- Title
-
Direct regulation of p53 by miR-142a-3p mediates the survival of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells in zebrafish
- Authors
- Lu, X., Wei, Y., Liu, F.
- Source
- Full text @ Cell Discov
|
Generation of miR-142a mutants by TALENs. (a) Schematic diagram showed the TALEN target sites at the miR-142a locus. (b and c) Indel mutations induced by TALENs showed a 13-base-pair deletion in the miR-142a locus. Green arrow shows the initiation of the mutation. (d) Predicted RNA secondary structure of wild-type and mutated pri-miR-142a by TALENs using the RNA Structure Software (version 4.6, Rochester, NY, USA). (e) Expression of miR-142a-3p was absent in 142T?/? embryos at 4?days post-fertilization (dpf) by WISH. Red dashed circles mark the expression of miR-142a-3p in the thymus and red arrowheads mark the expression of miR-142a-3p in the CHT. (f) qPCR demonstrated that the expression of miR-142a-3p and miR-142a-5p was nearly undetectable in 142T?/? embryos at 4?dpf. The expression of miR-142a-3p and miR-142a-5p was normalized to U6 (meanąs.d., n=3, **P<0.01). |
|
MiR-142a-3p is essential for HSPC emergence. (a) 142T?/? embryos showed decreased expression of HSPC marker runx1 at 26 and 36?hpf by WISH. (b) 142T?/? embryos displayed decreased expression of HSC marker runx1 at 26 and 36?hpf using qPCR. The expression of runx1 was normalized to ?-actin (meanąs.d., n=3, **P<0.05). (c) Runx1 was decreased in 142T?/? embryos at 26 and 36?hpf by western blot analysis (left panel) and the quantification (right panel). The protein level of Runx1 was normalized to ?-Actin. (d) The number of EGFP-labeled HSPCs (red arrowheads) in Tg (cmyb:EGFP) embryos was decreased in the AGM region in 142T?/? embryos at 36?hpf (meanąs.d., n=5, *P<0.05). White arrowheads indicate cmyb-positive cells in the pronephric duct. cmyb-labeled pronephric duct was counted as an internal control. (e) 142T?/? embryos displayed reduction of HSPC marker cmyb from 2 to 3.5?dpf by WISH. (f) Differentiated hematopoietic lineages were decreased in 142T?/? embryos including erythrocytes (gata1), neutrophils (lyz) and lymphocytes (ikaros and rag1) at 4?dpf by WISH. Red arrowheads mark hematopoietic cells in the caudal hematopoietic tissue (CHT), whereas red circles denote the thymus. (g) Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining of the kidney showed that decrease in cell population and the volume of the head kidney greatly in 142?/? adult fish of 12 weeks. |
|
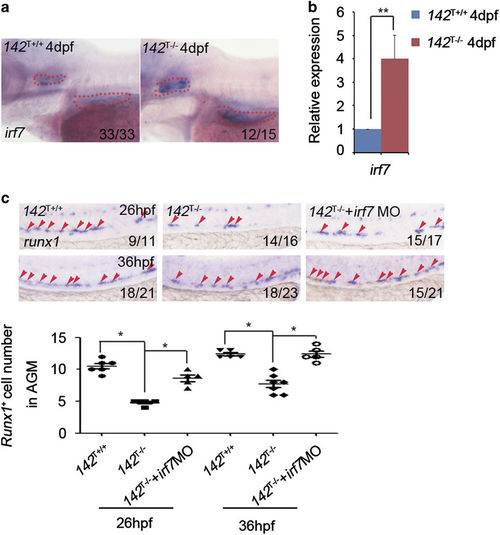
