- Title
-
Fgf-dependent otic induction requires competence provided by Foxi1 and Dlx3b
- Authors
- Hans, S., Christison, J., Liu, D., and Westerfield, M.
- Source
- Full text @ BMC Dev. Biol.
|
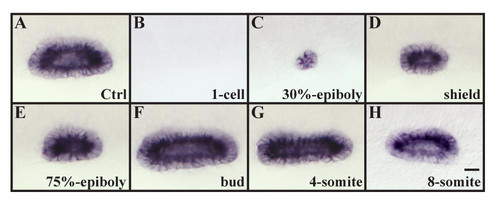
Otic vesicle size is affected by the overexpression of fgf8 depending on the developmental stage. (A, B) Overexpression of fgf8 by mRNA injections at the 1-cell stage completely ablates all indications of otic fate (27/40 embryos, B) in comparison to wild-type vesicles (A). (C-E) Misexpression of fgf8 at 30% epiboly (28/28 embryos, C), shield stage (27/28 embryos, D) and 75% epiboly (29/29 embryos, E) results in smaller otic vesicles. (F-H) Otic vesicles are increased in size if fgf8 is misexpressed at the tailbud (26/29 embryos, F) or the 4-somite stage (24/28 embryos, G) whereas at the 8-somite stage no change in vesicle size is observed (26/26 embryos, H). Lateral views of otic vesicles highlighted with starmaker at 24h with anterior to the left and dorsal towards the top. Scale bar: 30 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
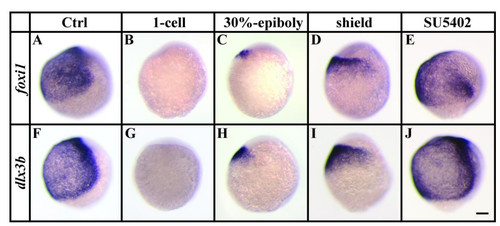
Ectopic Fgf-signaling represses foxi1 and dlx3b before and during gastrulation. (A, B, F, G) Expression of foxi1 and dlx3b is absent after overexpression of fgf8 by mRNA injections at the 1-cell stage in comparison to wild-type embryos. (C, D, H, I) Misexpression of fgf8 at 30% epiboly or shield stages results in smaller foxi1 and dlx3b expression domains. (E, J) Loss of Fgf-signaling after pharmacological inhibition with SU5402 from late blastula stages until the end of gastrulation has no effect on the ventral expression of foxi1 and dlx3b. Lateral views at the end of gastrulation with dorsal to the right and anterior towards the top. Scale bar: 100 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
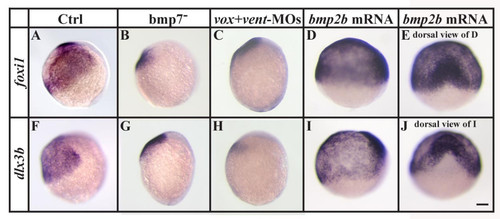
Bmp-signaling is required for foxi1 and dlx3b expression during gastrulation. (A-C, F-H) Expression of foxi1 and dlx3b is strongly reduced in bmp7 mutants or embryos injected with Vox and Vent morpholinos (MOs) in comparison to wild-type embryos. (D, E, I, J) Overexpression of bmp2b by mRNA injections at the 1-cell stage leads to an expansion of both foxi1 and dlx3b expression domains at the expense of anterior neural plate. (A-D, F-I) Lateral views at the end of gastrulation with dorsal to the right and anterior upward; (E, J) dorsal views of embryos shown in D and I with anterior towards the top. Scale bar: 100 μm EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
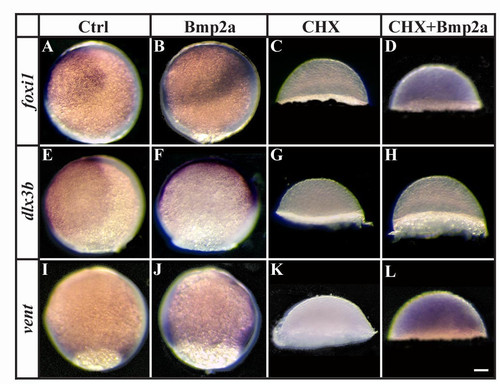
foxi1 and vent but not dlx3b are direct targets of Bmp-signaling during gastrulation. (A, B, E, F, I, J) Expression of foxi1, dlx3b and vent is expanded after Bmp2a protein injection at late blastula stages in comparison to wild-type embryos. (C, D, G, H, K, L) Pharmacological inhibition of protein synthesis with cycloheximide (CHX) at late blastula stages blocks all indications of foxi1, dlx3b and vent expression (C, G, K), whereas foxi1 and vent but not dlx3b expression is restored in CHX-treated embryos after Bmp2a protein injection (D, H, L). Lateral views at the end of gastrulation with dorsal to the right and anterior towards the top (note that CHX treatment blocks epiboly movements). Scale bar: 90 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
