of rpl5 on the zebrafish genome. ?rpl5; MOmix? indicates the mixture of MO116 and MO117. Control MOs that included 5 mispaired bases were also used; one example of a control MO injection is shown (rpl38; misMO). Control MOs that included 5 mispaired bases were also used; one example of a control MO injection is shown (rpl38; misMO). Scale bar, 500 μm. |
|
Specific Morphological Changes in Brain and Body Trunk Examples of morphants displaying characteristic deformations are shown. The targeted genes and the deformed areas of the morphants are indicated. (A, E) Wild type (WT). (B) rps15; enlarged 4th ventricle (white arrow). (C) rps29; enlarged lens (arrowhead) and undulated rhombencephalon (white arrow). (D) rpl28; protruded forehead. (F) rps3a; wider trunk and downward-curving tail. (G) rps29; wavy notochord and extremely bent tail. (H) rpl35a; sharply downward bent tail. Anterior is to the left. Bars: A~D, 100 μm; E~H, 200 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
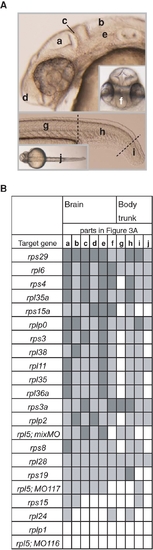
Schematic Representation of the Extent of Abnormalities in Brain and Body Trunk (A) 6 parts of the brain, 3 parts of the body trunk, and a dorsal view of the trunk are indicated in wild type embryo. a, optic tectum; b, 4th ventricle; c, midbrain-hindbrain boundary; d, anterior part of head; e, rhombencephalon; f, telencephalon; g, body along yolk sac extension; h, tail; i, tip of tail; j, dorsal view of the trunk. (B) The deformations were assessed using a 3-level severity scale; dark gray indicates a severe effect, light gray indicates a mild effect, and white represents no apparent effect. Detailed information and images of the abnormalities in the morphants are available at the zebrafish database (http://zebrafish.med.miyazaki-u.ac.jp). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
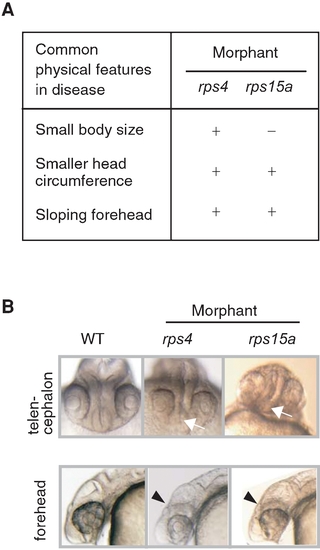
Similarities between the Clinical Features of Human Brain Diseases and Defects in Zebrafish Morphants (A) Common features shared between Abidi X-linked mental retardation and microhydranencephaly are listed on the left and the corresponding changes in rps4 and rps15a morphants are indicated on the right. (B) Telencephalon hypoplasia is seen in rps4 morphants, and reduction in size and deformity of the telencephalon is apparent in rps15a morphants (white arrows). Unclear subdivisions of the brain and flattened foreheads (arrowheads) can be seen in lateral views of these morphants. PHENOTYPE:
|

Rescued Embryos Co-Injected with the MO for rpl38 and Synthesized mRNA. Three days post fertilization embryos injected with the rpl38MO (0.5 µg/µl) displaying smaller head, shortened body and reduced yolk sac extension when compared to the wild type embryos. These phenotypes are rescued by co-injecting MO (0.5 µg/µl) and synthesized capped mRNA (0.5 µg/µl) for rpl38 gene. The mRNA included altered bases that did not bind with the MO. Scale bar, 500 µm. The sequence information of the mRNA used for rescue is available at http://zebrafish.med.miyazaki-u.ac.jp. PHENOTYPE:
|