Increased expression of irf7 in 142T?/? embryos and rescue of HSPC defects by irf7 knockdown. (a and b) 142T?/? embryos showed increased expression of irf7 at 4?dpf using WISH and qPCR (meanąs.d., n=3, *P<0.01). (c) Irf7 MO-injected 142T ?/? embryos showed the restoration of runx1 expression at 26 and 36?hpf using WISH. The quantification of runx1-positive cells in the AGM was shown in the lower panel (meanąs.d., n=5, *P<0.05). |
|
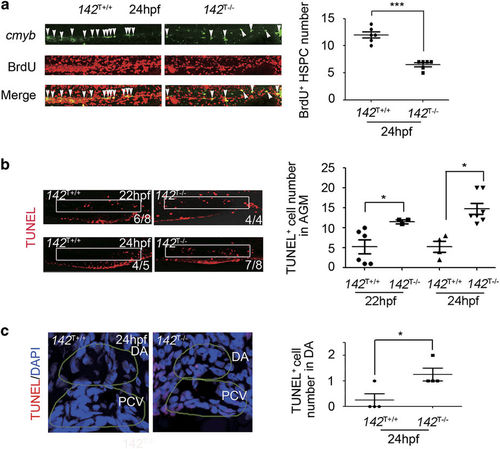
142T?/? embryos display decreased proliferation and increased apoptosis of HSPCs. (a) Percentage of the proliferative HSPCs labeled by BrdU (marked by white arrow heads) in the AGM of 142T?/? embryos and wild-type siblings 24?hpf (meanąs.d., n=6, *P<0.001). (b) TUNEL assay showed more apoptotic cells (white box) in the AGM of 142T?/? embryos at 22 and 24?hpf. The number of TUNEL-positive cells in the AGM region was quantified (meanąs.d., n=3, *P<0.05). (c) Transverse section showed increased apoptotic HSPCs in the AGM region of 142T?/? embryos. Yellow dashed circles denote the dorsal aorta and cardinal vein. TUNEL-positive cells were counted in the dorsal aortal region (meanąs.d., n=4, *P<0.05). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
142T?/? embryos display ectopic expression of p53. (a) The expression of p53 and p21 was increased in 142T?/? embryos at 26 and 36?hpf using qPCR (meanąs.d., n=3, *P<0.05, **P<0.01). (b) P53 was increased in the dorsal aorta region in 142T?/? embryos at 24 and 26?hpf by WISH. (c) The expression of p53 was increased in cmyb-positive cells in the trunk of 142T?/? embryos at 36hpf. |
|
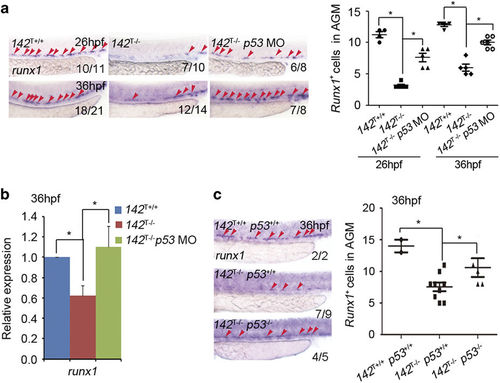
P53 mediates the decrease of HSPCs in miR-142a-3p mutants. (a) P53 MO-injected 142T?/? embryos showed the restoration of runx1 expression at 26 and 36?hpf by WISH (left panel). The quantification of runx1-positive cells in the AGM was shown in the right panel (meanąs.d., n=3, *P<0.05). (b) qPCR showed that compared with 142T?/? at 36?hpf, the decrease in runx1 expression was rescued in 142T ?/? embryos injected with p53 MO (meanąs.d., n=3, *P<0.05). (c) WISH showed the expression of runx1 in 142T+/+ p53+/+, 142T?/? p53+/+ and 142T?/? p53?/? embryos at 36?hpf. There was a rescue effect on the decreased runx1 expression in 142T ?/? p53?/? double mutants. The quantification of runx1-positive cells in the AGM was shown in the right panel (meanąs.d., n=60, *P<0.05). |
|
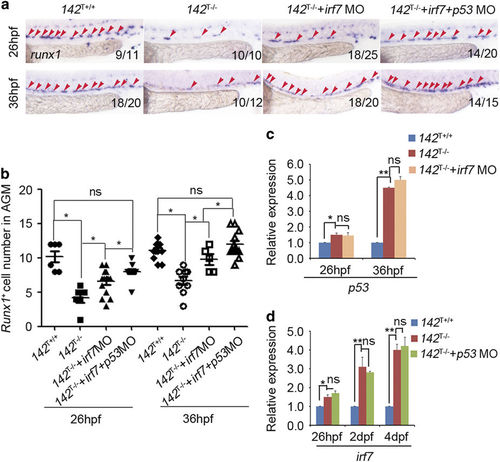
