- Title
-
Interaction with LC8 is required for Pak1 nuclear import and is indispensable for zebrafish development
- Authors
- Lightcap, C.M., Kari, G., Arias-Romero, L.E., Chernoff, J., Rodeck, U., and Williams, J.C.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
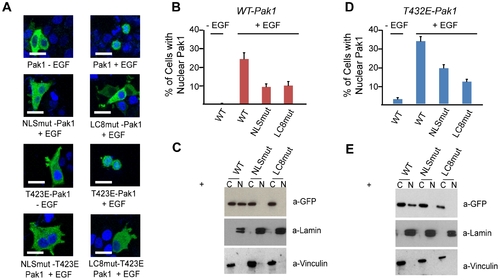
LC8 facilitates Pak1 nuclear import. (A) MCF-7 cells transiently transfected with either wild-type (WT), kinase active (T423E) GFP-Pak1, Pak1-LC8mut or Pak1-NLSmut mRNA. Scalebar shown is 10 microns. Mutations of either the NLS or the LC8 binding sequence in WT-Pak1 or T423E-Pak1 markedly reduced EGF-dependent nuclear import and stained with DAPI to visualize nuclei. (B) Quantification of nuclear accumulation of MCF-7 cells harboring either Pak1 or Pak1 mutants. Each bar represents percentage of cells with nuclear localized GFP (50 cells per experiment, done in triplicate). (C) The fraction of GFP located in cytoplasmic (C) and nuclear (N) fractions of MCF-7 cells after stimulation with EGF. Potential cross contamination of nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions was assessed by immunoblot analysis of Laminin A&C and Vinculin, respectively. (D) Nuclear import of T423E-Pak1 mutants after EGF stimulation. Nuclear percentages were calculated as in B. (E) Western Blot analysis of cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions of MCF-7 cells expressing T423E-Pak1 mutants after stimulation with EGF using an anti-GFP antibody. |
|
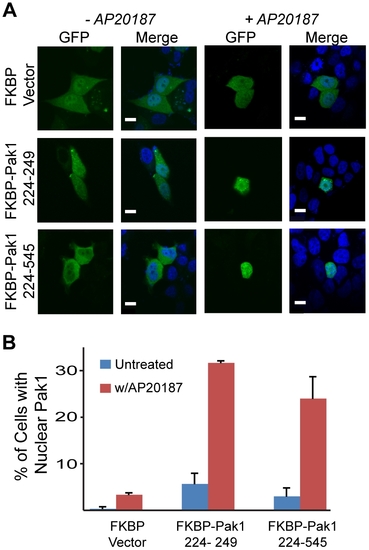
Pak1 nuclear import is contingent upon LC8 dimerization and is dynein independent. (A) Confocal microscopy images of MCF-7 cells transiently transfected with either the FKBP vector, Pak1 226?249, or Pak1 226?545 show either GFP-Pak1 construct is cytoplasmic in the absence of AP20187 and stained with DAPI to visualize nuclei. Scalebar shown is 10 microns. (B) Quantification of confocal images indicates an ∼5 fold increase in nuclear GFP over non-treated cells upon AP20187 treatment. Data quantified in the same manner as in Fig. 2B. |
|
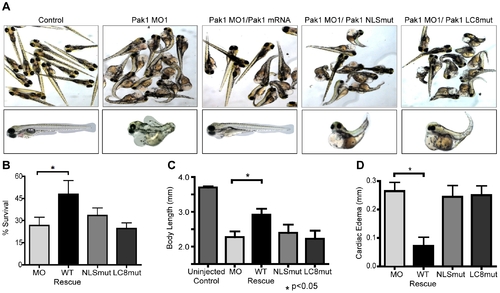
Pak1 nuclear import is critical for zebrafish development and survival. (A) Representative images of zebrafish embryos at 4 dpf. Embyros were co-injected with the morpholino (MO1) and either human wt-Pak1 mRNA, human Pak1-NLSmut or human Pak1-LC8mut (last three panels). Uninjected embryos and MO1 only injected embryos are also shown. (B?D) Quantitative analysis of differential zebrafish survival, body length, and extent of cardiac edema at 4 dpf in embryos injected with different morpholino/Pak1 mRNA combinations. For B, percent survival of uninjected control fish is approximately 90%. For D, cardiac edema for experimental fish was normalized to the control fish. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
