- Title
-
Ascl1b and Neurod1, instead of Neurog3, control pancreatic endocrine cell fate in zebrafish
- Authors
- Flasse, L.C., Pirson, J.L., Stern, D.G., Von Berg, V., Manfroid, I., Peers, B., and Voz, M.L.
- Source
- Full text @ BMC Biol.
|
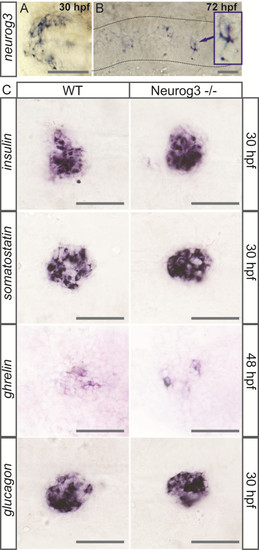
neurog3 is not expressed in the pancreas and null neurog3 mutant embryos do not display any apparent endocrine defects. (A-B) Whole-mount in situ hybridization (WISH) showing expression of neurog3 in the hypothalamus at 30 hpf (A) and in scattered cells of the gut (dotted lines) at 72 hpf (B). (C) WISH showing that the number of cells expressing insulin, somatostatin, ghrelin and glucagon is not changed in the neurog3 sa211 mutants compared to the wt siblings. All views are ventral with the anterior part to the left. Scale bars : 50 Ám hpf, hours post fertilization; wt, wild type. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
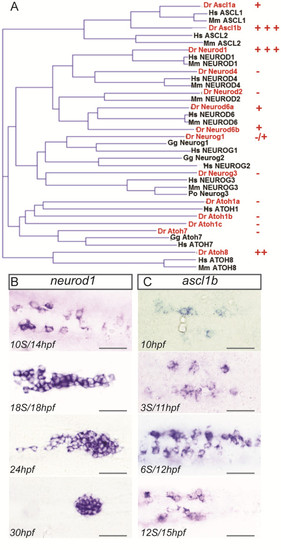
ascl1b and neurod1 are expressed during early pancreas development. (A) Phylogenetic tree calculated with full-length amino acid sequences from vertebrate members of the ARP/ASCL family. The pancreatic expression of zebrafish ARP/ASCL was tested by WISH and the expression levels are depicted by (+++) highly, (++) moderately, (+) weakly, (-/+) very weakly and (-) not expressed in the pancreas. (B-C) WISH showing expression of neurod1(B) and ascl1b(C) in the pancreatic region at the indicated stages. All views are ventral with anterior part to the left. Scale bars : 50 Ám WISH, whole-mount in situ hybridization. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
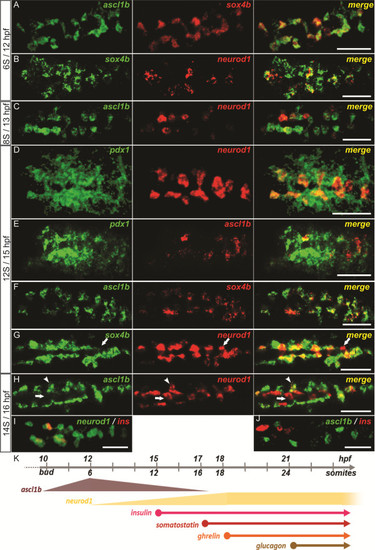
ascl1b and neurod1 are both expressed in pancreatic endocrine precursors. (A-J) Double fluorescent WISH comparing the expression of ascl1b and neurod1 with the expression of the pancreatic factor sox4b(A, B, F, G), pdx1(D, E) or with the insulin hormone (I, J) at early stages (12 to 16 hpf). The arrows point to a cell neurod1+/sox4b- (G) or neurod1+/ascl1b- (H). The arrowheads point to a cell neurod1+/ascl1b+(H). Z-plane confocal images. All views are ventral with anterior part to the left. (K) Diagram illustrating the time windows for the expression of ascl1b, neurod1 and the pancreatic hormones. Scale bars : 50 Ám hpf, hours post fertilization; WISH, whole-mount in situ hybridization. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Pancreatic expression of ascl1b and neurod1 is repressed by Notch signaling. Fluorescent WISH showing pancreatic expression of ascl1b(A-B) and neurod1(C-D) in wild-type (wt) embryos (A, C) and mind bomb (mib) mutants (B, D). Confocal projection images. All views are ventral views of 15 hpf embryos with anterior part to the left. Scale bars : 50 Ám hpf, hours post fertilization; WISH, whole-mount in situ hybridization. