- Title
-
Loss of plakophilin 2 disrupts heart development in zebrafish
- Authors
- Moriarty, M.A., Ryan, R., Lalor, P., Dockery, P., Byrnes, L., and Grealy, M.
- Source
- Full text @ Int. J. Dev. Biol.
|
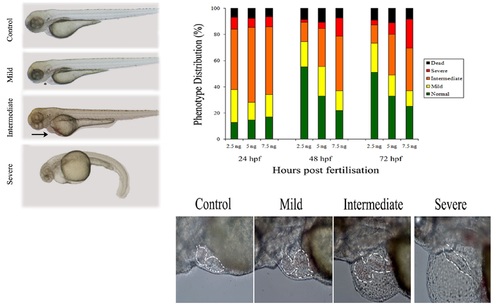
Effects of plakophilin 2 knockdown on zebrafish development. 5 ng control 5 bp mismatch morpholino (A) or plakophilin 2 morpholino (B,C,D), were injected into embryos at the 1- cell stage. Phenotypes were observed at 72 hpf. (B) Mildly affected morphant embryos displayed pericardial oedema (asterisk) compared to controls. Morphant embryos in the intermediate category (C) exhibited oedema coupled with blood pooling on the yolk (arrow). (D) Severely affected morphants showed increased cardiac oedema, blood pooling and a kinked tail. (E) Either 2.5 ng, 5 ng or 7.5 ng of plakophilin 2 morpholino were injected into embryos at the 1-cell stage. The resulting morphant phenotypes were scored at 24-, 48- and 72 hpf. The distribution of the four classifications of phenotypes - normal (green), mild (yellow), intermediate (orange), severe (red) and dead (black) - is given in percentages. An average of 60 embryos were injected per experiment, n=3 separate experiments. (F-I) Lateral view of 5 ng plakophilin 2 morphant embryo hearts at 72 hpf with anterior to the left and dorsal to the top. (F) Control-injected embryos were normal; morphant phenotypes ranged from (G) mildly affected to (H) intermediate to (I) severely affected. Outline of heart shape is indicated in each phenotype. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
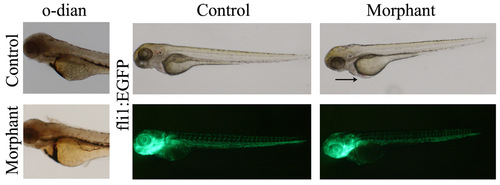
Blood pooling in morphant embryos. (A,B) Lateral view of O-dianisidine stained 72 hpf (A) control and (B) morpholino injected embryos. Blood was present in the anterior blood vessels, the heart, the common cardinal vein, the dorsal aorta, and posterior cardinal vein. In the morphant embryos, blood was pooled on the yolk prior to entering the heart. (C?F) The endothelial specific transgenic fli1:EGFP embryos injected with (E) control or (F) plakophilin 2 morpholino were analysed under light (C and D) and fluorescence microscopy (E and F) for vascular defects at 72 hpf. There was no alteration in vasculature in morphant embryos despite evident blood pooling (arrow). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
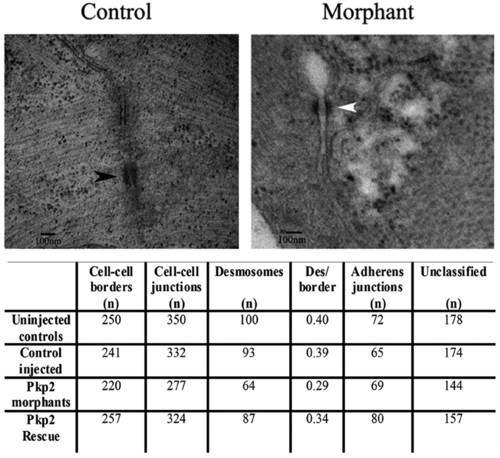
The ultrastructure of adhesion junctions in plakophilin 2 morpholino injected embryo hearts. Electron microscopy of the intercalated discs of zebrafish embryo hearts at 72 hpf. (A) In control morpholino injected embryos, intercellular junction elements (black arrowhead) were clearly evident. (B) In plakophilin 2 morphant embryos, junctions lacked these intercellular elements (white arrowhead) and the gap between cells was larger. (C) The table details the cell?cell border numbers, the number of adhesion junctions, and the number of each type of junction in control, morphant and rescued embryos. The number of desmosomes per border was decreased in plakophilin 2 morphants compared to controls, with an increase towards normal levels in the rescued embryos. Unclassified indicates adhesion junctions that could not be definitively classed as adherens junctions or desmosomes. N=3 embryos per sample. Scale bar is 100 nm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