Combined knockdown of irf7 and p53 restores decreased HSPCs in 142T ?/? embryos. (a and b) Injection of irf7 MO with p53 MO rescued the decreased expression of HSPCs marker runx1, and the extent of the restoration was greater than the single injection of irf7 MO at 26 and 36?hpf (meanąs.d., n=5, *P<0.05). (c) The increased expression of p53 was not affected in 142T?/? embryos injected with irf7 MO at 26 and 36?hpf by qPCR (each sample was composed at least 40 embryos, meanąs.d., n=3, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ns stands for no significance). (d) The increased expression of irf7 was not affected in 142T?/? embryos injected with p53 MO at 26?hpf, 2 and 4?dpf by qPCR (meanąs.d., n=3, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ns stands for no significance). |
|
Generation of miR-142a knock out zebrafish using CRISPR/Cas9. (a) Schematic diagram showing the CRISPR/Cas9 target sites 1 and 2 in the miR-142a gene. (b) Genotyping showed different lengths of PCR products from 142C+/+ and 142C-/- generated by CRISPR Cas9. (c) A 986 base-pair deletion caused by CRISPR/Cas9 in the miR-142a locus showed failure to form mature miR-142a-5p and miR-142a-3p. (d) Predicted RNA secondary structure of wide type and mutated pri-miR-142a by CRISPR/Cas9. (e) MiR-142a-3p was absent in 142C-/- embryos at 4 dpf by WISH. Red dashed circles mark the expression of miR-142a-3p in the thymus and red arrows mark the expression of miR-142a-3p in the CHT. |
|
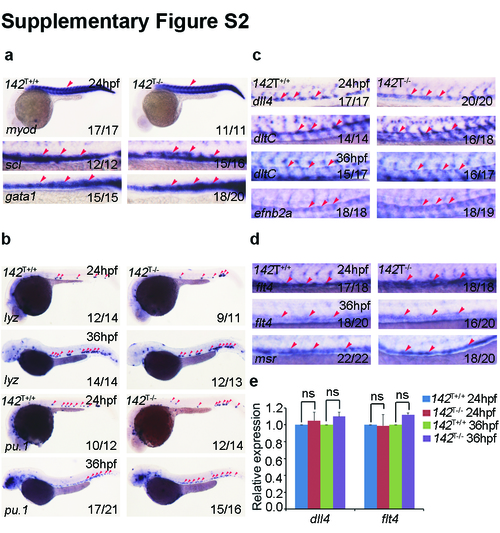
Normal primitive hematopoiesis and vascular development in miR-142a knock out mutants. (a) 142T-/- embryos displayed normal expression of primitive hematopoiesis marker scl and erythrocyte marker gata1 by WISH at 24 hpf. Somitic marker myod served as control. (b) 142T-/- embryos showed normal expression of primitive myeloid marker lyz and pu.1 by WISH at 24 and 36 hpf respectively. (c) Arterial marker dll4 dltC and efnb2a were unaffected in 142T-/- embryos by WISH at 24 and 36 hpf respectively. (d) Venous marker flt4 and msr were unaffected in 142T-/- embryos by WISH at 24 and 36 hpf respectively. (e) 142T-/- embryos showed normal expression of dll4 and flt4 at 24 and 36 hpf by qPCR (meanąSD, n=3, ns stands for no significance). |
|
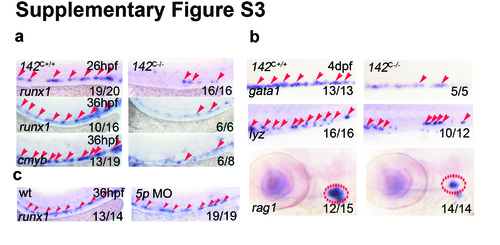
Defect of HSPC emergence is specifically caused by miR-142a-3p but not miR-142a-5p. (a) 142C-/- embryos showed decreased expression of HSPC marker runx1 at 26 and 36 hpf and cmyb at 36 hpf by WISH. (b) HSPC differentiated lineages showed reduction in 142C-/- embryos including erythrocytes (gata1), neutrophils (lyz) and lymphocytes (rag1) at 4 dpf by WISH. (c) MiR-142a-5p MO injected embryos displayed normal expression of HSC marker runx1 by WISH at 36 hpf. |
