- Title
-
Novel biallelic variants in the PLEC gene are associated with severe hearing loss
- Authors
- Zhang, T., Xu, Z., Zheng, D., Wang, X., He, J., Zhang, L., Zallocchi, M.
- Source
- Full text @ Hear. Res.
|
Pedigree and gene analysis of PLEC in a pediatric patient with ANSD (Family #1). A: Pedigree of the affected family member with ANSD. B: Trio whole exome sequencing, biallelic PLEC variants segregating in family #1 were confirmed by Sanger sequencing. C: Schematic representation of the plectin protein with the newly identified mutations. The central a-helical rod domain, which can form a coiled-coil structure after dimerization, links the N- and C-terminal globular domains. The plakin domain consists of 9 spectrin repeats. ABD: actin binding domain, PRD: plectin repeat domain. D: Amino acid alignment of the regions containing the plectin mutations. Capital letters at the top denote conserved amino acids among all the species. |
|
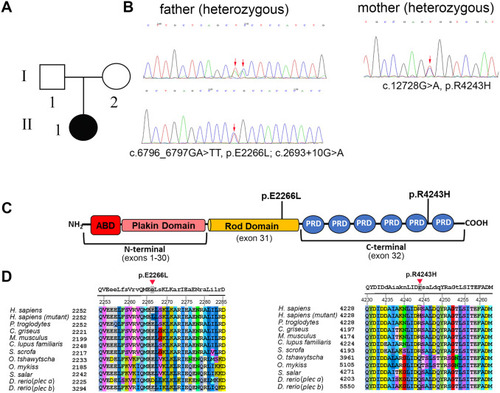
Pedigree and gene analysis of PLEC in family #2. A: Pedigree of the affected family members. B: Trio whole-exome sequencing analysis was performed on family #2 (father II-4, mother II-5 and daughter III-1). Sanger sequencing confirmed the presence of biallelic PLEC variants in II-4 and III-1 while II-5 was heterozygous carrier of a single mutation. C: Schematic representation of the plectin protein with the newly identified mutations. D: Amino acid alignment of the regions containing the plectin mutations. Capital letters at the top denote conserved amino acids among all the species. |
|
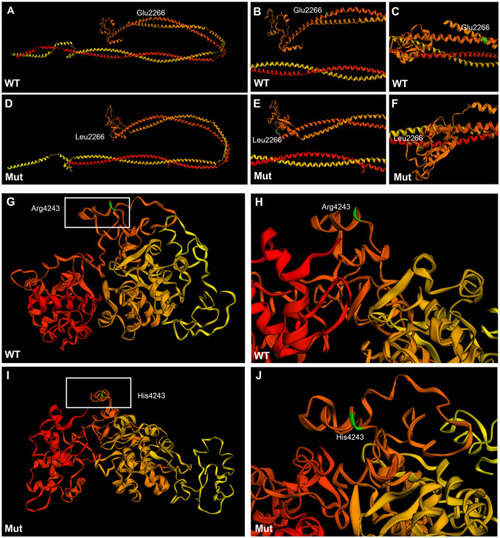
Tertiary structure prediction of wild type and mutant plectin in family #1. A-F: Sequence homology-based prediction approach of the 770 amino acid sequence encompassing the mutation E2266L. G-J: Sequence homology-based prediction approach of the 530 amino acid sequence encompassing the mutation R4243H. The 3D structure was predicted from the condensing complex from S. cerevisiae employing Phyre2 free tool. Amino acids are colored code in a gradient from red (N-terminus) to yellow (C-terminus).The amino acid of interest in colored in green. Wild type rod domain (A-C), mutant rod domain (D-F), wild type 5th and 6th plectin repeat domains (G-H), mutant 5th and 6th repeat domains (I-J). |
|
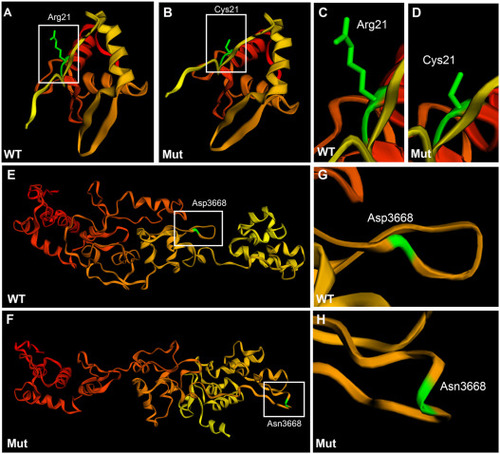
