- Title
-
Small heat shock proteins Hspb7 and Hspb12 regulate early steps of cardiac morphogenesis
- Authors
- Rosenfeld, G.E., Mercer, E.J., Mason, C.E., and Evans, T.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
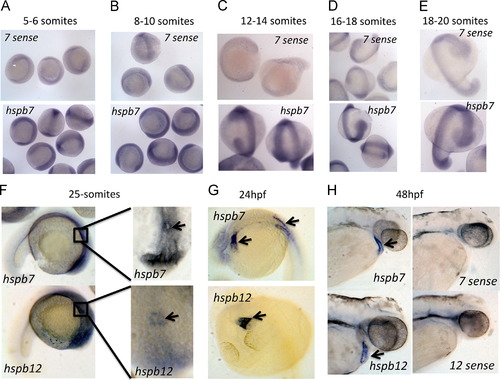
Expression of hspb7 and hspb12 during zebrafish embryogenesis. (A?E) In situ hybridization expression data for hspb7 at 5?6 somites, 8?10 somites, 12?14 somites, 16?18 somites, and 18?20 somites, as indicated. Upper panels (7-sense) are controls at each time points for comparison to anti-sense (hspb7), demonstrating ubiquitous staining pattern between 5 and 20 somites. (F?H) In situ hybridization expression data for hspb7 and hspb12 at 25-somites, 24 h post fertilization, and 48 h post fertilization, as indicated. Insets in right panels of (F) show dorsal views of boxed regions in the lateral views of the left panels. Arrows indicate areas of expression including the cardiac cone (F), heart tube and somites (G), and heart (H). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
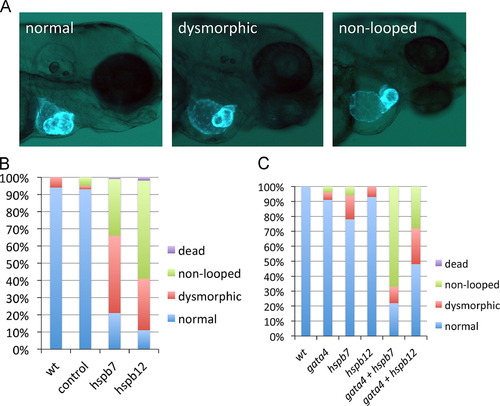
Cardiac small heat shock proteins are required for morphogenesis of the heart tube and they interact genetically with gata4. (A) Representative cardiac phenotypes observed at 3 dpf of myl7:gfp embryos. Non-looping is defined by the failure of the ventricle to align perpendicular to the atrium. (B) Quantification of the cardiac phenotypes in wildtype embryos (wt, n=54), embryos injected with standard control MO (control, n=46), hspb7 MO (hspb7, n=67), or hspb12 MO (hspb12, n=89). (C) Quantification of the cardiac phenotypes in wildtype embryos (wt, n=20) or embryos injected with sub-threshold concentrations of MO specific for gata4 (n=38), hspb7 (n=36), or hspb12 (n=29), or with the same concentrations combined (gata4+hspb7, n=29) or (gata4+hspb12, n=49). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
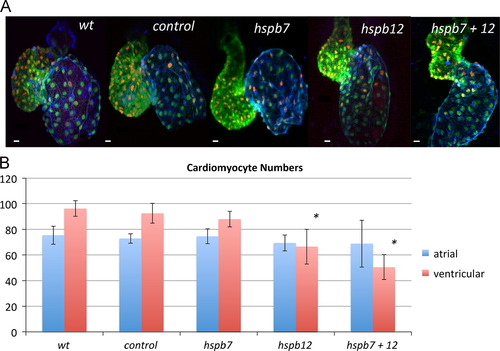
Hspb12 is required for normal numbers of ventricular cardiomyocytes. (A) Representative cardiac phenotypes observed at 48 hpf development in embryos derived from the myl7:gfp; myl7:dsRed-nls reporter strain stained with S46 antibody to differentiate the atrium (blue) from the ventricle (green). (B) Quantification of cardiomyocytes in wildtype embryos (wt, n=7) or embryos injected with standard control MO (control, n=7), hspb7 MO (hspb7, n=7), hspb12 MO (hspb12, n=8), or both hspb7 and hspb12 MOs (hspb7+12, n=6). Np<0.05 by Student′s t-test in comparison to standard control group. The bars represent 10 μm. |
|
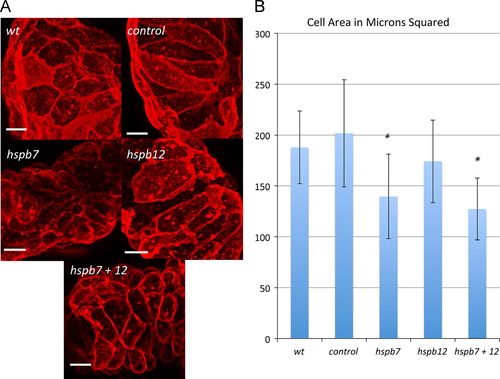
