- Title
-
THOC1 deficiency leads to late-onset nonsyndromic hearing loss through p53-mediated hair cell apoptosis
- Authors
- Zhang, L., Gao, Y., Zhang, R., Sun, F., Cheng, C., Qian, F., Duan, X., Wei, G., Sun, C., Pang, X., Chen, P., Chai, R., Yang, T., Wu, H., Liu, D.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS Genet.
|
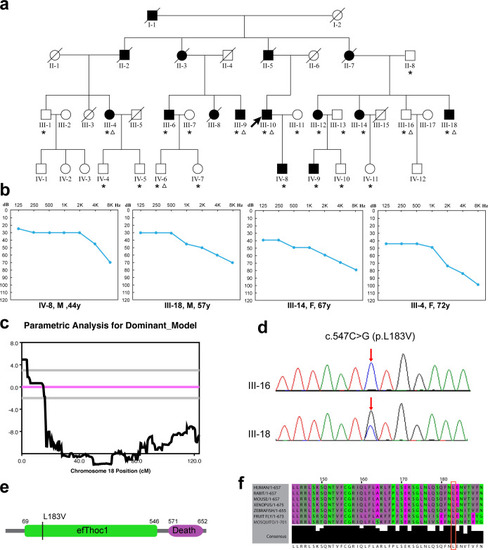
(a) Pedigrees of family SH. The individuals selected for linkage analysis and whole-exome sequencing was marked with asterisks and triangles, respectively. (b) Representative audiograms of family SH. (c) Logarithm of the odds (LOD) scores of genome-wide linkage analysis for chromosome 18. A maximum LOD score of 4.93 was obtained for marker rs928980. (d) Chromatograms of wild type (WT) and mutant (Mut) sequence for c.547C>G (p.L183V). (e) Diagram showing domains of human THOC1 protein and the location of the p.L183V mutation. (f) Multiple sequence alignment of THOC1 showing conservation of the leucine 183 residue. |
|
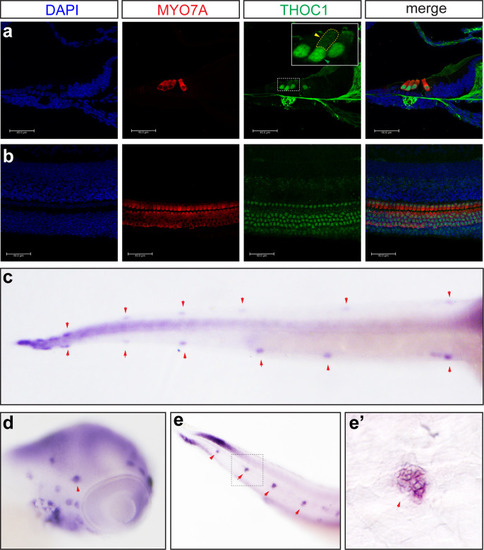
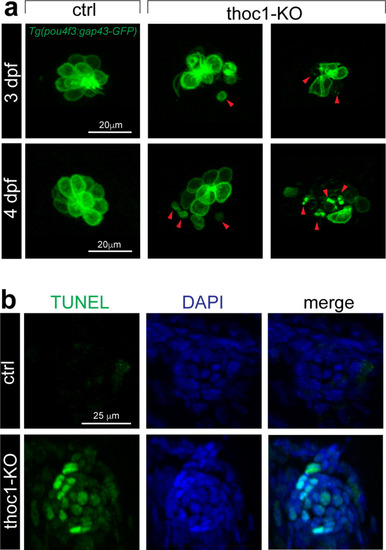
(a, b) Confocal microscopic imaging analysis of THOC1 antibody staining in mouse cochlea hair cells. THOC1 was enriched in outer hair cells (OHC) and inner hair cells (IHC) in the P0 mouse cochlea. Blue: DAPI staining of the cell nuclei. Red: Myosin 7a antibody staining marking hair cells. Green: THOC1 antibody staining. Bars, 40 μm. The region in yellow dash-line rectangle amplified in the white rectangle. Green arrowhead indicates nucleus; yellow arrowhead indicates cytoplasm. (c-e’) whole mount EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
(a) Fluorescence microscopic imaging analysis of PHENOTYPE:
|
|
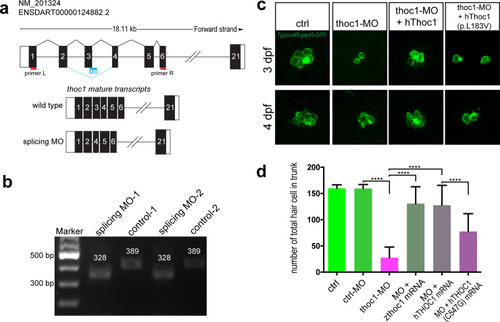
(a) The diagram shows the targeting site of PHENOTYPE:
|
|
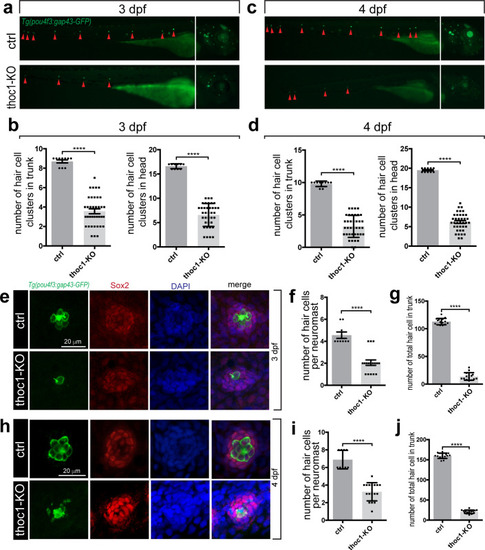
(a) Confocal microscopic imaging analysis of the hair cells in control and PHENOTYPE:
|
|
(a) Clustering analysis indicates the replicates within group have a good repeatability, while the control and mutated group are different. (b) Volcano diagram of different expression genes. Red dots indicate up-regulated genes; blue dots indicate down-regulated genes. Abscissa indicates gene fold change in different samples; ordinate represents statistical significance of gene expression change. (c) KEGG analysis plot of the differential gene, with the vertical axis representing the pathway and the horizontal axis representing the Rich factor. The size of the dot indicates the number of differentially expressed genes in the pathway, and the color of the dot corresponds to a different Qvalue range. (d) Relative mRNA levels of |
|
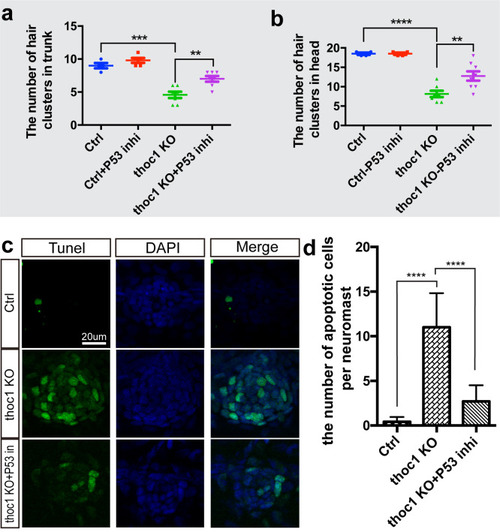
(a, b) Statistical analysis of the hair cell clusters in control (n = 8), ctrl + P53 inhibitor treatment (n = 9), PHENOTYPE:
|

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. PHENOTYPE:
|

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. PHENOTYPE:
|

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. PHENOTYPE:
|