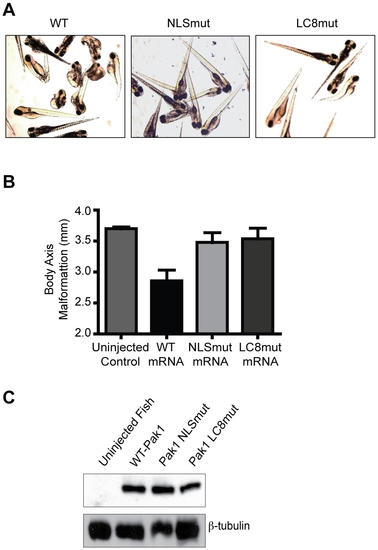
Overexpression of human Pak1 produces embryonic abnormalities in zebrafish that are contingent upon nuclear import of Pak1. (A) Images of zebrafish embryos at 4 dpf. Embryos were injected with either Pak1 WT-mRNA or one of the mRNA of the Pak1 nuclear import mutants (80 ng/μL). (B) Quantitative analysis of differential zebrafish body axis malformation at 4 dpf in embryos injected with either Pak1 WT-mRNA or one of the mRNA of the Pak1 nuclear import mutants. (C) Immunoblot analysis of lysates from zebrafish injected with either human Pak1-WT, NLSmut, or LC8mut mRNA. |
|
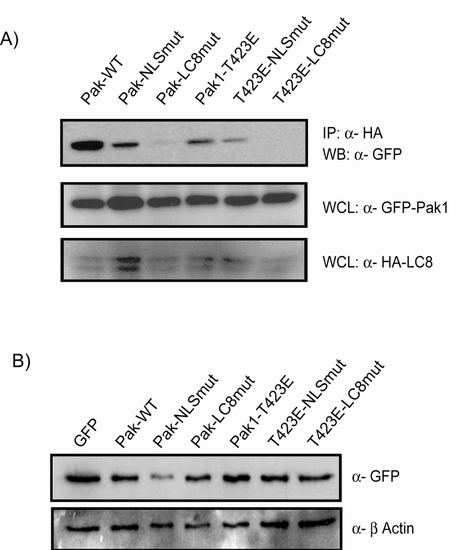
Binding assays and expression of Pak1 constructs (A) Co-immunoprecipitation of whole cell lysates overexpressing HA-LC8 and Myc-Pak1, and associated mutants. Results indicate mutation of the LC8 binding site in Pak1 abrogates the interaction. (B) Western blot of GFP-Pak1 constructs in MCF-7 cells. |
|
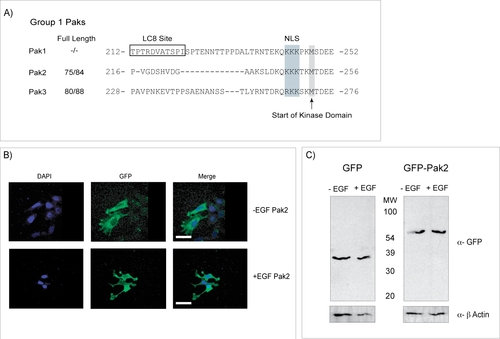
Pak2 is not cleaved after EGF Stimulation. (A) Sequence alignment of Group1 Pak kinases, highlighting that the Pak1 LC8 binding site (boxed) is absent in Pak2 and Pak3. By contrast, Pak1 and Pak2 share identical nuclear localization sequences (NLS) positioned at the same location upstream of the kinase domain. (B) Representative examples of subcellular distribution of Pak2 as determined by confocal microscopy. Pak2 does not translocate to the nucleus after EGF stimulation in MCF7 cells. (C) Western blot of MCF7 cells expressing either GFP alone or GFP-Pak2 before and after stimulation with EGF. Results show GFP runs at the same molecular weight after EGF treatment, showing that Pak2 is not cleaved in these experiments. |
|
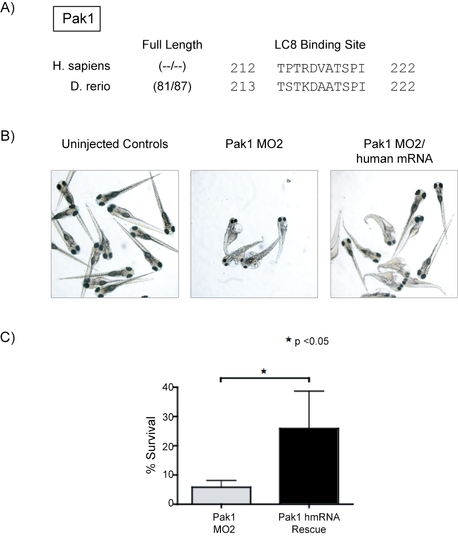
Zebrafish Pak1 Protein and Rescue. (A) Sequence alignment of Human and Zebrafish Pak1 protein. (B) Pak1 knockdown with a Pak1 MO to the 5′ intron/exon splice site (MO2) showed phenotypes identical to the Pak1 MO for the initial ATG codon. Co-injection of human Pak1 mRNA was able to recover the phenotype. Pictures were taken at a 12.5x magnification. (C) Quantification of zebrafish survival at 4 dpf in embryos injected with Pak1 MO2 and embryos rescued with human Pak1 wt-mRNA. |