|
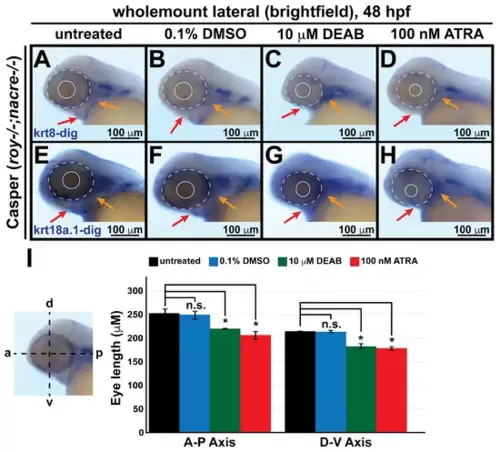
Changes in retinoic acid levels affect early ocular and craniofacial development. Wholemount in situ hybridization was performed using a chromogenic (blue) colorimetric assay. Lateral images (A–D,E–H) of treated zebrafish embryos taken at 48 hpf show the teratogenic effects of pharmacological insult with 10 μM DEAB and 100 nM ATRA on the ocular and craniofacial neural crest during early development. The solid and dashed circles highlight the reduced eye size. The red and orange arrows highlight jaw and pharyngeal arch malformation, respectively. (I) Quantitative analysis of this effect shows that treatment with both DEAB and ATRA delayed ocular development and significantly decreased the eye size of the treated fish, as measured along the anterior–posterior (a-p) and dorsal-ventral (d-v) axes. *, p-value < 0.05; n.s., not significant.
|