- Title
-
Hyaluronic acid synthesis is required for zebrafish tail fin regeneration
- Authors
- Ouyang, X., Panetta, N.J., Talbott, M.D., Payumo, A.Y., Halluin, C., Longaker, M.T., Chen, J.K.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
Zebrafish hyaluronan synthases are differentially expressed during larval and adult tail regeneration. Expression patterns of has1, has2, and has3 in regenerating larval (A-C; 1 dpa) adult (D-E; 2 dpa) tails, as determined by whole-mount in situ hybridization. (A?-C?) Equivalently stained uncut controls. At least 30 larvae or 10 adult zebrafish were analyzed for each experimental condition, and phenotypic descriptions were based on a penetrance of > 80%. Scale bars: A-C and A?-C?, 100 ?m; D-E: 300 ?m. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Zebrafish hyaluronidases are differentially expressed during larval and adult tail regeneration. Expression patterns of hyal2, hyal3, hyal4, and hyal6 in regenerating larvae (A-D; 1 dpa) and adult (A?-D?; 2 dpa) tails. At least 30 larvae or 10 adult zebrafish were analyzed for each experimental condition, and phenotypic descriptions were based on a penetrance of > 80%. Scale bars: A-D, 100 ?m; A?-D?: 300 ?m. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Dynamics of has3 expression during larval tail regeneration. (A-F) Expression patterns of has3 at different time points after caudal fin amputation at 2 dpf. Arrows mark the initial appearance of has3 transcripts at 6 hpa, localized to dorsal and ventral sides regions of the regenerative bud. (A?-F?) Equivalently stained uncut controls at the same time points. At least 30 larvae were analyzed for each experimental condition, and phenotypic descriptions were based on a penetrance of > 80%. Scale bar: 100 ?m. |
|
4-MU inhibits larval tail regeneration. (A) Representative micrographs of larval tails that were amputated at 2 dpf and then treated 0.5% DMSO or 150 ?M 4-MU for 3 days. Dotted lines indicate the amputation plane, and micrographs of uncut larval tails subjected to the same inhibitor regimen are shown for comparison. Scale bar: 100 ?m. (B-C) Time-course analysis of 4-MU action on larval tail regeneration. Caudal fin sizes at 5 dpf (3 dpa) after the indicated amputation and 4-MU treatment regimens. Data are the average caudal fin areas of 15 larvae ± s.e.m., normalized to the average fin size of uncut larvae treated with 0.5% DMSO. ***, P < 0.001. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
4-MU inhibits adult tail regeneration. Representative micrographs of adult tail fins that were amputated and then treated with 0.5% DMSO or 150 ?M 4-MU for 7 days. White dotted lines indicate the amputation site. 10 adult zebrafish were analyzed for each experimental condition, and phenotypic descriptions were based on a penetrance of > 80%. Scale bar: 1 mm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
