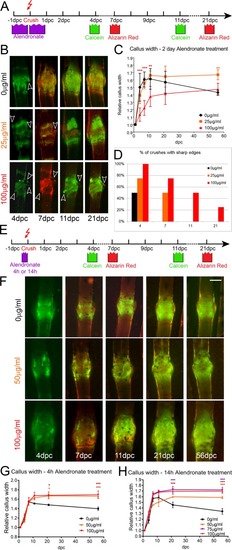
Bisphosphonate treatment alters bone callus resorption dynamics. Effect of extended and pulse exposure to alendronate on fracture bone callus. (A,E) Outlines of experimental regimes for extended (A) and pulse (E) treatment of fractures with alendronate and subsequent imaging. Fish were either treated for 1 day either side of the fracturing (A) or for a 4 h or 14 h pulse prior to fracturing (E). (B,F) Fluorescent images of fractures treated with indicated dose of alendronate following extended (B) or pulse (F) exposure as per regimes in A and E, respectively. The time points following crush are given. Arrowheads indicate bone debris. (D) Percentage of crushes showing bone debris (n=8 per point). (C,G,H) Relative callus width measurements at different time points for fractures treated with 25, 50, 75 or 100 µg/ml alendronate compared with untreated fractures for extended exposure (C), 4 h pulse pretreatment (G) or 14 h pulse pretreatment (H). Both alendronate concentration and time affected callus formation or resorption (n=4 per point). **P<0.01, ***P<0.001; ANOVA with Tukey post test. Scale bar: in F, 100 µm for B,F.
|

