- Title
-
Lhx3 and Lhx4 suppress Kolmer-Agduhr interneuron characteristics within zebrafish axial motoneurons
- Authors
- Seredick, S., Hutchinson, S.A., Van Ryswyk, L., Talbot, J.C., Eisen, J.S.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
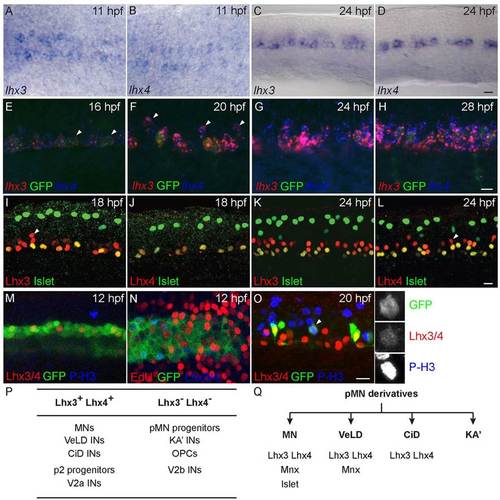
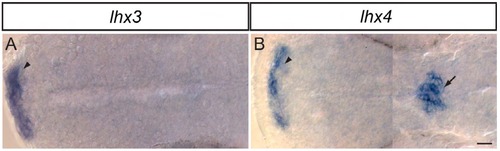
lhx4 and lhx3 are expressed in many cells in the ventral neural tube. All images oriented with anterior to the left. (A,B) Dorsal view of 11hpf embryos. Both lhx3 (A) and lhx4 (B) are expressed beginning at 11hpf in two medial cell stripes. (C,D) Lateral view of spinal cord adjacent to somites 8-12 of 24hpf embryo. Both lhx3 (C) and lhx4 (D) are expressed in the pMN domain; however, lhx4 is expressed in fewer cells than lhx3. (E-H) lhx3 and lhx4 expression in ventral neural tube of Tg(nrp1a:GFP) embryos. (E) At 16hpf, lhx3 and lhx4 are expressed at the dorsoventral level of GFP+ MNs, whereas some GFP+ cells express only lhx3 (arrowheads). (F) At 20hpf, lhx3 and lhx4 expression has expanded to include more dorsal GFP cells (arrowheads). (G,H) At 24hpf and 28hpf, lhx3 and lhx4 are broadly co-expressed in GFP+ and GFP cells throughout the lateral half of ventral spinal cord. (I-L) Lateral views of spinal cord hemisegments adjacent to somites 8-12 co-labeled for Islet and either Lhx3 or Lhx4. Dorsal Islet+ cells are Rohon?Beard sensory neurons. Anti-Islet labels PMNs at 18hpf, and PMNs plus a few SMNs at 24hpf. (I) At 18hpf, anti-Lhx3 labels all Islet+ PMNs as well as slightly more dorsal cells (arrowhead) in ventral neural tube. (J) At 18hpf, anti-Lhx4 labels almost exclusively Islet+ PMNs. (K) By 24hpf, anti-Lhx3 labels all Islet+ PMNs and SMNs and an increased number of cells in ventral neural tube. (L) Anti-Lhx4 also labels all Islet+ PMNs and SMNs in addition to other more dorsal cells (arrowhead) in ventral neural tube at 24hpf. (M) Lateral view of 12hpf Tg(olig2:GFP) embryo co-labeled with anti-Lhx3/4 and anti-phospho-Histone H3 (P-H3). (N) Dorsal view of 12hpf Tg(olig2:GFP) embryo incubated with EdU from 11hpf and labeled with EdU and anti-Lhx3/4. (O) Lateral view of 20hpf Tg(vsx1:GFP) embryo co-labeled with anti-Lhx3/4 and anti-P-H3. Enlarged, single channel images of indicated cell (arrowhead) demonstrate co-expression. (P) Summary of Lhx3- and Lhx4-expressing cells in the ventral spinal cord. (Q) Combinatorial expression of three transcription factors that uniquely label all four neuronal derivatives of the zebrafish pMN domain. Scale bars: 20µm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
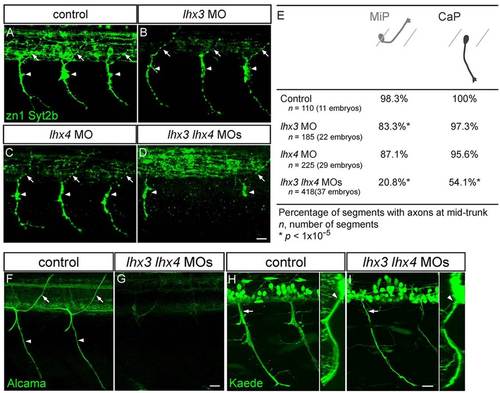
