Fig. 6
|
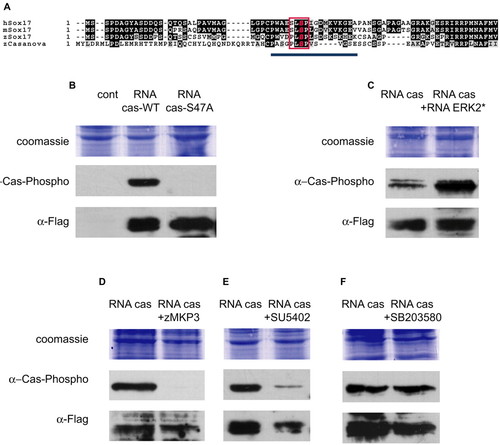
Casanova protein is phosphorylated by MAPK in vivo. (A) Putative conserved MAPK phosphorylation sites (red box) in Casanova and in Sox17 from human, mouse and zebrafish. The blue line corresponds to the 15 amino acid peptide used to generate antibodies (`α Casanova-Phospho' antibody). (B-F) Western blot of protein extracts of embryos at 30% epiboly (15 embryos per lane). Embryos were injected with cas-flag RNA at 100 ng/µl into one blastomere at the two-cell stage. Zebrafish mkp3 RNA (50 ng/µl) (D) or SB203580 (200 µM) (F) were co-injected with cas-flag RNA, while 15 µM SU5402 was added to the medium after the injection (E). Overexpressed Casanova proteins are Flag tagged and detected by a mouse anti-Flag antibody. (B) The `α Casanova-Phospho' antibody recognised the product of ectopically expressed Casanova RNA (lane 2). Product of casanova/sox32-S47A form RNA is not recognised by the antibodies directed against the phosphorylated consensus site (lane 3). (C-E) The level of phosphorylated overexpressed Casanova increases following overexpression of an activated form of ERK (C, compare lane 1 with 2) but decreases following inhibition of FGF-MAPK signalling (D,E). It is not affected by the P38-MAPK inhibitor that has been shown to work in zebrafish (F) (Fujii et al., 2000). |