- Title
-
Drainage of inflammatory macromolecules from brain to periphery targets the liver for macrophage infiltration
- Authors
- Yang, L., Jiménez, J.A., Earley, A.M., Hamlin, V., Kwon, V., Dixon, C.T., Shiau, C.E.
- Source
- Full text @ Elife
|
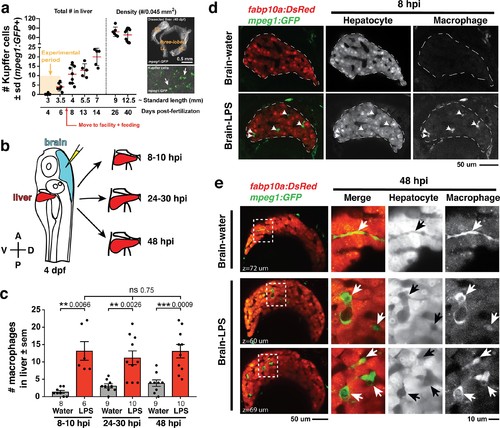
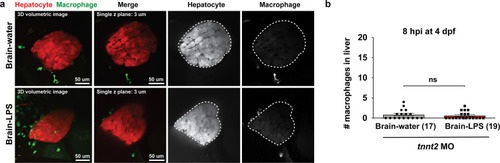
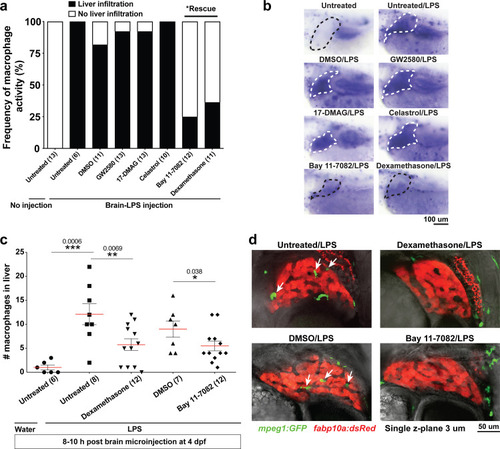
Induction of brain inflammation triggers macrophage infiltration into the liver.(a) Time-course of Kupffer cell development. Total macrophage numbers (mpeg1:GFP+) per liver from 4 to 14 days post-fertilization (dpf) and macrophage density (number per field of view) from dissected livers at juvenile adult stages from 26 to 40 dpf. Standard length corresponding to each stage is shown. Kupffer cells are not present at four dpf at the time of brain microinjection and during most of the experimental period (orange box). Feeding began after six dpf to ensure normal animal development. Fluorescent images on the right show dissected whole liver with the typical three-lobed structure at 40 dpf (top) and high magnification of top dotted box region showing Kupffer cells (bottom). LL, Left lobe; RL, right lobe; VL, ventral lobe. (b) Schematic of brain microinjection at four dpf and analysis of the hepatic response at 8–10 hr post injection (hpi), 24–30 hpi, and 48 hpi. A, anterior; P, posterior; V, ventral; D, dorsal. (c) Quantification of macrophage infiltration in the liver comparing between LPS and control water injections in the brain at four dpf and analyzed at different timepoints. Numbers below bar graphs represent n, number of animals analyzed. (d) At eight hpi, single-plane image from a z-stack shows infiltrated macrophages (GFP+, arrows) nested between hepatocytes (DsRed+) in the liver (dotted region) after brain-LPS injection, but no macrophages observed in control brain-water injection. (e) At 48 hpi, images from two separate z-planes show an abnormally large number of macrophages in the liver that persists after brain-LPS injection (arrows), while few presumably Kupffer cells begin to appear in control brain-water injected animals at this timepoint (arrow). Two-tailed Welch’s t-test was used to determine statistical significance for each pair-wise comparison. One-way ANOVA test for comparing the three LPS injection groups. sem, standard error of means; ns, not significant; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001. |
|
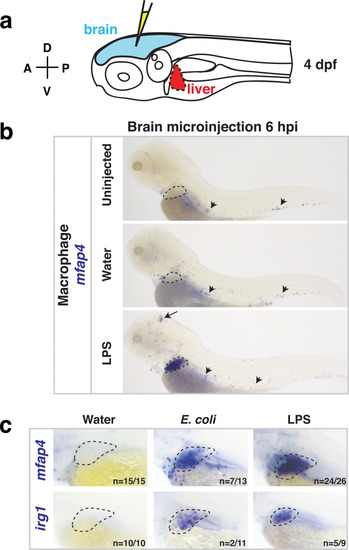
