Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-240913-20
- Publication
- Tayran et al., 2024 - ABCA7-dependent induction of neuropeptide Y is required for synaptic resilience in Alzheimer's disease through BDNF/NGFR signaling
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
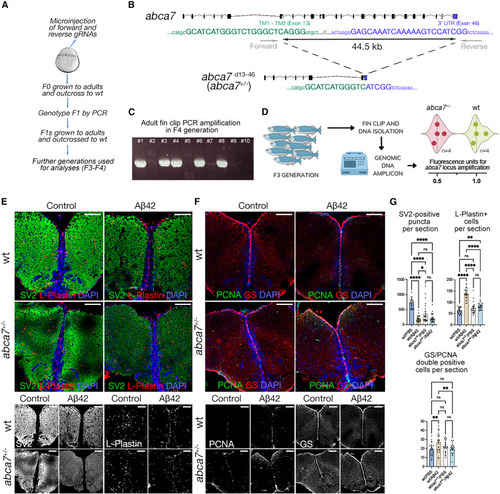
abca7 is required for synaptic integrity, microglial prevalence, and astroglial proliferation in zebrafish (A) Schematic view of generating abca7 knockout line. (B) 44.5-kb deletion in abca7 gene. (C) Representative genotyping PCR gel from F4 generation where positive bands indicate the deletion. Every column is one adult fin-clip DNA sample amplified with the forward and reverse primers in (B). (D) Genotyping results with genomic DNA qPCR in F3 adults. Eight animals (four wild-type and four heterozygous deletions) were used. Heterozygous deletions show reduced amplification (lower fluorescence). Results depicted as violin plots and individual values. (E) Immunofluorescence (IF) for SV2 (green) and L-plastin (red) with DAPI counterstain in wild type and abca7+/? with and without A?42. Black and white panels indicate individual fluorescent channels. (F) IF for PCNA (green) and GS (red) with DAPI counterstain in wild type and abca7+/? with and without A?42. Black and white panels indicate individual fluorescent channels. (G) Quantification of SV2-positive synaptic puncta, number of microglial cells, and number of proliferating astroglia. One-way ANOVA with Tukey?s multiple comparison test was used for statistical analyses. n = 4 animals from both sexes with 24 brain sections per group. ?p < 0.0332, ??p < 0.0021, ???p < 0.0002, ????p < 0.0001; not significant (ns), p > 0.0332. Scale bars, 100 ?m. See also Figures S1 and S4 , Data S1 , and Table S1 . |