- Title
-
Progranulin modulates zebrafish motoneuron development in vivo and rescues truncation defects associated with knockdown of Survival motor neuron 1
- Authors
- Chitramuthu, B.P., Baranowski, D.C., Kay, D.G., Bateman, A., and Bennett, H.P.
- Source
- Full text @ Mol. Neurodegener.
|
Zebrafish PGRN-A in situ expression in the Spinal cord and MNs. Lateral view of 24-27 hpf embryos revealed zfPGRN-A expression within the Peripheral and Central Nervous systems. In the head region, zfPGRN-A is expressed at 24 hpf in the head and brain particularly in the tectum, midbrain-hindbrain boundary and eye (Panel A). The sense control displayed minimal signal (Panel B). In addition zfPGRN-A is also expressed at 27 hpf in the somite boundaries (Panel C). At greater magnification of the boxed area in Panel C, zfPGRN-A expression in the somite boundaries is more apparent together with expression in the motoneurons (Panel D). Abbreviations: T: Tectum; E:Eye, MHB:Mid-Brain, Hind-brain Boundary; SB:Somite Boundary, MN:Motoneurons; ICM: Intermediate cell mass. Images were captured at 6X magnification and the hatched box was further subject to 2-3X Zoom EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
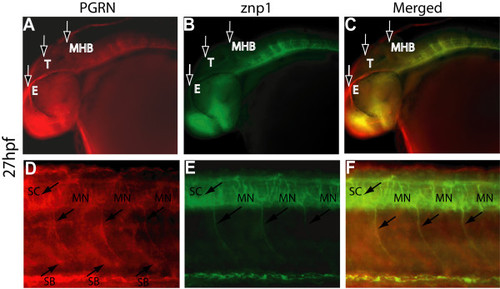
Colocalization of zfPGRN-A and znp1 immunoreactivity in Primary motor neurons at 27 hpf. Lateral views (anterior- left; dorsal- top) of whole-mount embryos labelled with zfPGRN-A (A, D) and znp1 mAb (B, E) at 27 hpf. Embryos show zfPGRN-A expression in the developing eye, tectum and hindbrain (A); Spinal Cord, Somite boundaries and motor neurons (D); znp1 expression in the eye, hindbrain, Spinal Cord and motor neurons (B and E). Merged images show co-localization of zfPGRN-A and znp1 (C, F). Abbreviations: T, Tectum; E, Eye; MHB, Mid-Brain Hindbrain Boundary; SB, Somite boundary; MN, Motoneurons.; SC, Spinal cord. Images were captured at 20 × magnification. Scale Bar = 50 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
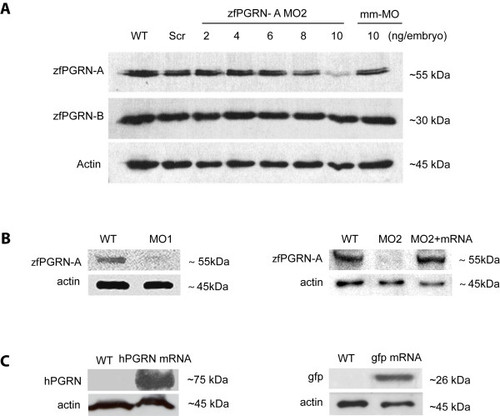
zfPGRN-A knockdown, rescue and over-expression. (A) Dose-dependent efficacy of morpholino (MO2) targeting the 5′ UTR of zfPGRN-A was assessed by Western blot analysis in comparison to its co-orthologue zfPGRN-B and actin. zfPGRN-A and B are represented by single bands of approximately 55 and 30 kDa, respectively. The Western blot analysis of MO knockdown efficacy is a representative of three independent injection sets. (B) Western blot analysis of protein extracts from embryos injected with 10 ng of zfPGRN-A MO1, 10 ng of zfPGRN-A MO2, zfPGRN-A-MO2 together with zfPGRN-A mRNA. Injection of 10 ng/embryo of the zfPGRN-A MO1 and MO2 effectively decreased zfPGRN-A translation, zfPGRN-A-MO together with mRNA resulted in normal zfPGRN-A translation. (C) Control experiments showing the results of the injection of 100pg hPGRN mRNA and 1ng gfp mRNA demonstrating translation into protein for both. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