Whole-body analysis using RNA in situ hybridization shows abnormal localization of macrophages in the liver after brain injection of LPS or bacteria.(a) Schematic showing injection of substances (yellow) in the tectum parenchyma (blue) in the four dpf zebrafish larva and subsequent analysis of the periphery that highlights the most prominent change in the liver (red). A, anterior; P, posterior; D, dorsal; V, ventral. (b) In the four dpf zebrafish, macrophages (mfap4+) are normally absent in the liver (dotted region) while sparsely spread throughout the body (arrowheads) as shown in larvae which were uninjected or water vehicle injected in the brain at six hpi. By contrast, after LPS injection in the brain, strong expression of macrophage marker mfap4 is found in the liver (dotted region), while the brain injection site is often also accompanied by a mfap4 expression increase (arrow). (c) Analysis of zebrafish macrophage-specific markers mfap4 and irg1 in the liver (dotted region) after brain injections with water vehicle, E. coli, or LPS. Results indicate that both LPS and E. coli injections induce ectopic localization of macrophages in the liver, which appear to be activated (expressing irg1) at least in a subset, but no macrophages in the liver in control animals. |
|
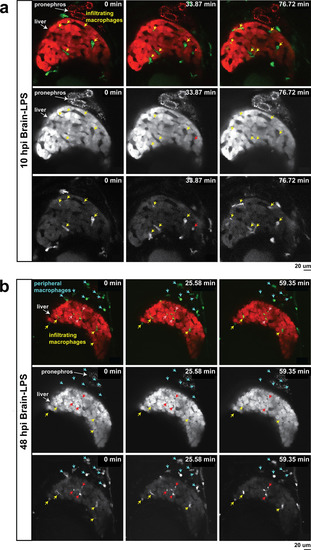
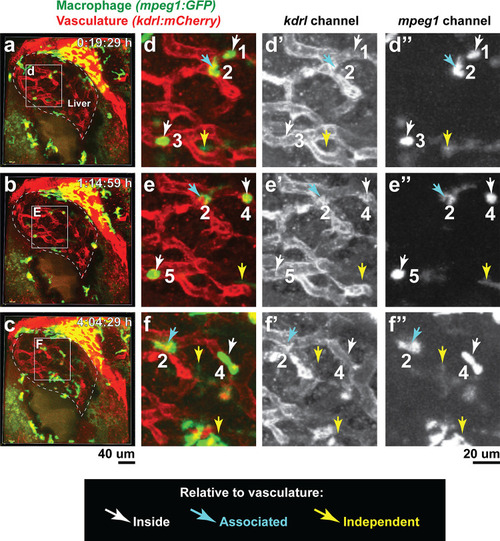
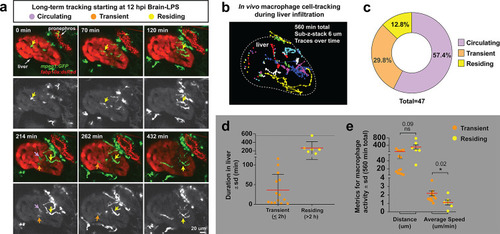
In vivo time-lapse imaging shows dynamic movements and processes of infiltrating macrophages in the liver at short- (10 hpi) and long- (48 hpi) term timepoints after brain-LPS injection.Single slice images from z-stacks taken using a 40x objective correspond to Videos 1 and 2. (a) Representative single-slice images of three timepoints from time-lapse imaging of macrophage infiltration at 10 hr post injection of LPS in the brain. Top, merged channels of mpeg1:GFPlabeling macrophages and fabp10a:DsRed labeling hepatocytes; middle, DsRed channel showing hepatocytes and pronephros; bottom, GFP channel showing macrophages. Pronephros are labeled because the red fluorescent dextran used as a tracer for the brain injection gets into circulation and is filtered by the pronephros. (b) Representative static single-slice images of the whole liver and macrophages at 48 hpi of LPS in the brain. Yellow arrows, infiltrating macrophages; red arrow in a), circulating monocyte/macrophage; red arrow in b), macrophage with elaborate long processes intercalated between hepatocytes. Blue arrows in b), peripheral macrophages not in the liver. |
|
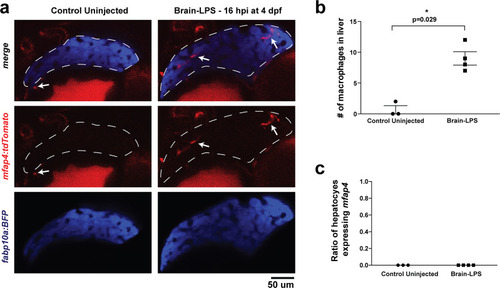
