Fig. 1
|
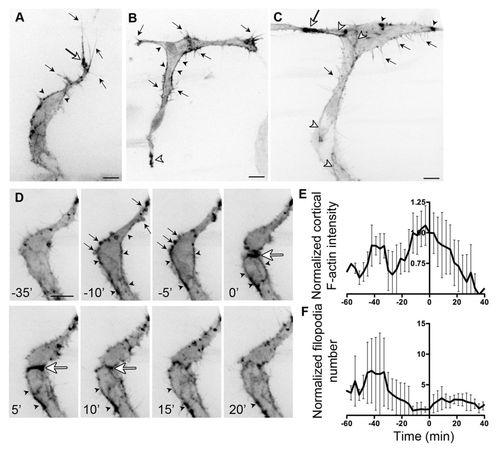
F-actin localisation in endothelial cells during angiogenesis. (A) Migrating intersomitic vessel (ISV) from a 32 hpf Tg(Fli1ep:Lifeact-EGFP) zebrafish embryo. F-actin is prominent in filopodia (black arrows), the base of filopodia (white arrow) and cell cortex (arrowheads). (B) Single-cell expression of Lifeact-EGFP in an endothelial cell (EC) spanning the ISV and dorsal longitudinal anastomotic vessel (DLAV) at 31 hpf. Cortical F-actin (black arrowhead) is present at the neck of the cell. Arrows indicate filopodia. White arrowhead points to enrichment of F-actin at the ventral end of the cell. (C) During anastomosis of ECs at the DLAV, there is enrichment of F-actin at points of contact (white arrow). F-actin is also found at cell junctions (white arrowheads), filopodia (black arrows) and in punctate structures (black arrowheads). (D) Still images of a time-lapse movie of ISV from a 31 hpf Tg(Fli1ep:Lifeact-EGFP) embryo undergoing cell division. Arrows point to F-actin-rich membrane blebs prior to cell division (-10 and -5 minutes). Arrowheads indicate accumulation of cortical actin. Strong accumulation of F-actin is observed at the contractile ring (white arrow) during cytokinesis. (E,F) Normalised cortical F-actin intensity (E) and filopodia number (F) before, during and after cell division. Raw values were normalised to the value at 0 minutes, at which two daughter cells are observed. Mean ± s.d. n=5 cells. Scale bars: 10 μm. |