- Title
-
Monorail/Foxa2 regulates floorplate differentiation and specification of oligodendrocytes, serotonergic raphe neurones and cranial motoneurones
- Authors
- Norton, W.H., Mangoli, M., Lele, Z., Pogoda, H.M., Diamond, B., Mercurio, S., Russell, C., Teraoka, H., Stickney, H.L., Rauch, G.J., Heisenberg, C.P., Houart, C., Schilling, T.F., Frohnhoefer, H.G., Rastegar, S., Neumann, C.J., Gardiner, R.M., Strähle, U., Geisler, R., Rees, M., Talbot, W.S., and Wilson, S.W.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
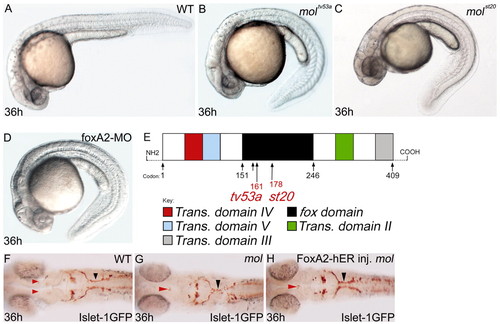
The mol locus encodes Foxa2. (A-D) Lateral views of 36 hpf wild-type (A), moltv53a (B), molst20 (C) and foxa2 morphant (D) embryos. (E) Structure of the Foxa2 protein showing the positions of the likely truncations within the forkhead domain caused by the moltv53a and molst20 mutations. moltv53a results in the complete loss of transactivating domains II and III, leaving a C-terminally truncated Foxa2 protein. molst20 disrupts the forkhead box DNA-binding domain, downstream of moltv53a. Trans. domain, transactivating domain; fox domain, forkhead box DNA-binding domain. (F-H) Dorsal views of brains of a wild-type (F) and two moltv53a mutant (G,H) embryos labelled to reveal the cranial motor nuclei. The fusion of the facial motor nucleus (black arrowheads) is rescued in the moltv53a embryo expressing functional Foxa2 (H). The embryo in H is a homozygous moltv53a mutant as it still shows midline fusion of a reduced oculomotor nucleus (red arrowhead). |
|
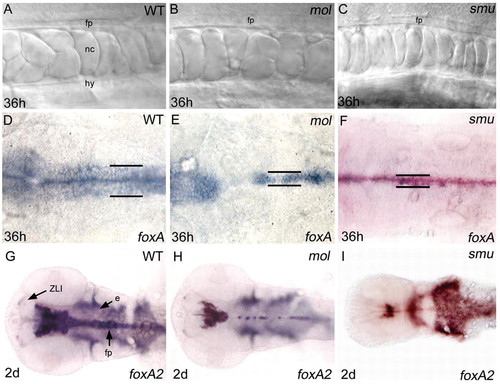
The floorplate is reduced in width in both mol-/- and smu-/- embryos. (A-C) Lateral views of the floorplate in the trunk of living wild-type, mol-/- and smu-/- embryos. Cuboidal floorplate cells are present in all embryos, although the cells are increased in size in mol-/-. (D-F) Dorsal views of foxa expression in the hindbrain floorplate. In the mol-/- and smu-/- mutants, expression is reduced from a six cell wide band to a one to three cell wide band (black lines). Additionally, gaps of expression are present in the mol-/- mutant. (G-I) Dorsal views of foxa2 expression in the head. Midline expression is narrow in both the mol-/- and the smu-/- mutant, and additionally is patchy in the midbrain and hindbrain in the mol-/- mutant. e, endoderm; fp, floorplate; hy, hypochord; nc, notochord; ZLI, zona limitans intrathalamica. |
|
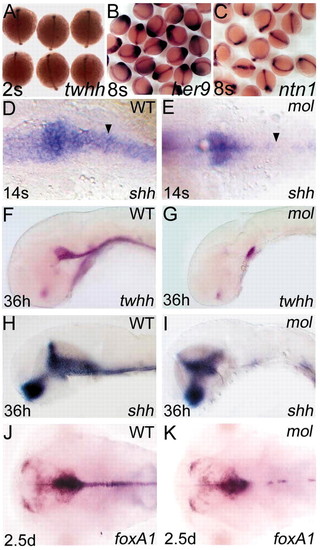