Brain-LPS injection was not found to induce mfap4 expression in the liver.(a) Comparison between control uninjected and brain-LPS injected in double transgenic four dpf larvae was made at 16 hpi. Fluorescent reporters for liver (fabp10a:BFP) and macrophages (mfap4:tdTomato) were used for in vivo imaging to determine whether ectopic induction of mfap4 may occur in hepatocytes due to LPS activation. Representative single 2 µm z-plane images do not show ectopic expression of mfap4 other than in infiltrating macrophages in the liver (which are stereotypically located near or within liver sinusoids or gaps between hepatocytes) after LPS injection. Coinciding with a lack of macrophage infiltration in the control animals, no mfap4 expression was observed in the liver (demarcated by dotted line). (b) Scatter plot shows analysis of macrophage infiltration in the liver using the double transgenic larvae. Brain-LPS injection causes infiltration of mfap4:tdTomato expressing macrophages but not in the control uninjected animals. (c) Quantification of liver cells expressing mfap4 shows none did. Individual slices through entire z-stack of whole liver were assessed for co-expression of hepatocyte reporter with the mfap4 reporter. In all plots, each symbol represents an independent larva analyzed. Two-tailed student’s t-test was used to determine statistical significance. |
|
Double transgenic zebrafish expressing the macrophage |
|
( |
|
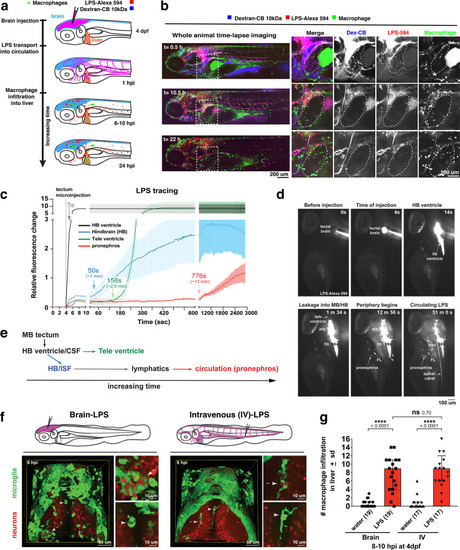
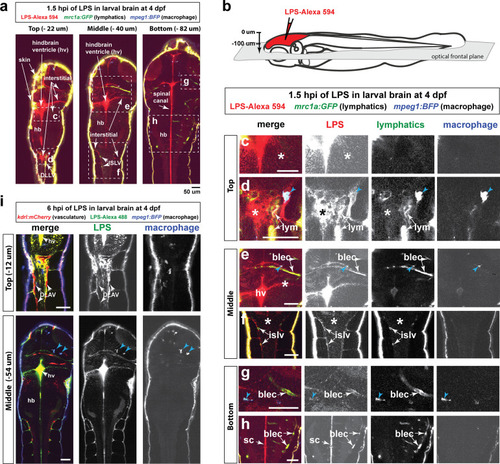
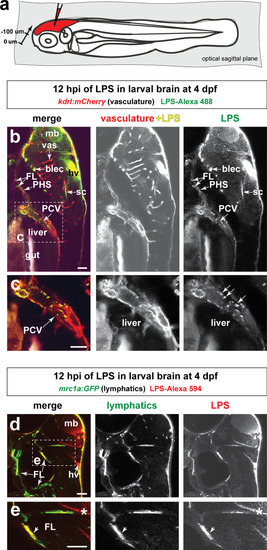
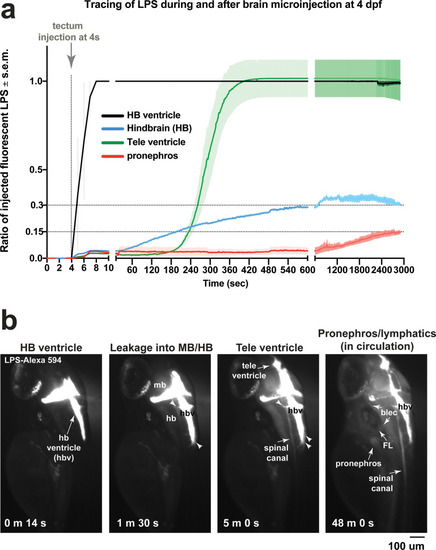
Brain-LPS microinjection leads to drainage of LPS molecules into circulation, and causes a hepatic response similar to intravenous LPS injection.(a) Schematic showing time-course of LPS and macrophage distribution. Fluorescently Alexa 594 tagged LPS shown in red, co-tracer dextran-cascade blue shown in blue, and detection of both is shown in magenta. (b) Left, representative 3D images from three timepoints of a 24-hour time-lapse imaging of a large frame stitched from four z-stack tiles (corresponding to Video 5). Right, high magnification of the 3D images in dotted box region on the left panel showing liver (dotted region) and surrounding area. Merged overlays and individual channels showing Dex-CB (blue), LPS-594 (red), and macrophages (mpeg1:GFP+). (c) Live recording of the brain microinjection at four dpf using Alexa 594 or Alexa 488 conjugated LPS was conducted to trace the distribution of LPS in real time at 1 frame per second using an automated acquisition software on a Leica M165 FC stereomicroscope with a high speed and high sensitivity deep-cooled sCMOS camera (DFC9000 GT). Kinetic time plot of relative fluorescence change ± sem of fluorescently tagged LPS