- Title
-
Effects of Constitutive and Acute Connexin 36 Deficiency on Brain-Wide Susceptibility to PTZ-Induced Neuronal Hyperactivity
- Authors
- Brunal, A.A., Clark, K.C., Ma, M., Woods, I.G., Pan, Y.A.
- Source
- Full text @ Front. Mol. Neurosci.
|
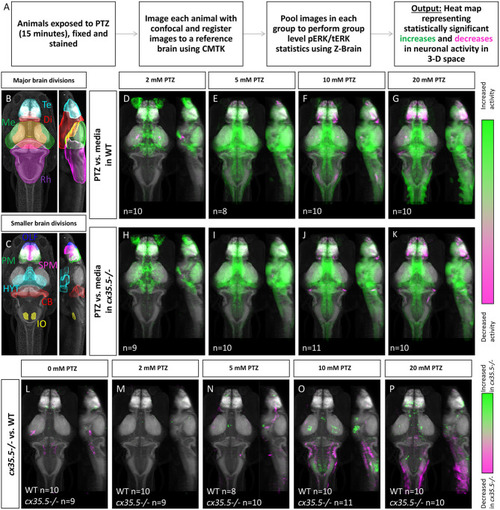
Whole-brain activity map showing significant regional differences in neuronal activity following various PTZ concentration exposure in wild-type and PHENOTYPE:
|
|
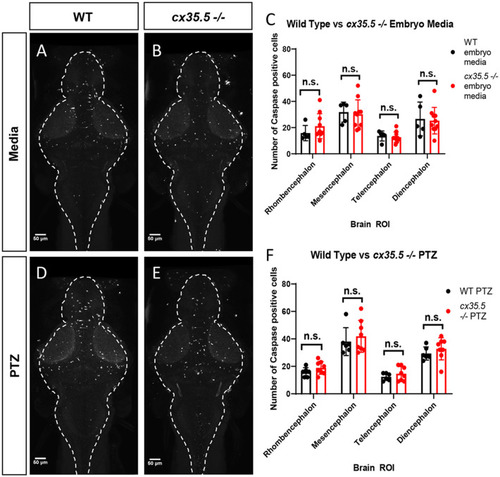
Activated caspase 3 positive cells by major brain division, comparing PHENOTYPE:
|
|
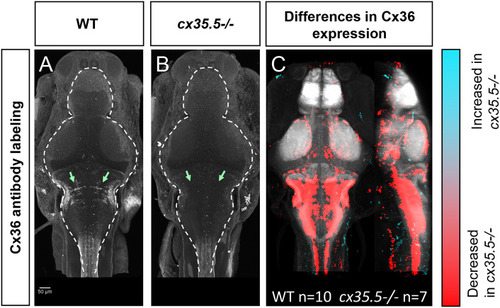
Whole-brain expression map of |
|
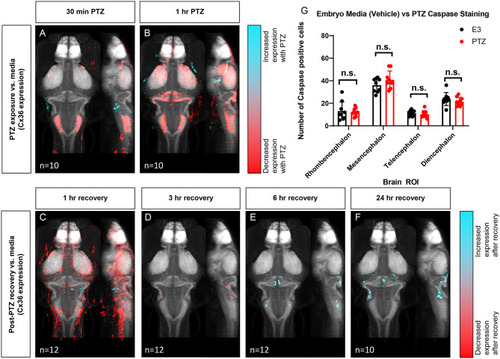
Wild type whole-brain immunostaining Cx36 expression map in E3 vs. PTZ treated zebrafish larvae. Dorsal and lateral view of zebrafish larvae brain. Whole-brain expression of Cx36 using an anti-Cx36 antibody and tERK. Cyan indicates increases in Cx36 labeling in PTZ treated fish, and red indicated decreases in Cx36 labeling in PTZ treated fish. |
|
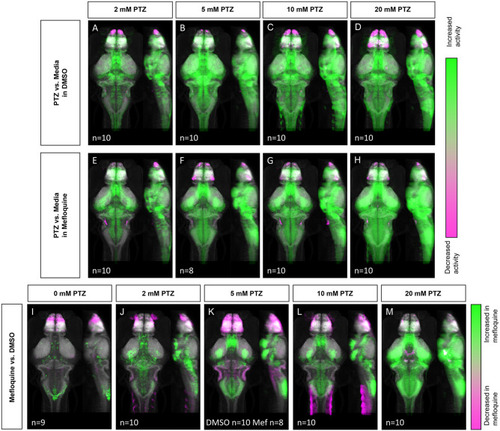
Whole-brain activity map showing significant regional differences following Cx36 blocking drug mefloquine and PTZ exposure in wild-type zebrafish larvae. Dorsal and lateral view of zebrafish larvae brain. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
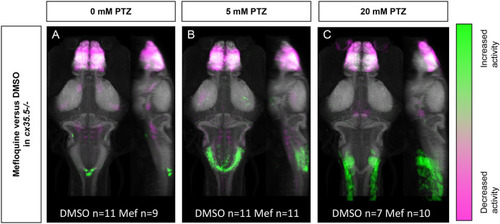
Whole-brain activity of PHENOTYPE:
|