Hspb7 regulates ventricular cardiomyocyte size. (A) Representative phenotypes demonstrating the ventricular cell size observed in the indicated experimental conditions at 48 hpf in embryos derived from the myl7:actn3b; myl7:mKate-Caax reporter strain. The bars represent 10 μm. (B) Wildtype embryos (wt, n=3) or embryos injected with the standard control MO (control, n=4), hspb7 MO (hspb7, n=5), hspb12 MO (hspb12, n=3), or hspb7+12 MOs (hspb7+12, n=4) were evaluated with ImageJ to measure average cell area. At least seven cells were analyzed for each embryo to determine the average. The asterisk indicates p<0.05 by Student′s t-test in comparison to the standard control group. |
|
Hspb7 is required for normal jogging of the heart tube. (A) Representative phenotypes of morphant embryos derived from myl7:gfp reporter fish displaying normal (left) or abnormal (center or right) heart tube jogging at 30 hpf. (B) Quantification of the phenotypes from several independent experiments for uninjected wildtype embryos (wt, n=110), standard control MO injected (control, n=100), hspb7 morphants (hspb7, n=75), or hspb12 morphants (hspb12, n=64). |
|
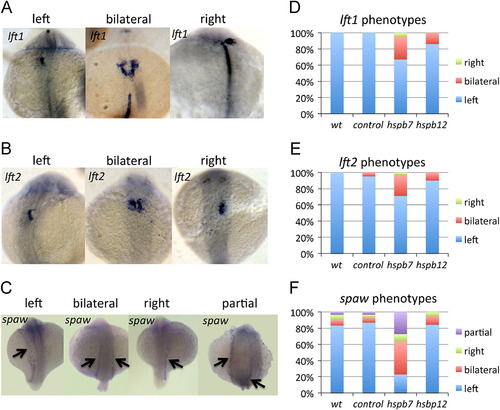
Hspb7 is required for establishment of left?right asymmetry. (A?C) Representative in situ hybridization expression patterns of the left?right asymmetry markers lft1 (A), lft2 (B), or spaw (C). Panels in (A) and (B) show, left to right, normal (leftward), bilateral, or right-sided expression in embryos at the 22-somite stage. Panels in (C) are likewise, but the embryos are at the 18 somite stage, and some hspb7 morphants show a partial pattern of bilateral expression (far right panel). All views are dorsal, with anterior to the top. (D?F) Quantification of these phenotypes, and in each case n is at least 18 embryos. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Hspb7 is required in the YSL for proper cardiac tube formation. (A) Representative phenotypes observed at 24 hpf in myl7:gfp embryos. (B) Quantification of phenotypes in wildtype embryos (wt, n=37) or embryos injected into the YSL with standard control MO (control, n=29), hspb7 RNA (n=30), hspb7 MO (n=53), hspb7 MO+RNA (n=74), or hspb12 MO (n=21). Np<0.05 comparing the embryos co-injected with RNA compared to those injected only with MO, according to Chi-squared test. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Hspb7 is required in Kupffer′s vesicle for normal morphogenesis. (A, B) Confocal stack and DIC images, respectively, of the KV in wildtype and morphant embryos derived from the sox17:gfp reporter strain, as indicated at the 8?10 somite stage. In this case, embryos were injected with MOs at the 1K stage, and selected for YSL-specific deposition using a reporter dye. Embryos in (A) were stained with anti-acetylated tubulin antibody (red). The bars represent 10 Ám. (C?E) Quantification of KV phenotypes noting average cilia number (C), cilia length (D) or KV width (E). In each sample n was at least five embryos. The asterisk indicates p<0.05 according to Student′s t-test in comparison to the standard control group. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
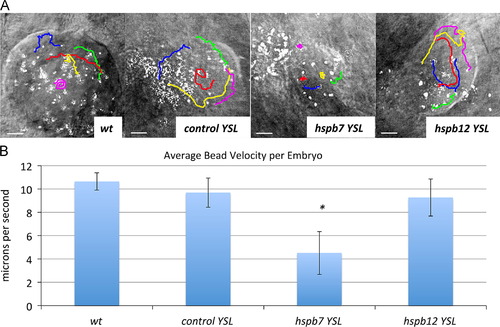