Expression of regulatory genes expressed in the MFP of wild-type embryos is not maintained in mol-/- mutants. Dorsal (A-E,J,K) and lateral (F-I) views of wild-type (D,F,H,J) and mol-/- embryos (E,G,I,K), at ages shown in the bottom left-hand corner, analysed for expression of various genes (indicated in the bottom right-hand corner). (A-C) Clutches of embryos from parents heterozygous for the moltv53a mutation. No obvious differences in twhh, her9 or ntn1 expression in prospective floorplate between wild-type and mol-/- mutants is evident at these early stages. The arrowheads in D,E show gaps in floorplate shh expression in the mol-/- embryo compared with wild type. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
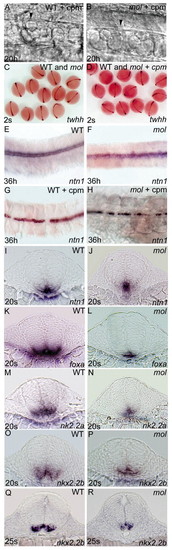
Floorplate develops in mol-/- embryos independently of Hh activity. Lateral views (A,B), dorsal views (C-H) and transverse sections (I-R) of wild-type (A,C,E,G,I,K,M,O,Q) and mol-/- (B,D,F,H,J,L,N,P,R) embryos with (A,B,D,G,H) and without (C,E,F,I-R) cyclopamine treatment. (A,B) Both the wild-type and the mol-/- embryo treated with cyclopamine have cuboidally shaped floorplate cells (arrowhead) at 20 hpf. (C,D) Clutches of embryos from parents heterozygous for the moltv53a mutation. Treatment with cyclopamine between the 4-hour and 2-somite stages did not appear to affect expression of twhh in either wild-type or mol-/- mutants. (E-H) Wild-type and mol-/- embryos showing patchy ntn1 expression after treatment with cyclopamine. (I-R) Transverse sections through the spinal cord of wild-type and mol-/- embryos showing changes in floorplate expression of various genes in the mutants. cpm, cyclopamine. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
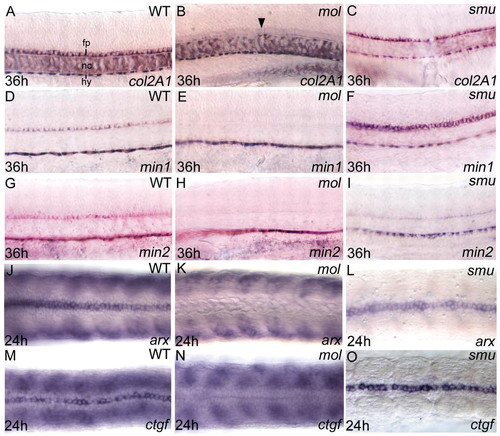
Floorplate differentiation fails in mol-/- but not in smu-/- embryos. Lateral (A-I) and dorsal (J-O) views of the trunk floorplate in 36 hpf (A-I) and 24 hpf (J-O) wild-type, mol-/- and smu-/- embryos. (A-O) Expression of floorplate differentiation markers col2a1, min1, min2, arx and ctgf is similar in wild-type and smu-/- embryos but expression is severely reduced or absent in the mol-/- embryos (despite the presence of floorplate cells, arrowhead in B). Although floorplate expression is retained, the somitic expression of arx and ctgf is lost in the smu-/- mutants (L,O). fp, floorplate; hy, hypochord; nc, notochord.
|
|
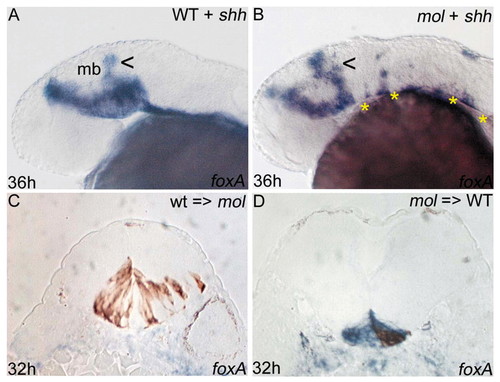
Floorplate phenotypes in mol-/- embryos are not only due to reduced Hh activity. (A,B) Lateral views of wild-type and mol-/- embryos following overexpression of exogenous shh. There is some dorsal expansion (arrowheads) of foxa expression in the midbrain of both the wild-type and the mol-/- embryo; however, foxa expression remains discontinuous and narrow along the CNS midline of the mol-/- embryo (asterisks in B). (C,D) Transverse sections of embryos in which wild-type cells were transplanted into the prospective floorplate of a mol-/- embryo (C) or mol-/- cells were transplanted into the prospective floorplate of a wild-type embryo (D). foxa is shown in blue and transplanted cells are stained brown.
