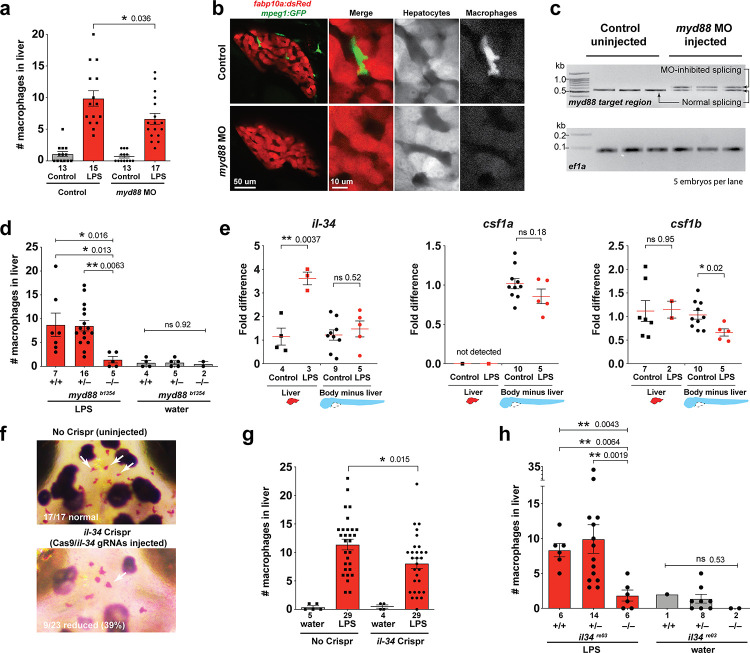
Figure 3
Infiltration of liver by macrophages triggered by brain-LPS injection is dependent on adaptor protein myd88 and cytokine il-34.
(a) Quantification of macrophage infiltration 6 hr after brain-LPS injection or control treatment (brain-water injection and no injection combined) in myd88-deficient morpholino-injected animals compared with control wild-type siblings at four dpf. (b) Left column, representative single plane of whole liver (DsRed+) showing macrophage infiltration (GFP+) in the control animal but not in the myd88 morpholino-injected animals. Second to fourth columns, high magnification of the merged overlay and single channels showing a single macrophage (GFP+) stationed between hepatocytes (DsRed+) in control but not in myd88 morpholino-injected animals. (c) RT-PCR analysis showing efficacy of myd88 morpholino in blocking normal myd88splicing at three dpf. Elongation factor one alpha (ef1a) PCR used as a sample quality control. (d) Complementary experiments using myd88 mutants derived from a heterozygous incross show either few or no macrophages in the liver after brain-LPS injection at 16–24 hpi similar to baseline brain-water injected animals, demonstrating a much stronger effect in reversing macrophage infiltration than the partial myd88 knockdown by morpholinos. (e) qPCR analysis of il-34, csf1a, and csf1b expression in liver only and body-minus-liver tissues comparing brain-LPS injected animals with the control group (brain-water injected and uninjected animals combined) at 6 hpi in four dpf zebrafish. (f) Representative images of control (top) and il-34 F0 Crispr-injected (bottom). Microglia reduction observed in transient il-34 F0 Crispr-injected animals shown by neutral red staining (microglia, white arrows), phenocopying previously described stable il-34 mutants (Kuil et al., 2019). (g) Quantification of macrophage infiltration indicates a significant reduction at 8–10 hpi in four dpf transient il-34 deficient F0 Crispr-injected animals. (h) Stable il34 mutants derived from a heterozygous incross show either few or no macrophages in the liver after brain-LPS injection at 16–24 hpi similar to baseline brain-water injected animals, showing a much stronger effect in eliminating macrophage infiltration than in the partial gene knockout in transient il-34 F0 Crispr-injected animals. Statistical significance was determined by a two-tailed t-test coupled with a F-test validating equal variances for two-way comparisons, and Kruskal-Wallis multiple comparisons test for three-way comparisons in d and h (shown by the top bar) followed by corrected two-way tests if the multiple comparisons test was significant. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ns, not significant; data points in scatter plots represent n, independent biological samples or animals. Numbers below bar graphs represent n.