4-MU inhibits regenerative cell proliferation. (A) Mitotic cells in the larval tail after the indicated amputation and 4-MU treatment regimens, as visualized with anti-pH3 immunostaining at 2 dpa (4 dpf). R1 and R2 demarcate distinct regions within the larval tail, with R1 corresponding to a highly proliferative 100-?m-wide zone associated with tail regeneration. (B) Quantification of pH3-positive cells in the R1 and R2 regions under the indicated treatment conditions. Data are the average number of pH3-positive cells in 30 larval tails ± s.e.m. **, P < 0.01. |
|
GSK3 inhibition rescues 4-MU-induced larval tail regeneration and cell proliferation defects. (A) Representative micrographs of larval tails that were amputated at 2 dpf and treated with 0.5% DMSO, 100 nM BIO, 150 ?M 4-MU, or 150 ?M 4-MU with 100 nM BIO for the next 24 hours. Caudal fins of 5-dpf (3-dpa) larvae are shown. Scale bar: 100 ?m. (B) Caudal fin sizes at 5 dpf (3 dpa) for the indicated amputation and inhibitor treatment regimens (compound administration from 2 to 3 dpf). Data are the average caudal fin areas of 15 larvae ± s.e.m., normalized to the average fin size of uncut larvae treated with 0.5% DMSO. (C) Cell proliferation within the 4-dpf caudal fin in response to the indicated amputation and inhibitor treatment regimens. Data are the average number of pH3-positive cells in 30 larval tails ± s.e.m. (R1 + R2 regions; see Fig 9). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. |
|
4-MU and GSK3 inhibition differentially control the expression of wound epithelium and blastema markers in larval tails. Effects of 0.5% DMSO, 100 nM BIO, 150 ?M 4-MU, or 150 ?M 4-MU with 100 nM BIO on junba (A), dlx5a (B), aldh1a2 (C), and junbb (D) expression in 1-dpa (3-dpf) larval tails. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
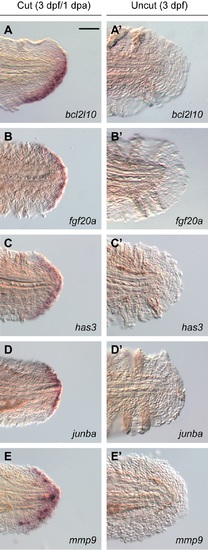
Genes expressed in distal cells during larval tail regeneration. (A-E) Expression patterns of selected genes transcribed in the regenerative bud at 1 dpa (3 dpf), as determined by whole-mount in situ hybridization. (A?-E?) Equivalently stained uncut controls. At least 30 larvae were analyzed for each experimental condition, and phenotypic descriptions were based on a penetrance of > 80%. Scale bar: 100 ?m. |
|
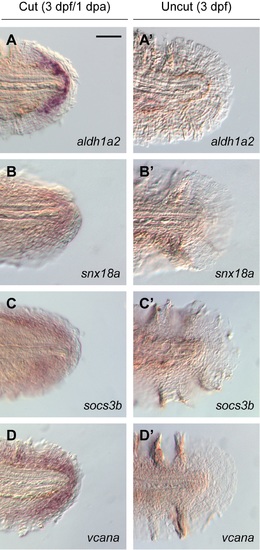
Genes expressed in blastema-like cells during larval tail regeneration. (A-D) Expression patterns of selected genes transcribed in the regenerative bud at 1 dpa (3 dpf), as determined by whole-mount in situ hybridization. (A?-D?) Equivalently stained uncut controls. At least 30 larvae were analyzed for each experimental condition, and phenotypic descriptions were based on a penetrance of > 80%. Scale bar: 100 ?m. |
|
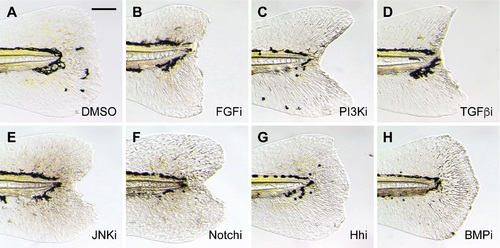