|
|
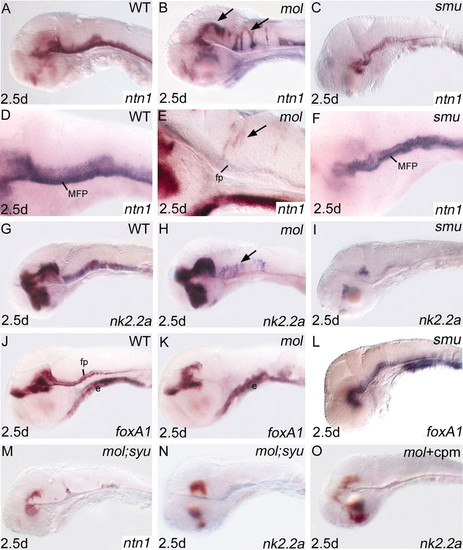
Expression of nk2.2a and ntn1 is expanded dorsally in the midbrain and hindbrain neural tube of mol-/- embryos, but is reduced in smu-/- embryos. Lateral views of brains of wild-type (A,D,G,J), mol-/- (B,E,H,K), smu-/- (C,F,I,L) and mol-/-;syu-/- double mutant (M,N) embryos and mol-/- embryos treated with cyclopamine (O) (cpm) analysed for expression of genes indicated bottom right. Arrows indicate ectopic dorsal expression of ntn1 (B,E) and nk2.2a (H) in mol-/- embryos. cpm, cyclopamine; e, endoderm; fp, floorplate; MFP, medial floorplate.
EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
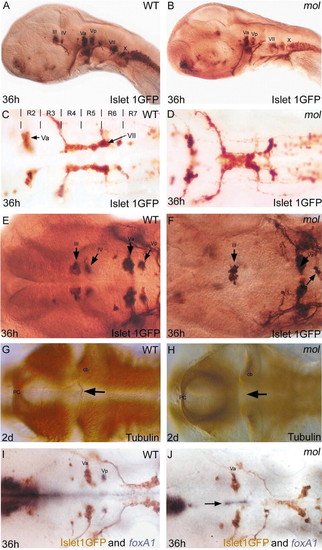
mol-/- embryos exhibit cranial motoneurone induction and patterning defects. Lateral (A,B) and dorsal (C-J) views of wild-type (WT) and mol-/- embryos labelled with various antibodies and RNA probes (indicated bottom right) to reveal cranial motoneurones and their axons. The unlabelled arrow in F shows a few Vp neurones in the mol-/- embryo. Arrows in G and H show the trochlear decussation in wild type (G) and its absence in mol-/- (H) embryos. The arrow in J indicates foxa1 expression retained between the two bilateral Va nuclei of the mol-/- mutant. III, oculomotor nucleus; IV, trochlear motor nucleus; Va and Vp, anterior and posterior components of the trigeminal motor nucleus; VII, facial motor nucleus; X, vagal nucleus cb, cerebellum; pc, posterior commissure; R, rhombomere.
|
|
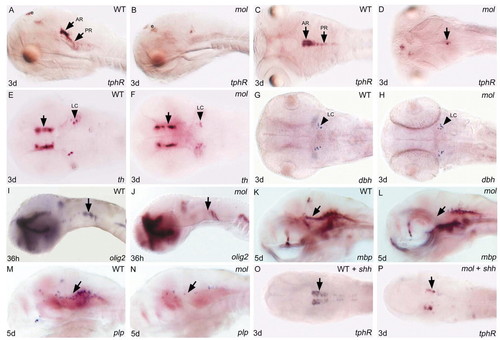
Both serotonergic raphé neurones and oligodendrocyte precursor cells are severely depleted in mol-/- embryos. Lateral (A,B,I-N) and dorsal (C-H,O,P) views of brains of wild-type and mol-/- embryos and wild-type and mol-/- embryos overexpressing shh (WT + shh; mol + shh) analysed for genes indicated bottom right. (A-D) tphR expression reveals serotonergic neurones. Arrows indicate anterior (AR) and posterior (PR) raphé neurones. Unlabeled arrow in D indicates a few residual tphR + neurons. (E-H) th reveals dopaminergic diencephalic neurones (arrows in E,F); noradrenergic neurones of the LC are labelled both with th and dbh probes. (I-N) olig2 labels oligodendrocyte precursor cells and mbp and plp expression marks nascent oligodendrocytes. Arrows indicate areas of reduced olig2, mbp and plp expression in mol-/- mutant embryos. (O,P) Arrows indicate increased number of tphR-expressing serotonergic neurones in the wild-type embryo and a rescue of serotonergic neurones in the mol-/- embryo following shh injection. e, epiphysis; LC, locus coeruleus. |