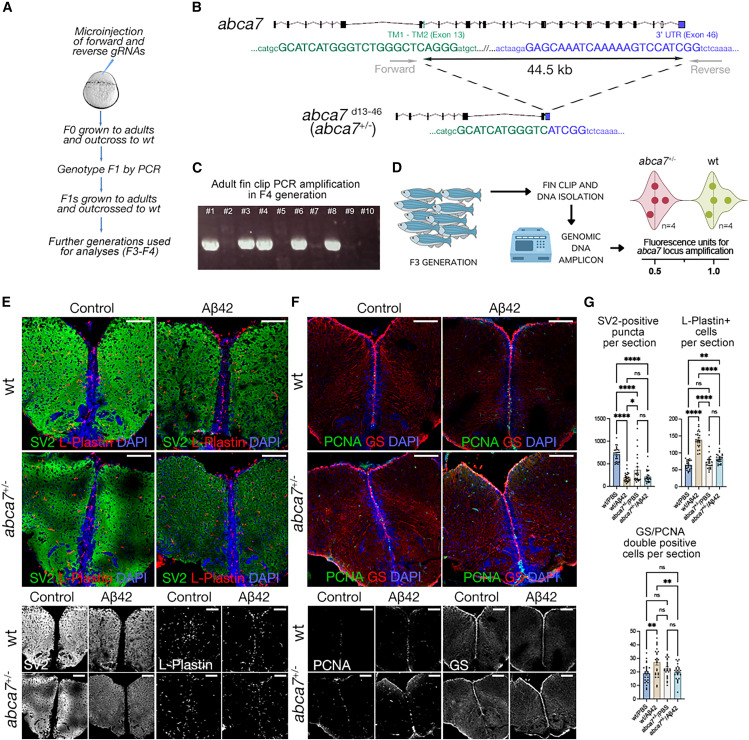
Fig. 1 abca7 is required for synaptic integrity, microglial prevalence, and astroglial proliferation in zebrafish (A) Schematic view of generating abca7 knockout line. (B) 44.5-kb deletion in abca7 gene. (C) Representative genotyping PCR gel from F4 generation where positive bands indicate the deletion. Every column is one adult fin-clip DNA sample amplified with the forward and reverse primers in (B). (D) Genotyping results with genomic DNA qPCR in F3 adults. Eight animals (four wild-type and four heterozygous deletions) were used. Heterozygous deletions show reduced amplification (lower fluorescence). Results depicted as violin plots and individual values. (E) Immunofluorescence (IF) for SV2 (green) and L-plastin (red) with DAPI counterstain in wild type and abca7+/? with and without A?42. Black and white panels indicate individual fluorescent channels. (F) IF for PCNA (green) and GS (red) with DAPI counterstain in wild type and abca7+/? with and without A?42. Black and white panels indicate individual fluorescent channels. (G) Quantification of SV2-positive synaptic puncta, number of microglial cells, and number of proliferating astroglia. One-way ANOVA with Tukey?s multiple comparison test was used for statistical analyses. n = 4 animals from both sexes with 24 brain sections per group. ?p < 0.0332, ??p < 0.0021, ???p < 0.0002, ????p < 0.0001; not significant (ns), p > 0.0332. Scale bars, 100 ?m. See also Figures S1 and S4 , Data S1 , and Table S1 .
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Cell Genom