Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-240913-24
- Publication
- Tayran et al., 2024 - ABCA7-dependent induction of neuropeptide Y is required for synaptic resilience in Alzheimer's disease through BDNF/NGFR signaling
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
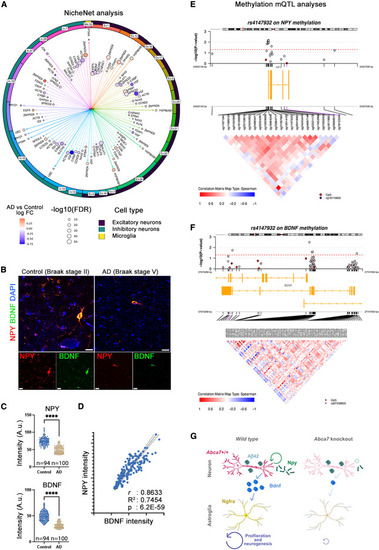
NPY interacts with BDNF-NGFR signaling (A) NPY-centered NicheNet analysis in human brain datasets of single-nucleus RNA-seq. Excitatory neurons cluster 1 showed reduced BDNF in AD in an NPY-dependent manner. Arrows represent the cumulative measure for log fold change. (B) Double immunohistochemistry for NPY and BDNF in postmortem control and AD brains. Scale bars, 10 ?m. (C) Quantification results of NPY and BDNF intensities in neurons. Two postmortem brains used per group. n denotes the number of neurons analyzed. Asterisks denote p < 1.0E?15 (non-parametric Kolmogorov-Smirnov test). (D) Correlation analyses between BDNF and NPY in 194 neurons analyzed (simple linear regression). (E and F) CpG methylation mQTL analyses with ABCA7 variants in humans. The epigenetic changes on NPY (E) and BDNF (F) are shown. Red line indicates statistical significance cutoff. Every circle represents one methylation site. Blue indicates hypermethylation, and red indicates hypomethylation. Yellow bars indicate the gene location and coding direction. Enlarged region lists all methylation sites in the corresponding genomics window. Correlation matrices between different methylation sites are depicted as positive (red) and negative (blue). ABCA7 variants exert methylation changes in NPY and BDNF promoters in a highly correlated manner. (G) Working model for Abca7-dependent Npy activity. ????p < 0.0001. See also Figure S4 ; Data S1 , S2 , S3 , S4 , and S5 ; Tables S1?S3 . |