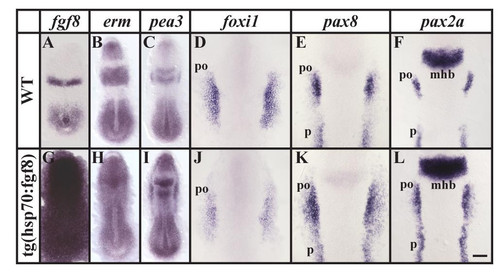
Ubiquitous fgf8 expression at late gastrulation stages leads to ectopic otic induction within the preotic field. (A, G) Ectopic fgf8 expression can be detected throughout the embryo after a 30 minute heat shock in transgenic hsp:fgf8 embryos in comparison to non-transgenic embryos. (B, C, H, I) Within 2 hours, expression of the two Fgf reporter genes, erm and pea3, is upregulated in cells of the transgenic embryos whereas non-transgenic siblings are unaffected. (D-F, J-L) After misexpression of fgf8 at late gastrulation stages, expression of foxi1 is reduced, whereas the preotic expression domains of pax8 and pax2a are enlarged. Dorsal views of 2?5-somite stage embryos with anterior towards the top. mhb, midbrain-hindbrain border; po, preotic region; p, pronephros. Scale bar: 100 μm for A-C, G-I; 40 μm for D-F, J-L. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
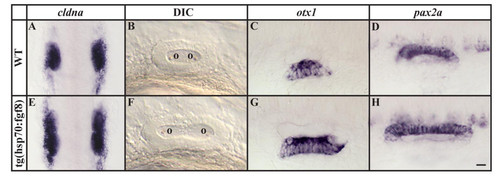
Ectopic otic induction after fgf8 expression at late gastrulation stages leads to formation of larger but correctly patterned placodes and vesicles. (A, E) Otic placodes labeled by cldna expression are increased in size in transgenic hsp:fgf8 embryos in comparison to non-transgenic embryos following a heat shock at late gastrulation stages. (B-D, F-H) The enlarged otic vesicles of transgenic embryos show no apparent patterning defects in comparison to non-transgenic siblings assessed by morphology and marker gene expression, including otx1 and pax2a. (A, E) Dorsal views of 12-somite stage embryos with anterior towards the top; (B-D, F-H) lateral views of otic vesicles at 24h with anterior to the left and dorsal towards the top. o, otolith. Scale bar: 50 μm for A, E; 30 μm for B-D, F-H. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Ectopic otic induction after fgf8 expression at late gastrulation stages requires both, Foxi1 and Dlx3b. (A-D) Inactivation of Dlx3b or Foxi1 in wild-type embryos by morpholino injection (MO) leads to a reduction of ear size in comparison to wild-type embryos, and combined loss of Dlx3b and Foxi1 results in loss of all indications of otic specification. (E-H) Ear size reduction by depletion of Dlx3b or Foxi1 but not combined loss of Dlx3b and Foxi1, can be partially rescued in transgenic hsp:fgf8 embryos heat shocked at late gastrulation stages. Lateral views of otic vesicles hybridized with starmaker at 24h with anterior to the left and dorsal towards the top. Scale bar: 40 μm. |
|