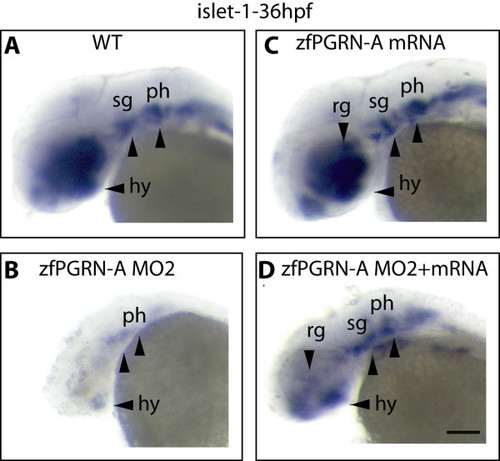
zfPGRN-A knockdown results in disrupted development of multiple neural structures. Lateral views of whole-mount embryos probed with islet 1 at 36 hpf. (A), uninjected embryos (B) embryos injected with zfPGRN-A MO2 (C) embryos injected with 100 pg zfPGRN-A mRNA, or (D) embryos co-injected with zfPGRN-A MO2 + 100 pg zfPGRN-A. 96% (48/50) of uninjected embryos (A) and 90% (45/50) of embryos injected with 100 pg zfPGRN-A mRNA (B) showed islet1 expression in the developing hypothalamus, retinal ganglia, sensary ganglia and pharyngeal arches. 84%(31/37) of embryos injected with 10 ng of zfPGRN-A MO2 (C) showed disrupted development of multiple neural structures. Co-injection of embryos with 10 ng MO2 and 100 pg zfPGRN-A mRNA (D) resulted in the rescue of 80% (40/50) embryos displaying islet 1 positive neural populations. Scale Bar = 100 μm |
|
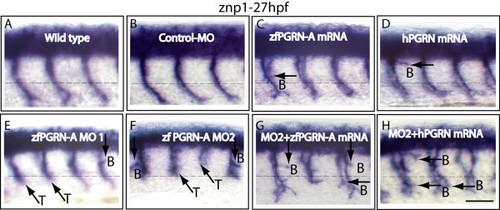
Progranulin modulates motoneuron development in vivo: zfPGRN-A knockdown induced CaP MN defects that were partially rescued by either zfPGRN-A or hPGRN mRNA. Lateral views (anterior to the left; dorsal to the top) of embryos labelled with znp1 mAb at 27 hpf in (A) wild type embryos, (B) embryos injected with Control MO, (C) 100 pg zfPGRN-A mRNA, (D) 100 pg hPGRN mRNA, (E) zfPGRN-A MO1, (F) zfPGRN-A MO2, (G) zfPGRN-A MO2+100 pg zfPGRN-A mRNA and (H) zfPGRN-A MO2+100 pg hPGRN mRNA. Observed phenotypes were normal MN development (A, B), increase in branched axons (C-H), truncation of axons (E, F) and partial rescue of truncated MNs (G, H). Dashed lines represent horizontal myoseptum. Abbreviations: T-truncation; B-Branching. Scale Bar = 50 μm. |
|
Progranulin protects CaP MNs in a model of Spinal Muscular Atrophy SMA): zfPGRN-A mRNA co-injection partially rescues SMN-MO induced CaP MN defects. (A, B) Lateral views of embryos injected with 9 ng SMN-MO and (C) embryos co-injected with 9 ng SMN-MO + 100 pg zfPGRN-A mRNA. Symbols as in Figure 1. Truncated (A) and branched (B) neurons were observed upon injection of SMN MO while co-injection with zfPGRN-A rescued truncation (white arrow) and increased axon branching (C). Abbreviations: T-truncation; B-Branching. Scale Bar = 50 μm. |
|
Co-injection of zfPGRN-A mRNA exaggerated NRP1a-MO induced Cap MN defects particularly branching. (A, B) Embryos injected with NRP1a-MO and (C) co-injected with NRP1a-MO + 100 pg zfPGRN-A. Multiple exits (A, C), Branched motor axons (B and C), and displaced neurons (B, C) were observed. Abbreviations: ME, Multiple Exits; DN, Displaced Neurons; B, Branching. Scale Bar = 50 μm. |
|
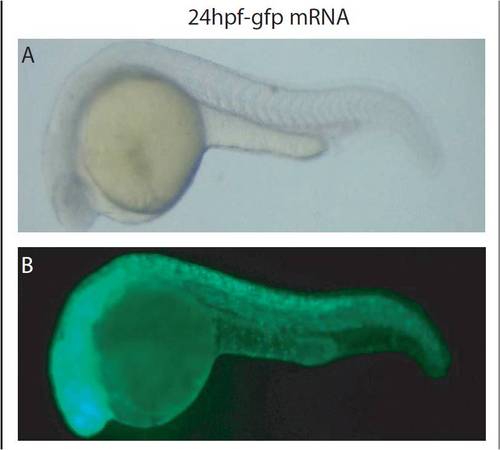
In vivo translation of 1 ng gfp mRNA. (A) bright field image showing no developmental abnormalities and (B) widespread appearance of gfp signal within the developing embryo at 27 hpf. |