Hspb7 is required for normal KV function. (A) Traces of fluorescent bead movement in the KV from a representative 5 s video for wildtype or morphant embryos injected into the YSL at the 1K stage as indicated. Movies were acquired when the embryos reached the 10-somite stage. The bars represent 10 μm. (B) Average bead velocity for each sample (n=at least 5). The asterisk indicates p<0.05 by Student′s t-test in comparison to the standard control group. For each KV, the velocity of five beads was measured to determine the average. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
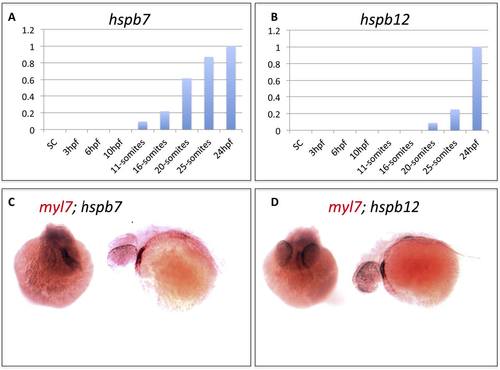
Expression patterns of hspb7 and hspb12 transcripts in the embryonic heart. A, B) qRT-PCR results measuring relative expression levels for hspb7 and hspb12 transcripts during early zebrafish embryogenesis. C, D) In situ hybridization analysis showing representative 48 hpf embryos stained with probes for the cardiac marker myl7 (red) and hspb7 or hspb12 (black). The stains overlap in the embryonic heart, shown in either head-on (left) or anterior-left (right) views. |
|
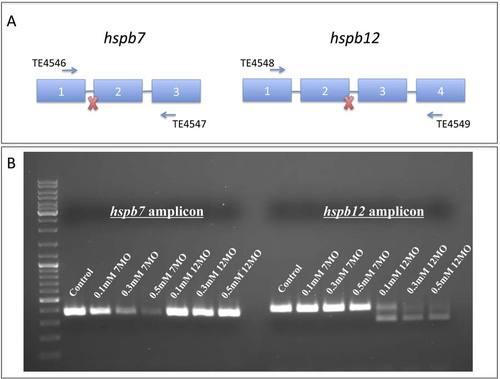
Validation of the splice-blocking morpholinos. MOs targeting hspb7 or hspb12 transcripts demonstrate specific knockdown of each gene product. A) Schematic demonstrating the target splice sites for each morpholino. The 7MO targets the splice acceptor site of exon 1 of the hspb7 transcript while 12MO targets the splice donor site of exon 2 of the hspb12 transcript. Primers used to generate amplicons are also indicated. B) Semi-quantitative PCR of the amplicons generated by primer pairs for hspb7 (TE4546 and TE4547) and hspb12 (TE4548 and TE4549). Transcripts are largely depleted when MOs were used at 0.3mM and above, which correlates to the concentrations used to generate phenotypes in our experiments. |
|
Sarcomere formation appears relatively normal in hspb7 or hspb12 morphants. Shown are representative images illustrating ventricular cell sarcomere formation observed under the indicated experimental conditions at 48hpf in embryos derived from the myl7:actn3b-gfp; myl7-mKate-Caax trangenic reporter strain. Bars are 10 microns. |
|
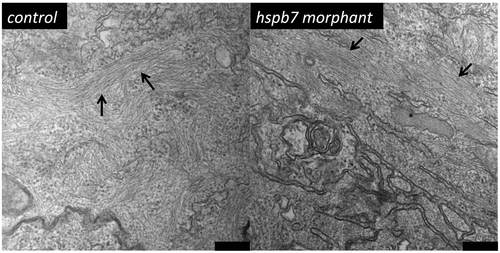
Myofibrils develop normally in embryos depleted of Hspb7. Shown are representative TEM images of frontal sections through the ventricles of 72 hpf embryos injected with 0.25 mM standard control MO (left, n = 2 embryos; 29 fields of view) or 0.25 mM hspb7 MO (right, n = 2 embryos, 31 fields of view). Bars indicate 200 nm. Arrows mark myofibrils. |
|
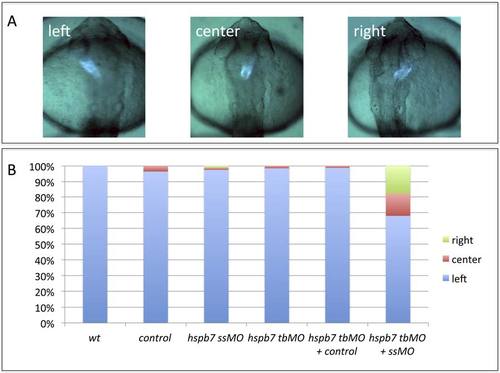
The hspb7 translation-blocker MO and hspb7 splicing-blocker MO synergize to cause jogging defects when used together at sub-threshold levels. A) Representative jogging phenotypes at 30hpf in embryos derived from the myl7:gfp reporter strain. B) Quantification of jogging phenotypes in wildtype embryos (wt, n=32), or embryos injected with the standard control MO (control, n=28), hspb7 7MO at 0.15mM (ssMO, n=81), hspb7 7MO1 at 0.075 mM (tbMO, n=66), 7MO1 + standard control (hsbp7 tbMO + control, n=82), or 7MO + 7MO1 (hspb7 tbMO + ssMO, n=78). The 7MO splice-blocker MO used at 0.15mM does not generate the left-right defects observed at the higher concentrations but does so when co-injected with a sub-threshold concentration of the translation blocker MO. |
