- Title
-
Zebrafish aussicht mutant embryos exhibit widespread overexpression of ace (fgf8) and coincident defects in CNS development
- Authors
- Heisenberg, C.P., Brennan, C., and Wilson, S.W.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
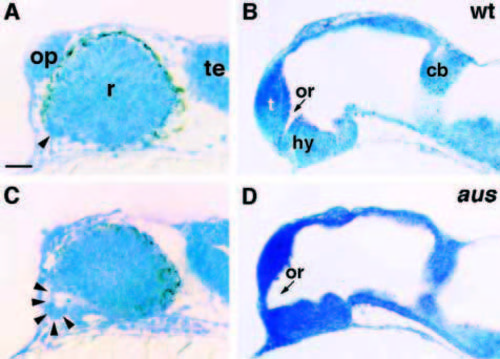
Optic stalks and optic recesses are enlarged in aus mutant embryos. Sections through the head region of prim-12 stage wildtype and aus mutant embryos. (A,C) Parasagittal section at the junction between retina and optic stalks. The optic stalks (arrowheads) are larger in the aus mutant embryo (C) as compared to a wild-type sibling (A). (B,D) Sagittal section. The optic recess is expanded in an aus mutant embryo (D) as compared to a wild-type sibling (B). Abbreviations: cb, cerebellum; hy, hypothalamus; op, olfactory placodes; or, optic recess; r, retina; t, telencephalon; te, tectum; wt, wild type. Scale bar: 25 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
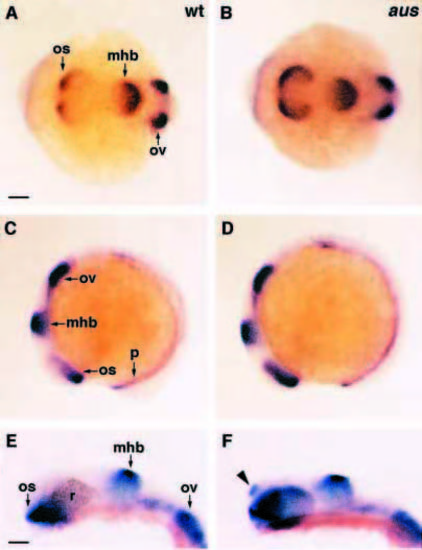
noi(pax2.1) expression is increased in aus mutant embryos. Dorsal (A,B) and lateral (C-F) views of whole embryos (A-D) or heads (E,F) with rostral to the left. (A-D) 6-somite-stage embryos. The expression domains of noi are expanded within the optic stalks and to a lesser extent at the mhb in the aus mutant embryo (B,D) compared to a wild-type sibling (A,C). (E,F) Prim-12 stage embryos. noi expression is upregulated within the optic stalk and mhb and ectopically expressed (arrowhead in F) within the telencephalon of the aus mutant embryo (F) as compared to a wildtype sibling (E). Abbreviations: d, diencephalon; mhb, midbrain/hindbrain boundary; os, optic stalk; ov, otic vesicle; p, pronephric duct; r, retina; wt, wild type. Scale bars: (A-D) 100 μm; (E,F) 50 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
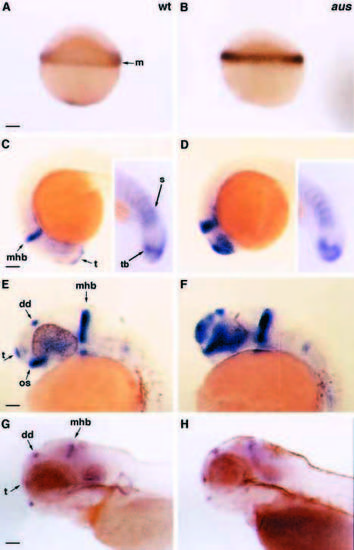
ace(fgf8) expression is upregulated in aus mutant embryos. Lateral views of whole embryos. (A,B) Sphere stage. ace expression in the blastula margin is upregulated in the putative aus mutant embryo (B) as compared to a putative wild-type sibling (A). (C-F) ace expression is upregulated at many sites of expression in 18-somite stage (C,D) and prim-12 stage (E,F) aus mutant embryos (D,F) as compared to wild-type siblings (C,E). Inset panels in C,D are close-up pictures of ace expression in the somites and tailbud. (G,H) By the fourth day of development, there is no apparent difference in the expression levels of ace in the aus mutant embryo (H) as compared to a wild-type sibling (G). Abbreviations: dd, dorsal diencephalon; m, margin; mhb, midbrain/hindbrain boundary; os, optic stalks; s, somites; t, telencephalon; tb, tailbud; wt, wild-type. Scale bars: (A-D) 125 μm; (E-H) 100 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
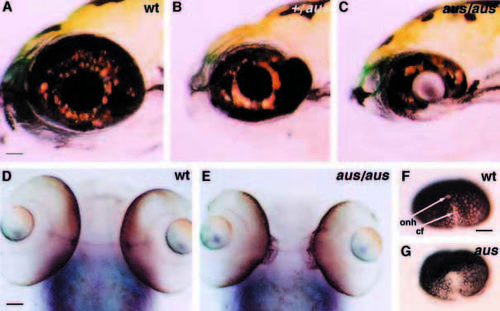
