- Title
-
Zebrafish endoderm formation is regulated by combinatorial Nodal, FGF and BMP signalling
- Authors
- Poulain, M., Fürthauer, M., Thisse, B., Thisse, C., and Lepage, T.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
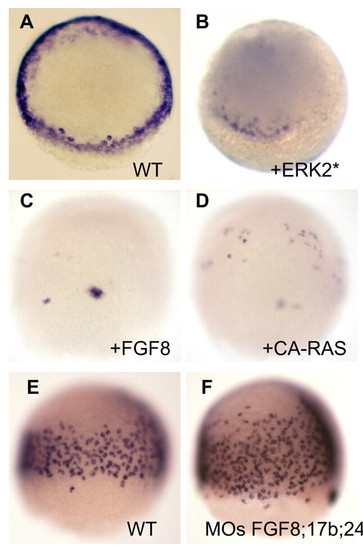
FGF/ERK signalling antagonises endoderm formation. (A-F) Expression of sox17 at 50% epiboly (A,B) or 80% epiboly (C-F). Injection of ERK2* RNA at 50 ng/µl (B), Fgf8 ligands RNA at 10 ng/µl (C) or RNA encoding constitutively activated form of Ras at 5 ng/µl (D) at the one-cell stage inhibits endoderm specification. (E,F) The triple morpholino knockdown of Fgf8, Fgf17b and Fgf24 causes overproduction of endoderm precursors. (A,B) Animal pole views; (C,D) dorsal views; (E,F) lateral views. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
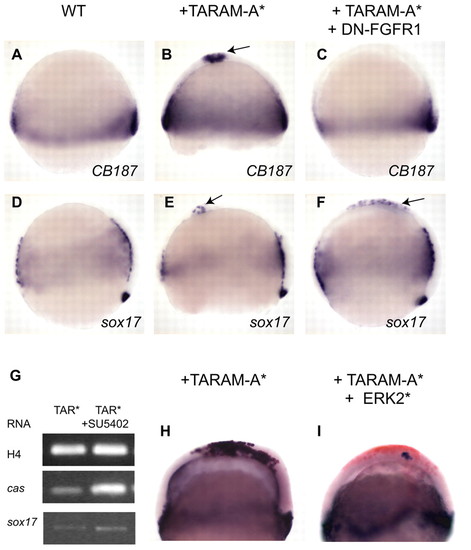
FGF/ERK activity antagonizes the ability of tar*/acvr1b to induce endoderm. Expression of CB187 (A-C) and sox17 (D-F) in embryos at 80% epiboly. (A,D) Wild type. (B,C,E,F) tar*/acvr1b RNA at 200 ng/µl was injected alone or in combination with DN-FGFR1 RNA at 500 ng/µl in one animal pole blastomere at the 64-cell stage embryo. Injection of tar*/acvr1b RNA alone is able to induce ectopic CB187 (B) and sox17 (E) expression at the animal pole (arrows). Co-injection with DN-FGFR1 abolishes the ability of tar*/acvr1b to induce CB187 (C), whereas DN-FGFR1 slightly increases the ability of tar*/acvr1b to induce sox17 (F). (G) RT-PCR analysis of three whole embryos injected with tar*/acvr1b RNA at 25 ng/µl. FGF signal inhibition by treatment with 15 µM of SU5402 after the 1000-cell stage enhances cas and sox17 responses. (H,I) tar*/acvr1b RNA at 1 ng/µl was injected alone or in combination with ERK2* RNA at 50 ng/µl into one blastomere of a 16-cell stage embryo. In both cases a lineage tracer (FLDX) was co-injected and later detected by immunostaining and sox17 expression was detected. (H) The clone of cells ectopically expressing sox17 in H is congruent with the territory containing the lineage tracer. (I) The size of the clone of cells ectopically expressing sox17 is greatly decreased in the presence of ERK*. (A-F,H,I) Lateral views. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
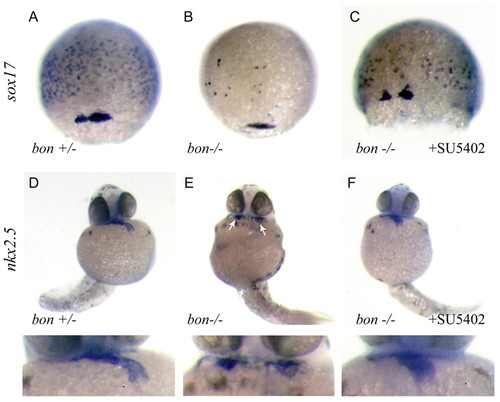
Inhibition of the FGF/MAPK pathway rescues the phenotype of bon mutants. (A-C) Dorsal views of embryos at 80% epiboly showing expression of sox17 in wild-type embryos (A), bon mutant embryos (B) and bon mutant embryos treated with SU5402 at 15 µM after 1000-cell stage (C). (D-F) Partial rescue of heart morphogenesis following SU5402 treatment into bon mutant embryos monitored by expression of nkx2.5 at 30 hours. The failure of heart primordia to migrate and fuse in the midline in bon mutants was partially restored by inhibition of FGF pathway (F). The genotype of the rescued embryos was verified by RFLP. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