starting before the injection at 0 seconds; data from three independent injected animals were used to generate plot. Time of injection was at the 4 seconds timepoint. Arrows indicate the timepoint at which initial LPS signals were detected in the corresponding anatomical location. In some injected animals, LPS also flowed anteriorly from the midbrain ventricle into the telencephalon ventricle starting at about 2.5 minutes after injection (see Figure 2—figure supplement 3). (d) Still images representing key events of the dispersion of LPS starting from before to nearly 1 hour after the brain microinjection corresponding to Video 7. hb, hindbrain; tele, telencephalon; hbv, hindbrain ventricle; mb, midbrain; FL, facial lymphatics; blec, brain lymphatic endothelial cells; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; ISF, interstitial fluid. (e) Schematic showing the major route through which LPS were transferred from the site of brain microinjection to peripheral circulation. (f) Top, illustration of brain and intravenous LPS injections. Bottom, 3D tectum brain volume from confocal live imaging at four dpf at 6 hours after brain or intravenous LPS injection using a 40x objective. Microglia (mpeg1:GFP+) and surrounding neurons (nbt:DsRed+) shown. Small panels show high magnification of microglia (arrows) and neurons corresponding to arrows in the large 3D brain volume image on the left. LPS injection in the brain led to a striking morphological activation of rounded and clustering microglia (arrows), but not by intravenous injection of LPS at 6 hpi. Superficial planes of the head are eliminated to allow visualization of the internal microglia, because the cranial skin surface is highly auto-fluorescent in the GFP channel. (g) Quantification of macrophage infiltration at 8-10 hpi in the four dpf zebrafish larvae. Two-tailed Welch’s t-test was used to determine statistical significance. sd, standard deviation; ns, not significant; ****, p<0.0001; LPS-594, LPS-Alexa 594; Dex-CB, cascade blue conjugated dextran, sem, standard error of means. Numbers in parenthesis represent n, number of animals analyzed. |
|
Wild-type double transgenic zebrafish at four dpf were microinjected with fluorescently tagged LPS in the tectal brain. To localize the LPS relative to the lymphatic and vasculature structures, two transgenes were used: |
|
( |
|
( |
|
( |
|
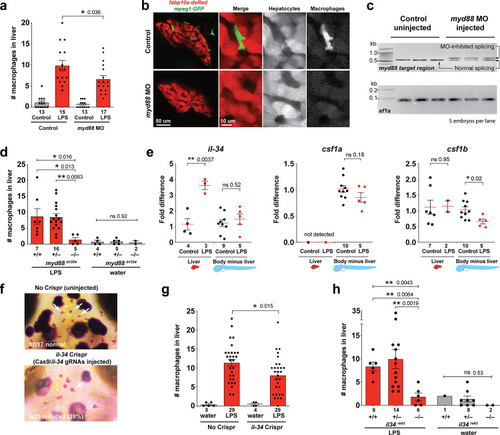
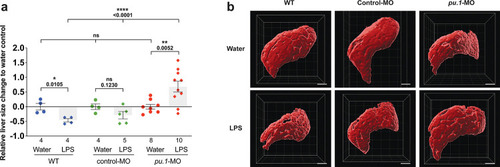