Tertiary structure prediction of wild type and mutant plectin in family #2. A-D: Sequence homology-based prediction approach of the 200 amino acid sequence encompassing the mutation R21C. E-H: Sequence homology-based prediction approach of the 500 amino acid sequence encompassing the mutation D3668N. In the case of the N-terminal region there was no 3D-predicted structure. For the C-terminal region the 3D structure was predicted from the plakin family member, desmoplakin. Phyre2 free tool was used for the analysis. Amino acids are colored code in a gradient from red (N-terminus) to yellow (C-terminus).The amino acid of interest in colored in green. Wild type N-terminus region (A, C), mutant N-terminus region (B, D), wild type 3rd and 4th plectin repeat domains (E, G), and mutant 3rd and 4th repeat domains (F, H). |
|
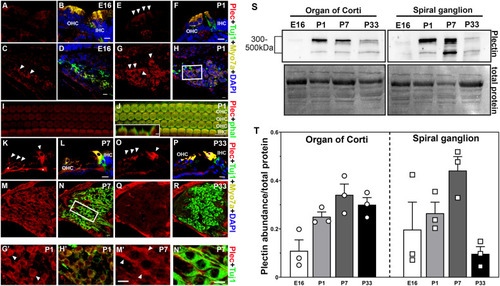
Spatiotemporal distribution of plectin in mouse inner ear. A-R: Representative images from at least three different animals at each time point. Cochlea cross sections of the organ of Corti at E16 (A-B), P1 (E-F), P7 (K-L) and P33 (O-P). Cochlea cross-sections of the spiral ganglion neurons at E16 (C-D), P1 (G-H, G?-H?), P7 (M-N, M?-N?) and P33 (Q-R). G?-H? and M?-N? correspond to higher magnification images of the framed areas in H and N, respectively. I-J: Whole mount P1 organ of Corti. Insert in J represent a Z-view of the outer hair cell apical structures. Arrowheads denote plectin immunopositive staining. Asterisks in K denote neuronal fiber staining. Plectin (plec, red), myosin 7A (Myo7A, yellow), beta-III tubulin (Tuj1, green), DAPI (blue). Scale bars: A-R, G?-H?, and M?-N?: 10 ?m. Inset in J: 2 ?m. S-T: Immunoblot analysis of the organ of Corti and spiral ganglion at the different developmental time points under study. S: Representative immunoblot. Numbers (left) indicate molecular weight markers. Total protein was used as a loading control. T: Quantification of at least 3 independent experiments. Results are presented as mean +/- SEM. OHC: outer hair cells. IHC: inner hair cells |
|
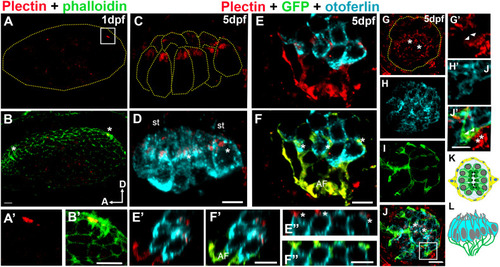
Analysis of plectin distribution in zebrafish. A-J?: Representative images of at least three fish at each time point. A-B: Otic vesicle from 1dpf wild type zebrafish embryo immunostained for plectin (red) and counterstained with phalloidin (green). Asterisks in B denote the hair cell precursors. A?-B?: High magnification of the framed area in A. Plectin localizes at the base of the hair cell bundle (A?). C-F: Apical (C-D) and basal (E-F) views of the medial crista from a 5dpf Tg(NeuroD-GFP). C-D: Plectin localizes at the base of the hair cell bundle (asterisk in D). E-F: The afferent fibers (GFP positive, AF) and the hair cell-neuron interface (asterisks) are also positive for plectin (red). E?