|
Injection of RNA encoding TALENs that target hspb7 generate cardiac defects that phenocopy the hspb7 morphants. A) Representative phenotypes of injected embryos at 3 dpf demonstrating cardiac morphogenetic defects including right-sided (left) or non-looping (right) abnormalities. B) Quantification of heart tube phenotypes at 30 hpf in wildtype (n = 29), or embryos injected with RNA encoding TAL1 alone (n = 58), TAL2 alone (n = 53), or TAL1+TAL2 (n = 57). C) Injection of TALEN RNA results in mutations at the hspb7 target site in embryos displaying cardiac morphogenetic defects when compared to uninjected controls. Lane 1) Amplicon from 5011/12 primer set using genomic DNA from uninjected embryos. Lane 2) Amplicon from lane 1 digested with HpyCH4V restriction enzyme. Lane 3) Amplicon from 5011/12 primer set using genomic DNA from Hspb7 TAL1+TAL2 injected embryos displaying cardiac morphogenetic defects. Lane 4) Amplicon from lane 3 digested with HpyCH4V restriction enzyme. The schematic above illustrates the PCR product that contains 3 potential HpyCH4V restriction sites (orange lines) one of which is in the TALEN-targeted sequence (red X). Unmodified DNA is digested to a 106/109 bp doublet, and a smaller 77 bp fragment (and a small 10 bp fragment that is not seen). Arrow indicates HpyCH4V resistant 183 bp fragment due to mutation of the HpyCH4V restriction site in the TALEN target region. Molecular size markers are in the leftmost lane. |
|
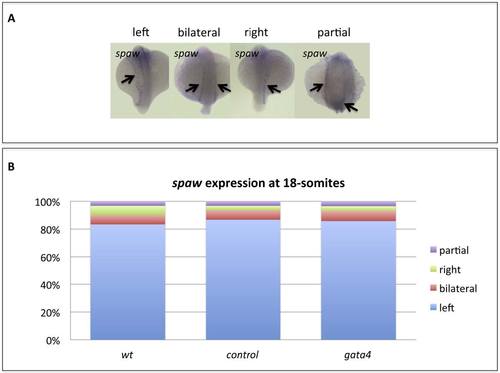
Gata4 is not required for establishment of left-right assymetry. A) Representative phenotypes of wildtype embryos at 18-somites. B) Wildtype embryos (wt, n=30) or embryos injected with standard control MO (control, n=30) or gata4 MO (gata4, n=28) were scored for the observed spaw expression patterns, of which the vast majority were normal. |
|
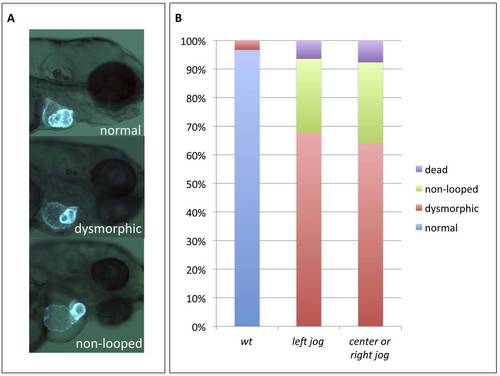
Early cardiac laterality defects are not responsible for the development of subsequent cardiac morphogenetic defects. A) Representative cardiac phenotypes observed at 3 dpf in myl7:gfp embryos. B) Quantification of the cardiac phenotypes in wildtype embryos (wt, n= 30) or hspb7 morphants pre-sorted at 30hpf for hearts jogging normally left (n=31) or hearts jogging to the center or right (n=39). |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 381(2), Rosenfeld, G.E., Mercer, E.J., Mason, C.E., and Evans, T., Small heat shock proteins Hspb7 and Hspb12 regulate early steps of cardiac morphogenesis, 389-400, Copyright (2013) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.