Lhx3 and Lhx4 are required for normal PMN axon morphology. (A-D) Lateral views of 28hpf embryos co-labeled with zn1 and anti-Syt2b. Control (A), lhx3 MO-injected (B) and lhx4 MO-injected (C) embryos have normal dorsal MiP axons (arrows) and ventral CaP axons (arrowheads). MiP, CaP, or MiP and CaP axons are often absent from lhx3+lhx4 MO-injected embryos (D). Apparent variation in intraspinal labeling in B and C was a consequence of embryo orientation and does not reflect differences in IN axon labeling. (E) Quantification of MiP and CaP phenotypes in control and MO-injected embryos. (F,G) Lateral views of somites 8-12 of 72hpf embryos labeled with anti-Alcama. Alcama labeling of SMN axons and somata was almost completely missing from embryos injected with lhx3+lhx4 MOs. (H,I) Lateral views of 48hpf s1020t;Tg(UAS-E1b:Kaede) embryos. Ventral nerves in lhx3+lhx4 MO-injected embryos were thinner (arrows), yet exited through the ventral root (arrowhead); inset shows an optical cross-section. Scale bars: 20µm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
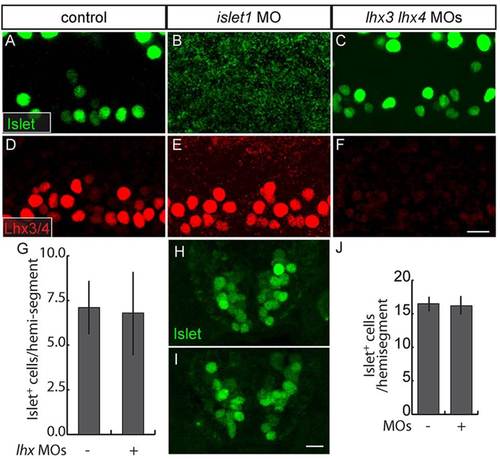
Islet and Lhx3/4 proteins are independently regulated in ventral spinal cord. (A-F) Lateral views of 28hpf embryos. MN Islet expression is absent from islet1 MO-injected embryos (A,B), but persists in lhx3+lhx4 MO-injected embryos (C). Lhx3/4 expression persists in islet1 MO-injected embryos (D,E) and is absent from lhx3+lhx4 MO-injected embryos (F). (G) Quantification of Islet+ PMNs and early-born SMNs in presence or absence of Lhx3 and Lhx4 (P=0.18; control, n=56 spinal hemisegments in seven embryos; MOs, n=80 spinal hemisegments in ten embryos). (H,I) Sections of ventral spinal cord of 48hpf embryos labeled with anti-Islet. Islet expression persists in embryos injected with lhx3+lhx4 MOs. (J) Quantification of Islet+ MNs in the presence or absence of Lhx3 and Lhx4 (P=0.44; n=10 alternating sections from ten embryos for both conditions). Scale bars: 20µm. |
|
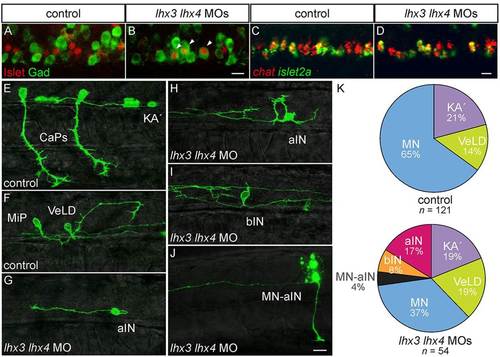
Lhx3 and Lhx4 prevent PMNs from acquiring KA2 IN characteristics. (A-D) Lateral views of 24hpf embryos. (A,B) Islet and Gad are co-expressed in lhx3+lhx4 MO-injected embryos (arrowheads). (C,D) MNs continue to express chat in lhx3+lhx4 MO-injected embryos. (E-I) Mosaically labeled pMN derivatives in 28-32hpf s1020t embryos. (E,F) Injection of UAS:EGFPCAAX DNA labels PMNs, including both CaP (E) and MiP (F), as well as KA2 (E) and VeLD (F) in control embryos. (G-I) Mosaically labeled pMN derivatives in 28-32hpf s1020t embryos injected with lhx3 and lhx4 MOs. (G) Aberrant neuron with an axon that initially projects caudally before turning laterally and ascending the spinal cord (aIN; n=9). (H) Aberrant neuron with axon that ascends without a proximal descending segment. (I) Aberrant neuron with bifurcating axons, one ascending and one descending (bIN; n=4). (J) Dye-labeled MN-IN hybrid neuron with both ascending IN and peripheral MN axons in embryo injected with lhx3+lhx4 MOs (n=2); dye dorsal to the labeled neuron is from an adjacent cell killed during labeling. (K) Relative proportions of labeled pMN-derived neurons. Three new neuron classes appear in lhx3+lhx4 MO-injected embryos; only MNs are under-represented relative to control embryos (P=2.2×105). The percentage of labeled cells is listed for each condition. Scale bars: 20µm. |