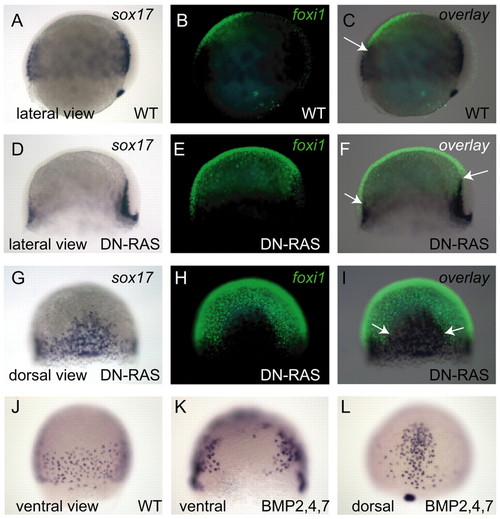
BMP signalling restricts ventral endoderm formation. sox17 (in blue) and foxi1 (green) expression at 70% epiboly in wild type (A-C) and in embryos injected with DN-Ras RNA (300 ng/µl) at the one-cell stage (D-I). Arrows in C,F,I indicate the boundary between the epidermis and endoderm. (J-L) sox17 expression at 75% epiboly in wild-type embryo (J); in an embryo injected into one ventral blastomere at the 16-cell stage with a mixture of RNAs encoding Bmp2b, Bmp4 and Bmp7 (5 ng/µl, 5 ng/µl and 40 ng/µl) (K); and in an embryo injected at the one- or two-cell stage with a mixture of Bmp2b, Bmp4 and Bmp7 RNAs (2.5 ng/µl, 2.5 ng/µl and 20 ng/µl) (L). (A-F) Lateral views; (G-I,L) dorsal views; (J,K) ventral views. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
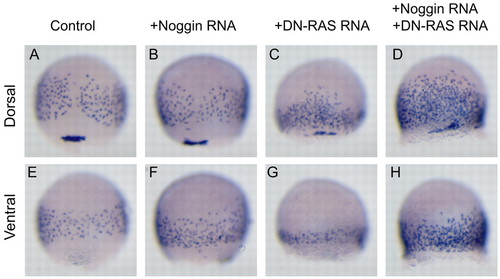
Double inhibition of the FGF and BMP pathways causes formation of an excess of endoderm precursors all around the embryo. (A-H) sox17 expression at 80% epiboly in wild-type embryos (A,E) or embryos injected at the one-cell stage with noggin RNA at 25 ng/µl (B,F), DN-Ras RNA at 300 ng/µl (C,G), or co-injected with noggin and DN-Ras RNA (D,H). Although inhibition of the BMP (B,F) or FGF/MAPK (C,G) pathways alone have modest effects on endoderm formation, blocking both pathways dramatically increases the number of endoderm precursors. (A-D) Dorsal views; (E,H) ventral views. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
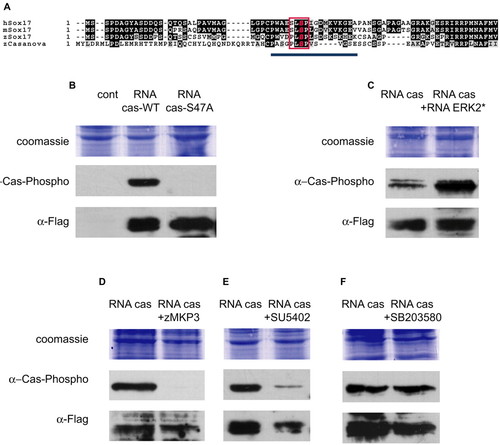
Casanova protein is phosphorylated by MAPK in vivo. (A) Putative conserved MAPK phosphorylation sites (red box) in Casanova and in Sox17 from human, mouse and zebrafish. The blue line corresponds to the 15 amino acid peptide used to generate antibodies (`α Casanova-Phospho' antibody). (B-F) Western blot of protein extracts of embryos at 30% epiboly (15 embryos per lane). Embryos were injected with cas-flag RNA at 100 ng/µl into one blastomere at the two-cell stage. Zebrafish mkp3 RNA (50 ng/µl) (D) or SB203580 (200 µM) (F) were co-injected with cas-flag RNA, while 15 µM SU5402 was added to the medium after the injection (E). Overexpressed Casanova proteins are Flag tagged and detected by a mouse anti-Flag antibody. (B) The `α Casanova-Phospho' antibody recognised the product of ectopically expressed Casanova RNA (lane 2). Product of casanova/sox32-S47A form RNA is not recognised by the antibodies directed against the phosphorylated consensus site (lane 3). (C-E) The level of phosphorylated overexpressed Casanova increases following overexpression of an activated form of ERK (C, compare lane 1 with 2) but decreases following inhibition of FGF-MAPK signalling (D,E). It is not affected by the P38-MAPK inhibitor that has been shown to work in zebrafish (F) (Fujii et al., 2000). |