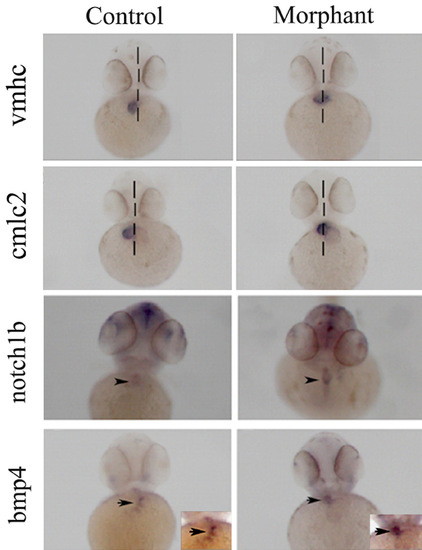
Expression of cardiac morphology marker genes in plakophilin 2 morphant and control morpholino injected embryos. Ventral views of 48 hpf wholemount embryos with (A-D) the midline denoted by a broken line. (A and B) vmhc delineates ventricle specification at 48 hpf in (A) control and (B) morphant embryos. In morphants the ventricle remained at the midline. (C,D) cmlc2 was expressed in both atrium and ventricle at 48 hpf in (C) control and (D) morphant embryos with midline placement in the latter. (E,G) Expression of both notch1b and bmp4 was restricted to the atrio-ventricular boundary (black arrowheads) in control morpholino injected embryo hearts; (F and H) in morphant embryos, both cardiac valve markers were expanded towards the ventricle (black arrows). The numbers of embryos with the displayed phenotype were (A) 67/70 (B) 34/61 (C) 68/70 (D) 28/45 (E) 47/47 (F) 28/49 (G) 49/49 (H) 43/67, numbers of morphant embryos showing the phenotype reflect the proportion of affected embryos (Fig. 1). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
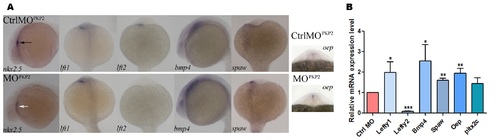
Expression of the cardiogenic marker genes in plakophilin 2 morphant and control morpholino injected embryos. (A) Wholemount in situ hybridization lateral view of nkx2.5 at 24 hpf and bmp4 at 18 somites. Dorsal views of lefty 1 (lft1), lefty 2 (lft2), spaw and oep at 18 somites. nkx2.5 was expressed to the left of the midline in control injected embryos ? black arrow; nkx2.5 signal intensity was reduced in morphant embryos, but in the correct location with an expanded domain ? white arrow. Expression of lefty 1 was unaffected in morpholino injected embryos while the expression domain of oep was expanded and the intensity of bmp4 and spaw was increased. lefty 2 expression was absent in plakophilin 2 morphant embryos compared to controls. The numbers of embryos with the displayed phenotype were: nkx2.5 control 29/29, nkx2.5 morphant 26/39; lft1 control 44/54, lft1 morphant 47/63; lft2 control 28/34, lft2 morphant 29/35; bmp4 control 34/36, bmp4 morphant 25/32; spaw control 50/57, spaw morphant 39/47; oep control 42/48, oep morphant 36/40. (B) qRTPCR expression of genes involved in cardiac laterality at 18 somites. lefty 1, bmp4, spaw, oep were significantly upregulated and lefty2 expression was significantly decreased in morphant embryos compared to control injected embryos (* P<0.05, ** P<0.005, *** P<0.0001). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. PHENOTYPE:
|