|
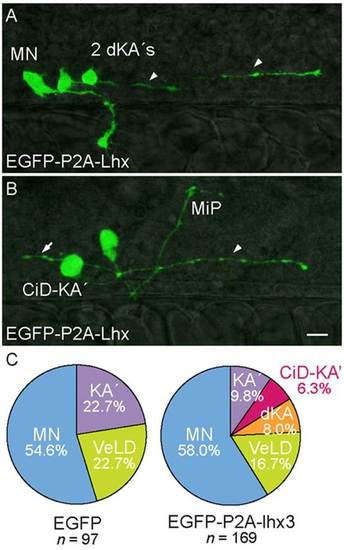
Forced expression of Lhx3 in KA2s promotes descending and CiD axon trajectories. (A,B) Lateral views of 28hpf s1020t embryos. Labeled pMN derivatives express EGFP-P2A-Lhx3. (A) Pair of aberrant ventromedially located KA2 neurons with descending axons (dKA2, arrowheads). A rostral primary (RoP) MN projecting to lateral muscle is also labeled. (B) Aberrant ventromedially located KA2 neuron with an axon that initially extends laterally before turning caudally and descending within the spinal cord (CiD-KA2, arrowhead). An ascending axon collateral (arrow) sprouts immediately adjacent to the intraspinal portion of a labeled MiP MN. (C) Relative proportions of labeled pMN-derived neurons. Two new IN classes appear in UAS:EGFP-P2A-lhx3-injected embryos; KA2s are under-represented relative to control embryos (P=1.6×105). The percentage of labeled cells is listed for each condition. Scale bar: 20µm. |
|
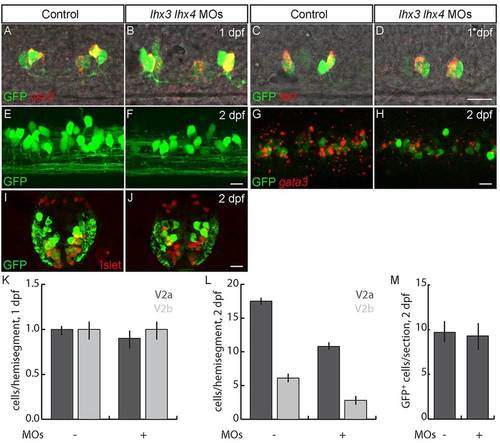
Lhx3 and Lhx4 promote differentiation of late-born V2a and V2b INs. (A-D) Lateral views of 24hpf Tg(vsx1:GFP) embryos. (A,B,K) The number of early-born V2a INs labeled with vsx2 is unchanged in lhx3+lhx4 MO-injected embryos. (C,D,K) The number of early-born V2b INs labeled with tal1 is unchanged in lhx3+lhx4 MO-injected embryos. (E-H) Lateral views of 2dpf Tg(vsx1:GFP) embryos. (E,F) V2as labeled by GFP in 2dpf Tg(vsx2:EGFP) embryos are reduced in lhx3+lhx4 MO-injected embryos. (G,H) Single optical section; the number of V2bs co-labeled by gata3 and GFP in Tg(vsx1:GFP) embryos is reduced in lhx3+lhx4 MO-injected embryos. (I,J) Cross-section through mid-trunk of 2dpf Tg(vsx1:GFP) embryos. The number of V2s and late p2 progenitors labeled by GFP is unaffected in lhx3+lhx4 MO-injected embryos. Islet was included to exclude MNs that weakly express GFP (Reimer et al., 2013). (K) Quantification of early-born V2a and V2b INs (P>0.05; n=40 segments in ten embryos for each condition). (L) Quantification of V2a and V2b INs at 2dpf (PV2a=1×1011; PV2b=2×105; n=60 segments from ten embryos for each condition). (M) Quantification of V2 INs plus late p2 progenitors (P=0.14; n=10 alternating segments from ten embryos for each condition). In control embryos some weakly GFP+ cells co-express Islet; these cells are MNs and were not included in p2 progenitor and V2 IN counts. Scale bars: 20µm. |
|
Lhx3 and Lhx4 are expressed in the anterior central nervous system. (A,B) Dorsal views of 24 hpf embryos labeled for lhx3 (A) and lhx4 (B). lhx3 and lhx4 both label the pituitary (arrowhead), while lhx4 additionally labels a dorsal population of INs between the eyes (arrow). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|

Unillustrated author statements PHENOTYPE:
|