Differentiation of the eyes is perturbed in aus mutant embryos. Lateral (A-C) and ventral (D,E) views of the eyes. (A-C) In heterozygous aus mutant embryos at early larval stage, there is ectopic outgrowth of the temporal retina (B) and, in putative homozygous aus mutant embryos, the ventral retina is reduced (C) as compared to wild-type siblings (A). (D,E) Ectopic outgrowth at the back of the retina is observed in the aus mutant embryo at early larvae stage (E) as compared to a wild-type sibling (D) (the faint blue staining is noi expression within the eyes, optic nerves and midline). (F,G) In the putative homozygous aus mutant embryo at prim-20 stage (G) there is incomplete closure of the optic fissure as compared to a wild-type sibling (F). See also Fig. 6G,H. Abbreviations: cf, choroid fissure; onh, optic nerve head; wt, wild type. Scale bars: (A-C) 50 mm; (D-G) 25 μm. |
|
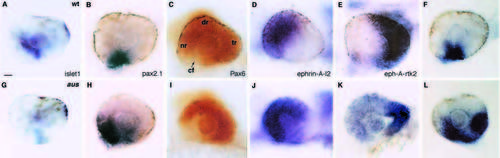
Gene expression is altered in the retinae of aus mutant embryos. Lateral views of eyes of wild-type (top row) and aus mutant (bottom row) prim-12 stage embryos. (A,G) islet1. Expression is reduced in the aus mutant embryo. (B,H) noi (pax2.1). Expression is expanded in the ventral retina of the aus mutant embryo. (C,I) Pax6. Expression is reduced in the ventral retina of the aus mutant embryo. (D,J) ephrin-A-l2. Expression is expanded into the temporal retina of the aus mutant embryo. (E,K) eph-A-rtk2. Expression is reduced in the temporal retina of the aus mutant embryo. (F,L) net1a. Expression is expanded in the ventral retina of the aus mutant embryo. Abbreviations: cf, choroid fissure; dr, dorsal retina; nr, nasal retina; tr, temporal retina. Scale bar: 25 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
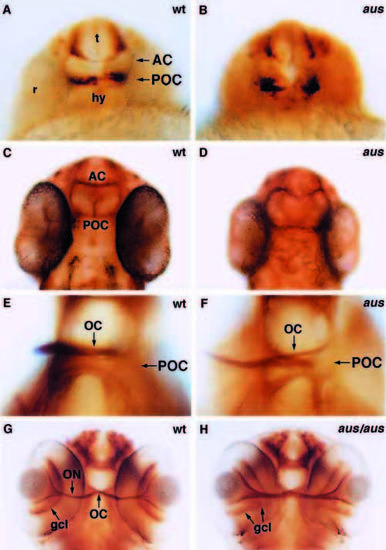
Commissure formation is delayed and perturbed in aus mutant embryos. Frontal/ventral views of whole-mount embryos stained with an antibody against acetylated tubulin focussed at the level of the anterior and postoptic commissures. (A,B) Prim-5 stage embryos. The anterior commissure and postoptic commissure are not formed in the aus mutant embryo. (C,D) Prim-25 stage embryos. By this stage, some axons have crossed the midline in both commissures in the aus mutant embryo. (E,F) Protruding-mouth stage embryos. The postoptic commissure and optic chiasm are defasciculated and slightly disorganised in the aus mutant embryo. (G,H) Protrudingmouth stage embryos. The optic axons are less tightly fasciculated as they exit the eye of the putative homozygous aus mutant embryo as compared to the wild-type sibling. The failure of the choroid fissure to fully close (coloboma) results in the retinal ganglion cells protruding towards the midline. Abbreviations: AC, anterior commissure; gcl, ganglion cell layer; hy, hypothalamus; OC, optic chiasm; ON, optic nerve; POC, postoptic commissure; r, retina; t, telencephalon. Scale bar: (A-D,G,H) 25 μm; (E,F) 10 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
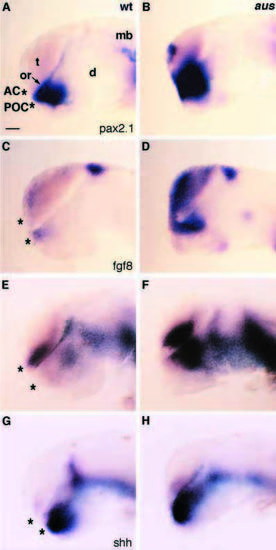
