Fig. 8
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-080325-112
- Publication
- Lachnit et al., 2008 - Alterations of the cytoskeleton in all three embryonic lineages contribute to the epiboly defect of Pou5f1/Oct4 deficient MZspg zebrafish embryos
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
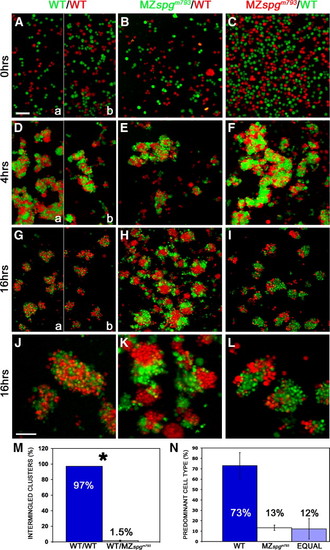
Altered adhesive properties of pou5f1 deficient cells. Embryos were labeled by microinjection at one cell stage either with Rhodamine-dextran (MW: 10 kDa) or Alexa488-dextran (MW: 10 kDa), and primary co-cultures of dissociated and mixed sphere stage embryo cells were plated on Fibronectin/Collagen coated dishes. Volume rendering of confocal stacks of cultures: (A?C) dissociation control after plating, (D?F) after 4 h, (G?I) after 16 h incubation. (J?L) Higher magnification of cell aggregates. (J) Intermingled status of homogeneous WT?WT clusters. (K, L) Distinct subcluster formation of heterogeneous WT-MZ clusters. (M) Measurements of the percentage of intermingled clusters including standard error: WT?WT co cultures showed in 97 ± 0% intermingled clusters, WT-MZspgm793 co-cultures in 1.5 ± 0.7%; p = 0.004. (N) Predominant cell types in heterogeneous clusters. WT cells = 73 ± 12.5%; MZspgm793 cells = 13.2 ± 2.5%; equal contribution of cell types = 12.2 ± 9.8%. In panels A, D, and G, the left (a) half images show WT control performed for the experiment in panels B, E, H, and K, and right (b) for panels C, F, I, and J. Scale bars: (A?I) 100 μm; (J?L) 50 μm. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Shield |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 315(1), Lachnit, M., Kur, E., and Driever, W., Alterations of the cytoskeleton in all three embryonic lineages contribute to the epiboly defect of Pou5f1/Oct4 deficient MZspg zebrafish embryos, 1-17, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.