|
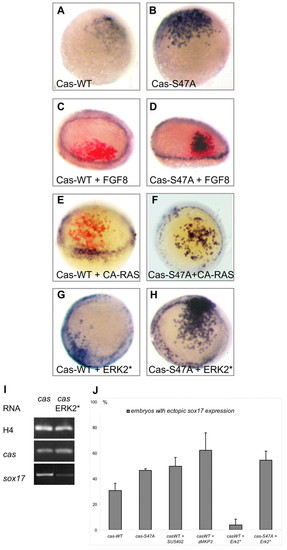
Casanova activity is negatively regulated by the FGF-ERK signalling pathway. Expression of sox17 (blue) in embryos at 30% epiboly (A,B) or 50% epiboly (C-H). In C-E, FLDX used as lineage marker was revealed by immunochemistry (red labelling). Embryos injected at the 16-cell stage with RNA encoding Casanova-WT (A) or Casanova-S47A (B), each at 10 ng/µl (see also Fig. S2 in the supplementary material). Mutation of the putative phosphorylation site slightly increases Casanova activity. Co-injection with fgf8 RNA at 10 ng/µl (C), CA-Ras RNA at 5 ng/µl (E) or ERK* RNA at 50 ng/µl (G) inhibits the ability of Casanova-WT to induce sox17 (see Fig. S3 in the supplementary material). However Casanova-S47A is insensitive to Fgf8 (D), CA-Ras (F) or ERK* (H) overexpression. (I) RT-PCR analysis from three embryos injected with cas RNA at 10 ng/µl alone or together with ERK2* RNA at 50 ng/µl. (J) Differential activity of Casanova WT and Casanova S47A, based on the percentage of embryos ectopically expressing sox17 (see Table 4). The activity of exogenous Casanova-WT was compared with the activity of Casanova-S47A, treated or not with MAPK, FGF inhibitors or an activated form of Erk2. |
|
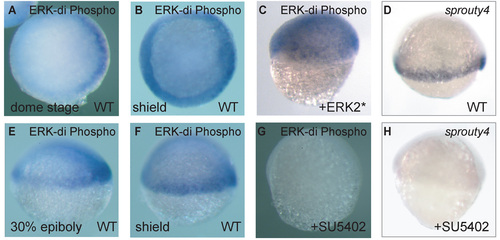
Localised activation of MAPK activity at the onset of gastrulation. ERK activity is detected with a dorsoventral gradient of activity in the mesendoderm progenitors by anti di-phosphorylated ERK antibody during different stages of development. (A) Dome stage, (E) 30% epiboly, (B,F) shield stage. (C) ERK activity is expanded towards the animal pole in ERK2*-injected embryos and is completely lost in SU5402-treated embryos (G). (D,H) sprouty4 expression at 60% epiboly. (H) Treatment with SU5402 induced the complete loss of sprouty4 expression. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
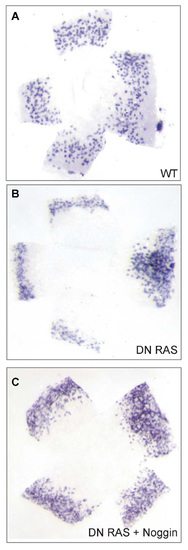
Flat preparations of the blastoderm after whole-mount in situ hybridization. sox17 expression at 80% epiboly stage in wild-type embryos (A; average number, 437; n=14) or embryos injected at the one-cell stage with DN-Ras RNA at 300 ng/ml (B; average number, 354; n) or co-injected with noggin and DN-Ras RNA (C; average number, 652; n=15) EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
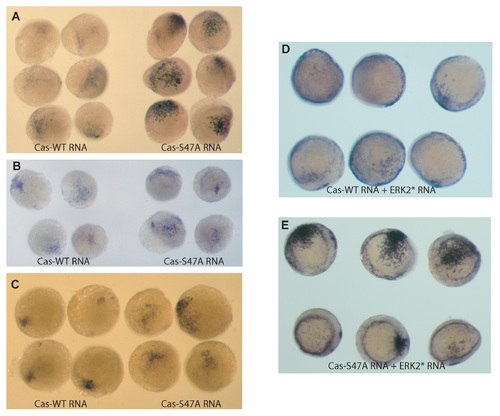
Induction of sox17 in response to overexpression of Cas-WT or Cas-S47A RNAs injected at 10 ng/ml into one animal blastomere at the 16-cell stage. (A-C) Results of three independent experiments. (D,E) Co-injection with ERK* RNA at 50 ng/ml decreases the ability of Cas-WT to induce sox17 (D). However, Cas-S47A is insensitive to overexpression of ERK2* (E). |