Ectopic foxi1 expression after treatment with retinoic acid (RA) results in ectopic Fgf-dependent otic induction. (A, B, E, F) In comparison to wild-type control embryos treated with DMSO, embryos treated with 20nM RA show ectopic pax8 and foxi1 expression surrounding the anterior neural plate border without affecting the neural expression of otx2. (C, G) In fgf3, fgf8 double mutants, pax8 is completely abolished in the control embryos, whereas RA-treated double mutant embryos show weak anterior expression of pax8. (D, H) In foxi1 mutants treated with DMSO, pax8 expression can not be detected in the preotic region; but in foxi1 mutants treated with RA, residual anterior pax8 expression is present. Dorsal views of 1?3-somite stage embryos with anterior towards the top. Scale bar: 40 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
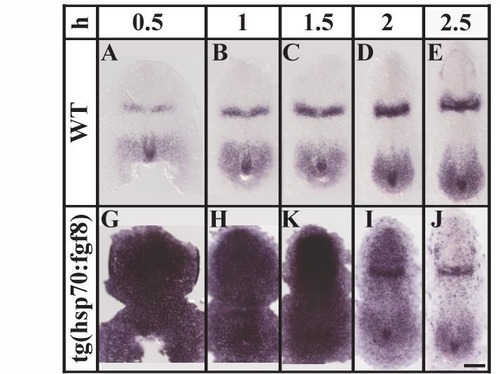
Heat shock at the end of gastrulation produces strong and ubiquitous fgf8 expression in transgenic animals. (A-C, G-K) Following a 30 minute heat shock, strong and ubiquitous expression of fgf8 can be observed in the transgenic embryos (G-K) up to 1.5 hours after heat shock, masking the endogenous fgf8 expression domains that are observed in the wild-type embryos (A-C). (D, I) Ectopic fgf8 mRNA is gradually lost and the endogenous fgf8 expression domains emerge at 2 hours after heat shock. (D, I) At 2.5 hours after heat shock only scattered cells show ectopic fgf8 expression in transgenic embryos. Dorsal views of 2?5-somite stage embryos with anterior towards the top. h, hours after heat shock; mhb, midbrain-hindbrain border; tb, tail bud. Scale bar: 100 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
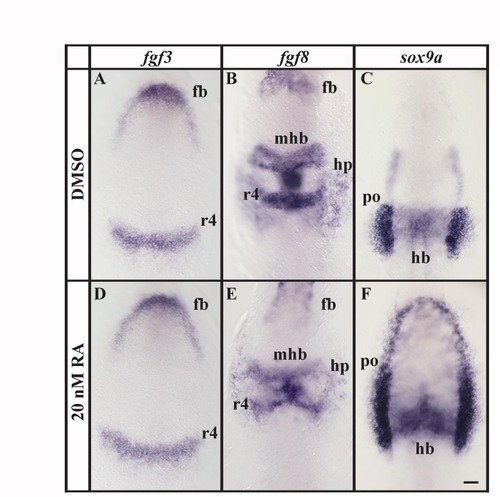
Retinoic acid treatment has little effect on patterning along the anterior-posterior axis. (A, B, D, E) Expression of fgf3 or fgf8 in embryos treated with 20 nM RA is indistinguishable from control embryos treated with DMSO. (C, F) In RA treated embryos expression of sox9a in the preotic region expands to surround the anterior neural plate border in comparison to control embryos. However, sox9a expression in the hindbrain is identical in RA and DMSO treated embryos. Dorsal views of 1?5-somite stage embryos with anterior towards the top. fb, forebrain; hb, hindbrain; hp, heart primordium; mhb, midbrain-hindbrain border; r4, rhombomere 4; po, preotic region. Scale bar: 40 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
The increase in otic tissue, following a heat shock at late gastrulation stages of transgenic hsp:fgf8 embryos, is transient. (A, D) At 28 hours post fertilization, otic vesicles in transgenic fish heat shocked at late gastrulation stages are still larger than in non-transgenic siblings. (B, C, E, F) The size difference of otic vesicles in transgenic and non-transgenic embryos is less prominent at 50 hours post fertilization, and indistinguishable by 72 hours post fertilization. Lateral views of live otic vesicles with anterior to the left and dorsal towards the top. o, otolith. Scale bar: 120 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|