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Impaired endocrine cell differentiation in neurod1 morphants. Ventral views with anterior to the left of WISH showing expression of insulin(A-C), somatostatin(D-F), ghrelin(G-I) and glucagon(J-L) in control (A, D, G, J), Mo1-neurod1(B, E, H, K) and Mo2-neurod1(C, F, I, L) morphants at 30 hpf. The quantifications on the right side of the figure represent the number of positive cells per embryo for controls and neurod1 morphants. Asterisks (***) indicate that the difference between cell number in controls and neurod1 morphants is statistically significant by Student?s t-test (P <0.001). Scale bars : 50 Ám hpf, hours post fertilization; WISH, whole-mount in situ hybridization. |
|
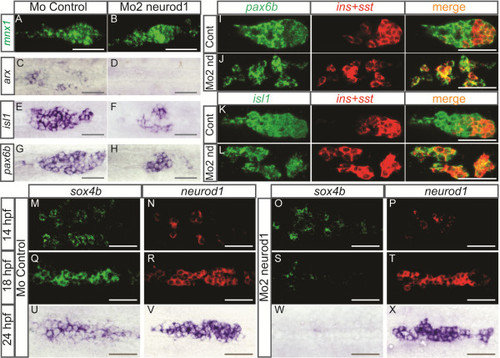
Pancreatic cells are arrested in their differentiation process in neurod1 morphants and the expression of sox4b is not maintained. Ventral views with the anterior to the left of the pancreas of embryos analyzed by visible (C-H, U-X) or fluorescent (A-B, I-T) WISH. (A-H) Pancreatic expression of mnx1, arx, isl1 and pax6b in controls and Mo2-neurod1 morphants at 24 hpf, the number of isl1+ cells in control morphant (50.4 ▒ 2.1) was reduced about 2.1 fold in the Mo2-neurod1 morphant (24.1 ▒ 1.2) and the number of pax6b+ cells in control morphant (40.7 ▒ 1.2) was reduced about 1.8 fold in the Mo2-neurod1 morphant (22.1 ▒ 1.2). (I-L) Double fluorescent WISH performed with pax6b(I, J) or isl1(K,L) probe together with a mix of insulin (ins) and somatostatin (sst) probes on 24 hpf controls or Mo2-neurod1 morphants. Z-plane confocal images (M-T) Double fluorescent WISH performed with sox4b and neurod1 on 14 hpf and 18 hpf controls or Mo2-neurod1 morphants. Confocal projection images (U-X) WISH performed with sox4b and neurod1 on 24 hpf controls or Mo2-neurod1 morphants. Scale bars : 50 Ám hpf, hours post fertilization; WISH, whole-mount in situ hybridization. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
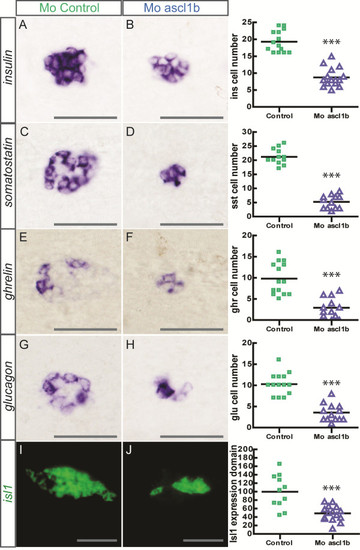
Impaired endocrine cell differentiation in ascl1b morphants. Ventral views with the anterior part to the left of WISH showing expression of insulin(A-B), somatostatin(C-D), ghrelin(E-F) and glucagon(G-H) in control (A, C, E, G) and ascl1b morphants (B, D, F, H) at 30 hpf. The quantifications on the right side of the figure represent the number of positive cells per embryo for controls and ascl1b morphants. (I-J) Confocal projections of ventral views of fluorescent WISH showing expression of isl1 in control (I) and ascl1b morphants (J) at 24 hpf. The quantification of isl1 expression domain is depicted on the right side of the figure. The graph shows the relative volume of isl1+ cells in control and ascl1b morphants, the mean of the volume occupied by the isl1+ cells in control morphants being arbitrarily set to 100%. Asterisks (***) indicate that the difference between controls and ascl1b morphants is statistically significant by Student?s t-test (P <0.001). Scale bars : 50 Ám hpf, hours post fertilization; WISH, whole-mount in situ hybridization. |