-F?: High magnification Z-view images from E and F, showing the contacts between the neuronal fibers and the base of the hair cells (asterisks). G-J: Neuromast from a 5dpf Tg(NeuroD-GFP), showing apical localization of plectin (asterisks). G?-J?: High magnification images from frame in J showing expression of plectin by the neuronal fibers (asterisks) and at the interface between the hair cells and the neurons (arrowheads). K-L: Cartoons depicting a 5dpf neuromast (K, top view) and a crista (L, lateral view). Plectin (red). Phalloidin (green). GFP (green). Otoferlin (cyan). A: anterior, D: dorsal, st: stereocilia. Scale bars: A-D, A?-B?, E?-F?, E?-F?, G-J, G?-J?: 5 ?m, E-F: 10 ?m. |
|
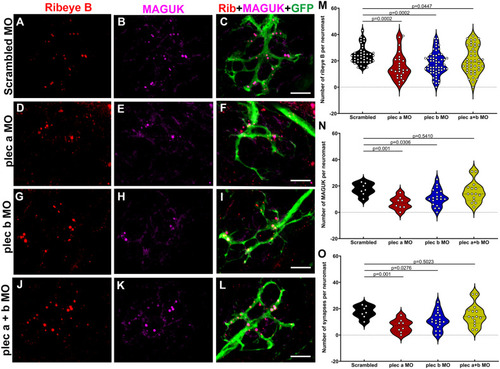
Plectin knockdown results in abnormal hair cell synapses. A-L: Representative images of 3dpf Tg(NeuroD-GFP) neuromasts from scrambled (A-C), plectin a (D-F), plectin b (G-I), plectin a + b (J-L) morphants. Samples were immunostained for the pre-synaptic marker, ribeye B (red), the post-synaptic marker, MAGUK (magenta), and the afferent neuronal marker, GFP (green). Scale bar: 5 ?m. M-O: Violin plots comparing the number of pre-synaptic puncta (M), post-synaptic puncta (N) and ribbon synapses (O) in the different groups. Each dot represents the number of puncta per neuromast, with at least two neuromasts inspected per fish, and between 6 and 10 fish inspected. One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett T3 multiple comparisons test. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
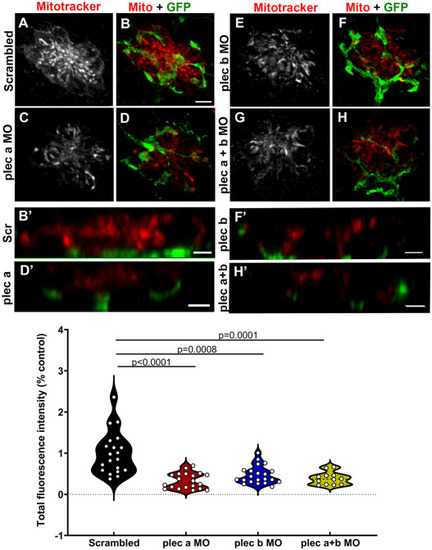
Synaptic mitochondrial activity is reduced in plectin morphants. A-H: 3dpf Tg(NeuroD-GFP) live morphants were incubated with Mitotracker as a proxy for mitochondria activity. A-B: Scrambled animals. C-D: plectin a morphants. E-F: plectin b morphants. G-H: plectin a + b morphants. Mitotracker (red). GFP (green). B?, D?, F? and H?: Z-view high magnification images of the base of the hair cells from the different groups. Scale bar: A-H: 5 ?m. B?, D?, F?, H?: 2 ?m. I: Violin plots comparing the total fluorescence intensity (% from control) of the incorporated Mitotracker in the different groups. Each dot represents the total fluorescence per neuromast, with at least two neuromasts inspected per fish, and between 6 and 10 fish inspected. One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett T3 multiple comparisons test. PHENOTYPE:
|
Reprinted from Hearing Research, 436, Zhang, T., Xu, Z., Zheng, D., Wang, X., He, J., Zhang, L., Zallocchi, M., Novel biallelic variants in the PLEC gene are associated with severe hearing loss, 108831108831, Copyright (2023) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Hear. Res.