Midline gene expression is expanded in aus mutant embryos. Lateral views of gene expression in wild-type (A,C,E,G) and aus mutant (B,D,F,H) dissected prim-12 stage brains with rostral to the left. The asterisks indicate the positions of the anterior and postoptic commissures. (A,B) noi/pax2.1. Expression around the optic recess is expanded and there is ectopic expression within the telencephalon of the aus mutant embryo. (C,D) ace/fgf8. Expression is upregulated throughout much of the rostral/dorsal forebrain of the aus mutant embryo. (E,F) net1a. Expression is upregulated in the aus mutant embryo, particularly around the optic recess. (G,H) shh. Expression domains are slightly disrupted in the aus mutant but generally similar to the wild-type embryo. Abbreviations: AC, anterior commissure; d, diencephalon; mb, midbrain; POC, postoptic commissure; t, telencephalon; wt, wild type. Scale bar: 30 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
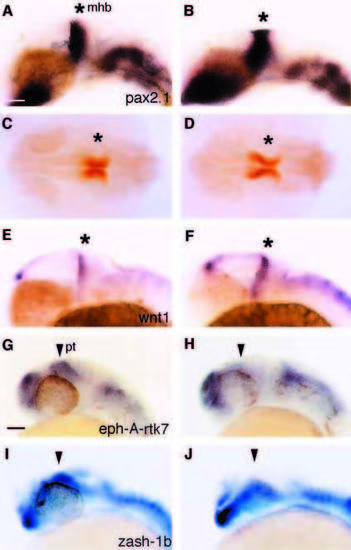
Midbrain and pretectal gene expression is altered in aus mutant embryos. Lateral (A,B,E-J) and dorsal (C,D) views of prim- 12 stage wild-type (A,C,E,G,I) and aus mutant (B,D,F,H,J) embryos. (A,B) noi (pax2.1). Expression is slightly expanded in the midbrain of the aus mutant embryo, particularly in ventral regions. (C,D) En. Expression appears expanded in the midbrain of the aus mutant embryo. (E,F) wnt1. Levels of transcripts are enhanced in the caudal diencephalon and mhb of the aus mutant embryo. Expression also appears to be increased in the dorsal hindbrain. (G,H) eph-A-rtk7. Pretectal expression (arrowhead) of eph-A-rtk7 is reduced in the aus mutant embryo. (I,J) zash-1b. Pretectal expression (arrowhead) of zash-1b is reduced in the aus mutant embryo. Abbreviations: mhb, midbrain/hindbrain boundary (*); pt, pretectum; wt, wild type. Scale bar: 50 μm (A-F); 60 μm (G-J). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
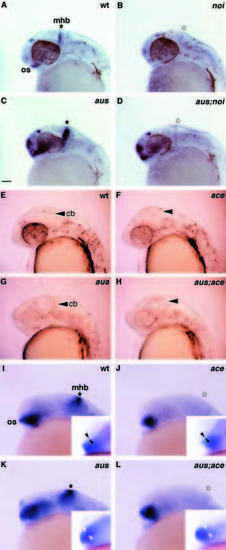
aus is unlikely to represent a mutation in the ace or noi genes. Lateral views of prim-12 (A-H) and prim-5 stage (I-L) embryos with rostral to the left. Asterisks indicate the position of the mhb. (A-D) Analysis of ace expression in wild-type (A), noi (B), aus (C) and aus;noi double mutant (D) embryos. ace expression is absent at the mhb in the absence of functional Noi and is upregulated in the forebrain both in aus and aus;noi double mutant embryos. (E-H) Appearance of wild-type (E), ace (F), aus (G) and aus;ace double mutant (H) embryos. In the aus;ace double mutant, the rostral brain looks similar to the aus phenotype while the absence of cerebellum (arrowheads) is characteristic of the ace phenotype. (I-L) Analysis of noi expression in wild-type (I), ace (J), aus (K) and aus;ace double mutant (L) embryos. noi expression is absent at the mhb in the absence of functional Ace. The aus dependent upregulation of noi in the eyes and forebrain (K) is much reduced in the absence of functional Ace (L). The inset panels in I-L show the width of the optic recess (arrowheads) used as a landmark to infer the genotype the embryos – phenotypic morphological differences are much more visible in living embryos prior to the in situ protocol (see E-H). Abbreviations: cb, cerebellum; mhb, midbrain/hindbrain boundary; os, optic stalk. Scale bar: 50 μm. |