|
The onset of sox4b expression is delayed in ascl1b morphants and is restricted to neurod1 expressing cells. Ventral views with the anterior part to the left of double fluorescent WISH showing expression of sox4b and neurod1 at 12 hpf (A-F), 13 hpf (G-L) and 17 hpf (M-R) in control and ascl1b morphants. The domain occupied by sox4b+ and neurod1+ cells was reduced respectively 3.3- and 2.6-fold in the Mo-ascl1b at 17 hpf. The arrows point to a cell expressing sox4b and neurod1 while the arrowheads points to a cell expressing only sox4b. Z-plane confocal images. Scale bars : 50 Ám hpf, hours post fertilization; WISH, whole-mount in situ hybridization. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Simultaneous knock-down of Ascl1b and Neurod1 blocks the differentiation process of the precursors. Ventral views with the anterior part to the left of the pancreas of control (A,C,E,G,I) or Mo-ascl1b/Mo2-neurod1 morphants (B,D,F,H,J) analyzed by fluorescent (A-D, G-J) or visible (E-F) WISH. (A-B) Confocal projections of isl1 expression in the pancreatic islet (dotted line) and in the adjacent mesoderm (*) at 38 hpf (C-D) and of sox4b expression at 17 hpf. (E-F)ascl1b transcript expression at 13 hpf (8s). (G-H) Confocal projections of pax6b (green) and mnx1 (red) expression at 17.5 hpf showing that the pancreatic expression of pax6b and mnx1 is completely lost in the double morphants. In contrast, the expression of pax6b in the neural tube and the expression of mnx1 gene in the motoneurons and the hypochord is not perturbed. (I-J)neurod1 transcript expression at 15 hpf (12s). hpf, hours post fertilization; WISH, whole-mount in situ hybridization. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Endocrine cell differentiation is abolished in the double ascl1b and neurod1 morphants. Ventral views of WISH showing expression of insulin(A-B, I-J), somatostatin(C-D), ghrelin(E-F) and glucagon(G-H) in control (A,C,E,G,I) and Mo-ascl1b/Mo2-neurod1(B,D,F,H,J) morphants at 38 hpf (A-H) or 17 hpf (I-J). The quantifications on the right side of the figure represent the number of positive cells per embryo for controls and double ascl1b/neurod1 morphants. Asterisks (***) indicate that the difference between cell number in controls and double ascl1b/neurod1 morphants is statistically significant by Student?s t-test (P <0.001). hpf, hours post fertilization; WISH, whole-mount in situ hybridization. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Neurog3 is not involved in the formation of the second wave endocrine cells. (A-B) Ventral views of immunohistochemistry against GFP of five dpf wt(A) or neurog3 null mutant (B) tg(pax6b:GFP) embryos treated from three to five dpf with the Notch signaling inhibitor LY411575. The generation of pax6b endocrine cells from the intrapancreatic duct (indicated by a dash line) is not perturbed in the neurog3 null mutant (n = 6). (C) Confocal projections of ascl1b (green) and neurod1 (red) expression of four dpf embryos treated from three to four dpf with the Notch signaling inhibitor LY411575 showing a strong expression in the intrapancreatic duct. Anterior part to the left. dpf, days post fertilization; wt, wild type. |
|
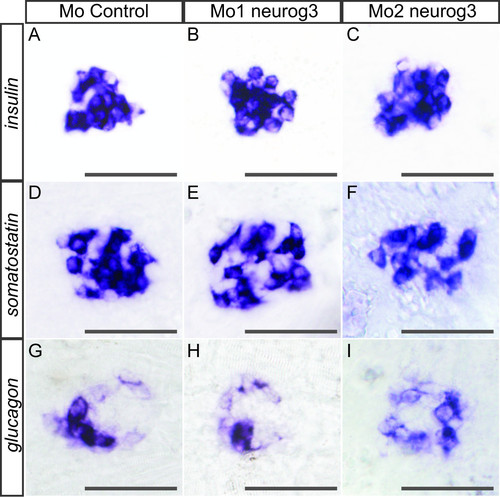
neurog3 morphants do not display any apparent endocrine defects. WISH showing that the number of cells expressing insulin (A-C), somatostatin (D-F) and glucagon (G-I) is not changed in the Mo1-neurog3 (B,E,H) or Mo2-neurog3 (C,F,I) morphants compared to the Mo-control (A,D,G) morphants at 30 hpf. All views are ventral with the anterior part to the left. |
|
ascl1a, neurod6b, neurog1, atoh8 and neurod6a are expressed in the pancreatic area. WISH showing expression of neurog1(A) ascl1a (B), neurod6b (C) neurod6a (D) and atoh8 (E) in the pancreatic region at the indicated stages. All views are ventral with anterior part to the left. |
|
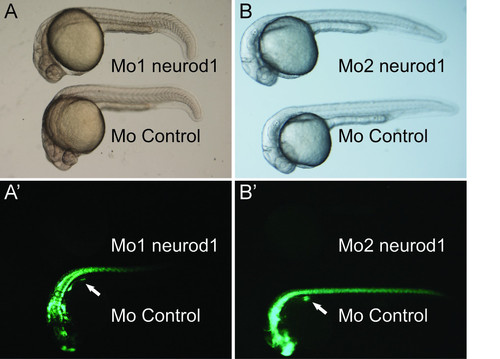
Mo1-neurod1 and Mo2-neurod1 morpholinos efficiently block the expression of GFP from the neurod1: egfp transgenic line. Lateral views of 26 to 30 hpf tg(neurod1:egfp) embryos injected with Mo1-neurod1 (A), Mo2-neurod1 (B) or control morpholinos analyzed by bright field illumination (A,B) or by epifluorescence illumination (A′,B′) showing that both morpholinos efficiently block the expression of GFP from the neurod1:egfp transgenic line [40] without disturbing the general morphology of the embryos. |
|
TUNEL assays on control and morphant embryos. (A?D) Confocal image projections of 30 hpf and 40 hpf control and neurod1 morphants after TUNEL labeling for apoptotic cells (in green) and immunodetection of insulin cells. The arrows highlight individual TUNEL+ cells in the neural tube. No TUNEL+ cells were found in the pancreatic region of control or neurod1 morphants at analyzed stages. (E?H) Confocal image projections of 14S and 19S control and ascl1b/neurod1 double morphants after TUNEL labeling for apoptotic cells (in red) and immunodetection of GFP cells. No TUNEL+ cells were found in the pancreatic region of control or morphants at analyzed stages. Somites 1 (S1) to somites 4 (S4) are shown on the panels G and H. |
|
The double ascl1b/neurod1 morphants do not display general developmental defects. Bright field views of wt embryos injected with Mo-ascl1b and Mo2-neurod1 morpholinos (A) or control morpholinos (B) showing no general developmental defects in the double morphants at 22 hpf. |