|
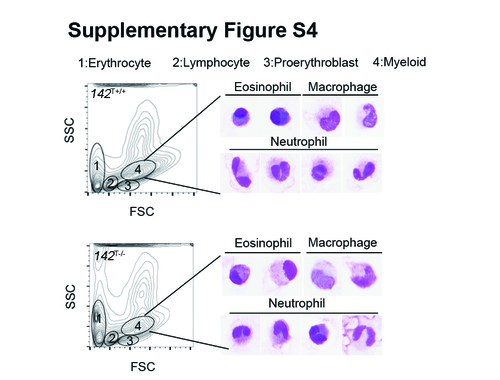
Analysis of the neutrophil morphology of adult 142T-/- fish. Zebrafish kidney cells were gated and sorted by FACs to collect fractions of cells including erythrocytes, lymphocytes, proerythroblasts and myeloid cells. Wright-Giemsa staining of sorted cells from 142T-/- fish of 12 weeks showed normal morphology of three myeloid cell types (eosinophils, macrophages and neutrophils) compared with wide-type siblings. |
|
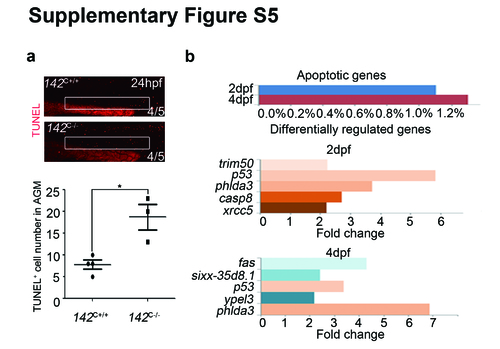
Increased apoptosis in 142C-/- embryos and upregulated expression of apoptotic genes upon knock down of miR-142a-3p. (a) TUNEL assay displayed more apoptotic cells in the AGM region of 142C-/- embryos. The number was quantified according to the TUNEL positive cells in the AGM region (meanąSD, n=3, *P<0.05). (b) Microarray analysis revealed that apoptotic genes represented by different colors of graph bar including trim50, p53, phlda3, caspase8, xrcc5, fas, sixx-35d8.1, and ypel3 were increased in the miR-142a-3p morphants at 2 and 4 dpf. |
|
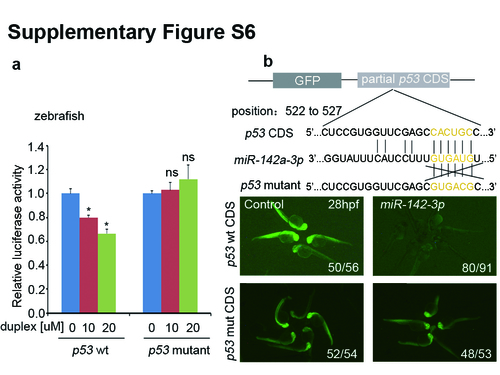
MiR-142a-3p inhibits p53 through the putative target sites in luciferase reporter assay and GFP reporter assay in vivo. (a) Luciferase reporter assay showed that there was a suppression of the luciferase activity in wild-type but not mutated p53 by miR-142-3p duplex in a dose dependent manner in zebrafish embryos (meanąSD, n=3, *P<0.05, ns stands for no significance). (b) The scheme of the reporter constructs of partial p53 coding region containing the miR-142a binding site and GFP reporter. GFP mRNA fused with the recognition site of p53 was co-injected with miR-142-3p negative control and duplex into one-cell stage embryos. GFP reporter assay showed that there was a suppression of the luciferase activity in wild-type but not mutated p53 by miR-142-3p duplex in zebrafish embryos. |
|
P53 knock down rescues excessive apoptosis and reduced differentiated populations in 142T -/- embryos. (a) P53 MO-injected 142T -/- embryos showed the restoration of excessive apoptosis at 24 hpf by TUNEL assay and statistical analysis (meanąSD, n=4,*P <0.05). (b) P53 knock down by p53 MO partially rescued decreased differentiated lineages in 142T -/- including erythrocytes (gata1), neutrophils (lyz) and T cells (rag1). |