Inhibition of larval tail regeneration by pathway-specific antagonists. Representative micrographs of larval tails that were amputated at 2 dpf and then treated with the following signaling pathway inhibitors for 3 days: (A) 0.5% DMSO; (B) 75 ?M PD173074 (FGF); (C) 10 ?M LY294002 (PI3K); (D) 50 ?M SB431542 (TGFß); (E) 5 ?M SP600125 (JNK); (F) 50 ?M DAPT (Notch); (G) 100 ?M cyclopamine (Hh); or (H) 50 ?M dorsomorphin (BMP). At least 30 larvae were analyzed for each experimental condition, and phenotypic descriptions were based on a penetrance of > 80%. Scale bar: 100 ?m. |
|
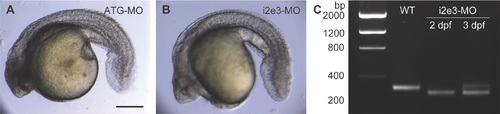
Developmental defects in has3 morphants. Representative micrographs of 28-hpf embryos injected with morpholino oligonucleotides targeting either the has3 translational start site (A; ATG-MO, 10 ng/embryo) or the has3 intron 2-exon 3 splice junction (B; i2e3-MO, 16 ng/embryo). Scale bar: 200 ?m. (C) Confirmation of has3 i2e3-MO-dependent target mRNA missplicing by RT-PCR. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
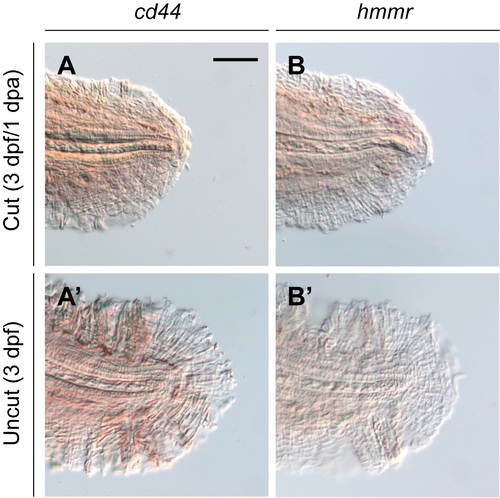
Zebrafish cd44 and hmmr are not visible upregulated during larval tail regeneration. Whole-mount in situ hybridization of 1-dpa (3-dpf) larval tails with riboprobes for cd44 (A) or hmmr (B) at 1 dpa. (A? and B?) Equivalently stained uncut controls. At least 30 larvae were analyzed for each experimental condition, and phenotypic descriptions were based on a penetrance of > 80%. Scale bar: 100 ?m. |
|
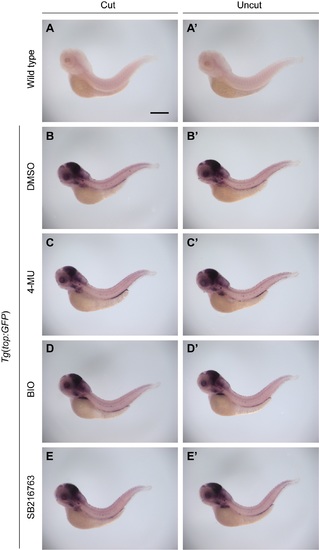
Wnt pathway activity is not upregulated during larval tail regeneration or modulated by 4-MU or GSK3 inhibitors. Whole-mount analysis of GFP expression in both wild type (A-A?) and Tg(top:GFP) embryos (B-E and B?-E?) at 1 dpa (3 dpf), following treatments with DMSO, 150 ?M 4-MU, 100 nM BIO, or 50 ?M SB216763 from 2 to 3 dpf. The Tg(top:GFP) embryos express a destabilized form of GFP under control of a minimal cFos promoter with four TCF/LEF binding sites, providing a dynamic readout of Wnt pathway state. At least 30 larvae were analyzed for each experimental condition, and phenotypic descriptions were based on a penetrance of > 80%. Scale bar: 300 ?M. |
|
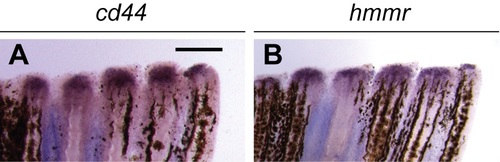
Hyaluronic acid receptors are expressed during adult zebrafish tail regeneration. Expression patterns of cd44 (A) and hmmr (B) in adult tails at 2 dpa. 10 adult zebrafish were analyzed for each experimental condition, and phenotypic descriptions were based on a penetrance of > 80%. Scale bar: 300 ?m. |
|
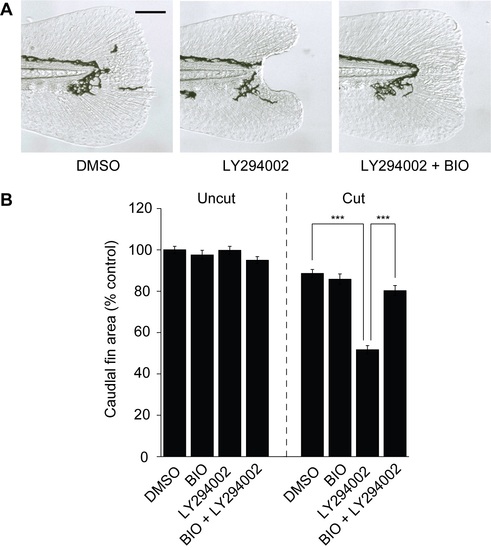
GSK3 inhibition rescues LY294002-induced tail regeneration defects. (A) Representative micrographs of 5-dpf larval tails that were amputated at 2 dpf and treated with 0.5% DMSO, 10 ?M LY294002, or 10 ?M LY294002 + 100 nM BIO for the next 24 hours. Scale bar: 100 ?m. (B) Caudal fin sizes at 5 dpf (3 dpa) for the indicated amputation and inhibitor treatment regimens (compound administration from 2 to 3 dpf). Data are the average caudal fin areas of 15 larvae ± s.e.m., normalized to the average fin size of uncut larvae treated with 0.5% DMSO. ***, P < 0.001. |