Infiltration of liver by macrophages triggered by brain-LPS injection is dependent on adaptor protein myd88 and cytokine il-34.(a) Quantification of macrophage infiltration 6 hr after brain-LPS injection or control treatment (brain-water injection and no injection combined) in myd88-deficient morpholino-injected animals compared with control wild-type siblings at four dpf. (b) Left column, representative single plane of whole liver (DsRed+) showing macrophage infiltration (GFP+) in the control animal but not in the myd88 morpholino-injected animals. Second to fourth columns, high magnification of the merged overlay and single channels showing a single macrophage (GFP+) stationed between hepatocytes (DsRed+) in control but not in myd88 morpholino-injected animals. (c) RT-PCR analysis showing efficacy of myd88 morpholino in blocking normal myd88splicing at three dpf. Elongation factor one alpha (ef1a) PCR used as a sample quality control. (d) Complementary experiments using myd88 mutants derived from a heterozygous incross show either few or no macrophages in the liver after brain-LPS injection at 16–24 hpi similar to baseline brain-water injected animals, demonstrating a much stronger effect in reversing macrophage infiltration than the partial myd88 knockdown by morpholinos. (e) qPCR analysis of il-34, csf1a, and csf1b expression in liver only and body-minus-liver tissues comparing brain-LPS injected animals with the control group (brain-water injected and uninjected animals combined) at 6 hpi in four dpf zebrafish. (f) Representative images of control (top) and il-34 F0 Crispr-injected (bottom). Microglia reduction observed in transient il-34 F0 Crispr-injected animals shown by neutral red staining (microglia, white arrows), phenocopying previously described stable il-34 mutants (Kuil et al., 2019). (g) Quantification of macrophage infiltration indicates a significant reduction at 8–10 hpi in four dpf transient il-34 deficient F0 Crispr-injected animals. (h) Stable il34 mutants derived from a heterozygous incross show either few or no macrophages in the liver after brain-LPS injection at 16–24 hpi similar to baseline brain-water injected animals, showing a much stronger effect in eliminating macrophage infiltration than in the partial gene knockout in transient il-34 F0 Crispr-injected animals. Statistical significance was determined by a two-tailed t-test coupled with a F-test validating equal variances for two-way comparisons, and Kruskal-Wallis multiple comparisons test for three-way comparisons in d and h (shown by the top bar) followed by corrected two-way tests if the multiple comparisons test was significant. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ns, not significant; data points in scatter plots represent n, independent biological samples or animals. Numbers below bar graphs represent n. |
|
( |
|
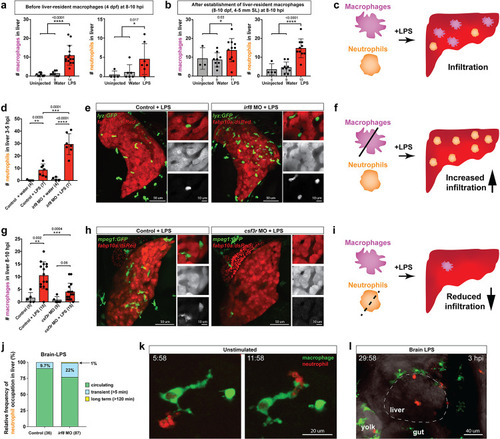
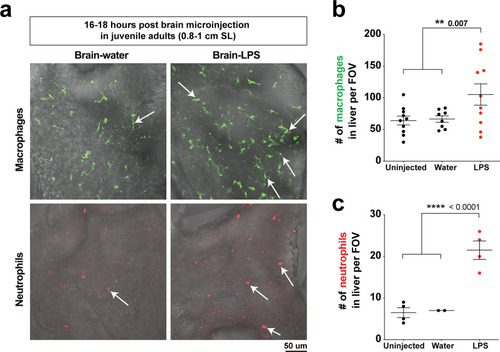
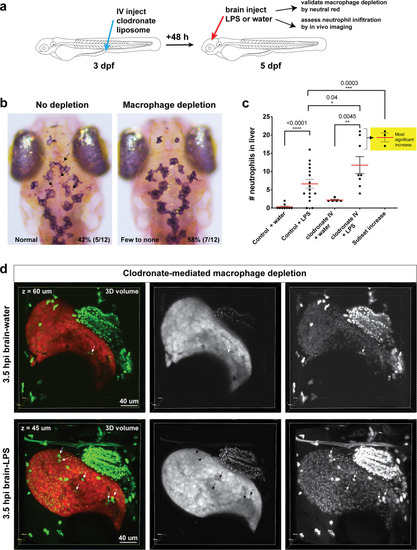
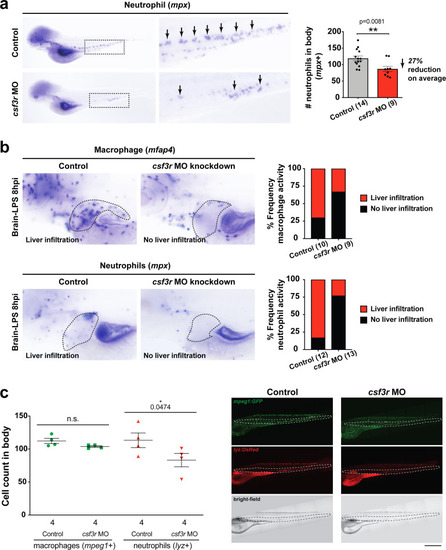
Neutrophils and macrophages coordinate to infiltrate the liver during a systemic inflammatory response.(a–b) Total count of macrophages or neutrophils in liver in control (uninjected and brain-water injected) or brain-LPS challenged animals before and after development of liver-resident macrophages (Kupffer cells) at four dpf and 8–10 dpf, respectively. (c) Diagram showing typical immune infiltration after LPS addition in wild-type animals. (d-e) Effects of macrophage ablation by irf8 knockdown on neutrophil numbers in the liver 3.5–5 hr after brain-LPS injection at four dpf. (d) Quantification of neutrophil numbers. (e) Confocal 3D volume imaging of the whole liver with high magnification of a small region shown on the right that is showing a single z-plane image: top, merged channels; middle, hepatocytes (DsRed+); and bottom, neutrophils (GFP+). (f) Diagram summarizing the effect of macrophage ablation on causing an increase in neutrophil infiltration after LPS injection. (g–h) Depletion of neutrophils using the csf3r morpholino reduced macrophage infiltration compared with control LPS injections 8–10 hpi at four dpf. (g) Quantification of macrophage numbers. Significantly fewer macrophages were observed in the liver after neutrophil ablation in brain-LPS injected animals. (h) Same format of images as in e. (i) Diagram summarizing the effect of neutrophil reduction. (j) Comparison of relative frequency of each type of neutrophil occupation in the liver with normal (Control) or depleted (irf8 MO-injected) levels of macrophages after brain-LPS injection, as determined by in vivo time-lapse imaging. (k) Representative 3D images of normal macrophage and neutrophil interactions around the liver at four dpf (corresponding to Video 9). (l) 3D image of macrophage and neutrophil interactions after brain-LPS injection at three hpi in the four dpf larvae showing entry of neutrophils into liver prior to macrophages (corresponding to Video 8). Statistical significance was determined by a two-tailed t-test and with Welch’s correction for unequal variances as determined by a F-test. MO, morpholino. Each data point in scatter plots represents an independent animal; n, number of animals analyzed is shown below each bar graph. Transgenes used: mpeg1:GFP for macrophages, lyz:GFP for neutrophils, and fabp10a:DsRed for hepatocytes. |
|
( |
|
( |
|
( |
|
( |