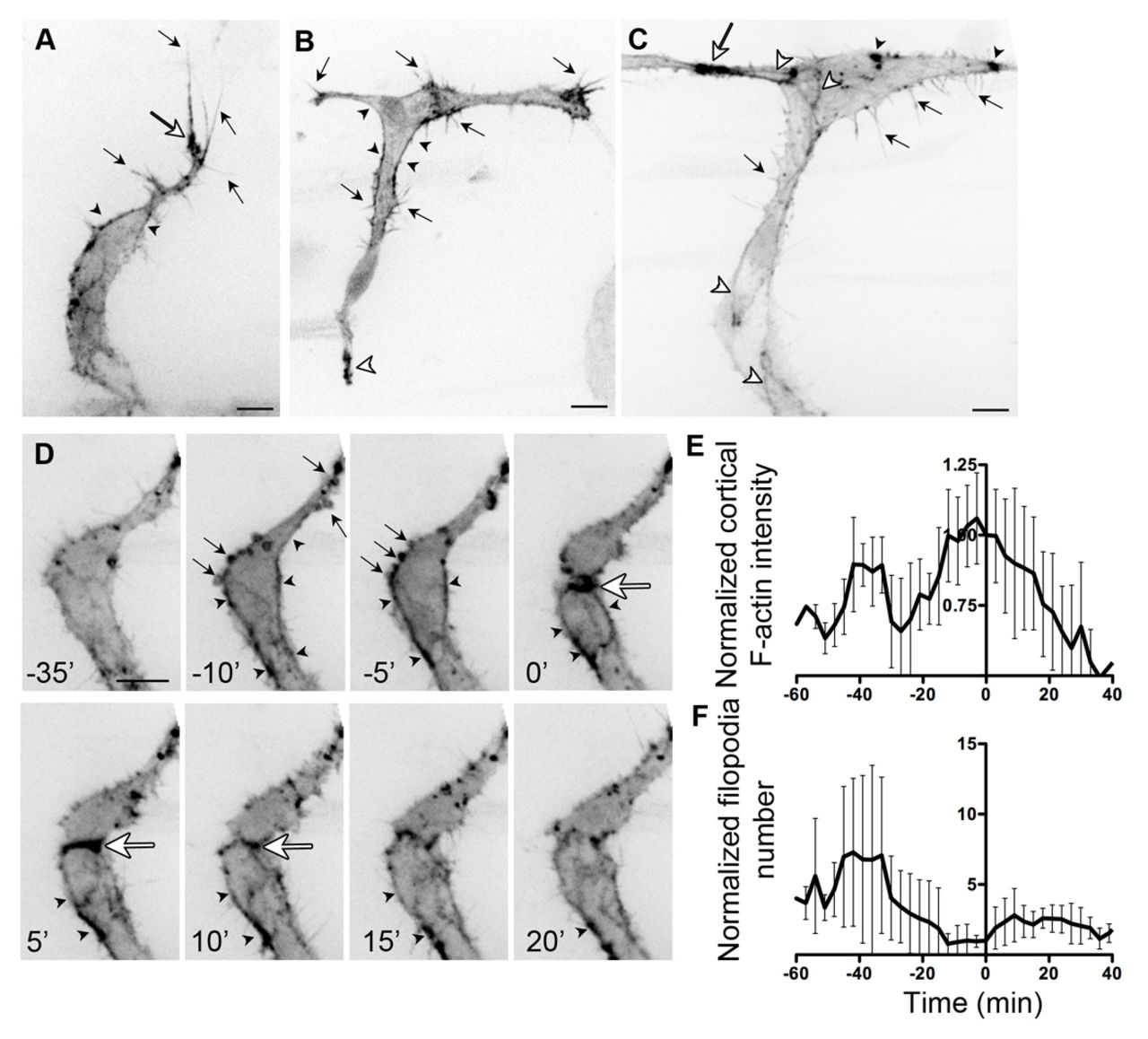
Fig. 1 F-actin localisation in endothelial cells during angiogenesis. (A) Migrating intersomitic vessel (ISV) from a 32 hpf Tg(Fli1ep:Lifeact-EGFP) zebrafish embryo. F-actin is prominent in filopodia (black arrows), the base of filopodia (white arrow) and cell cortex (arrowheads). (B) Single-cell expression of Lifeact-EGFP in an endothelial cell (EC) spanning the ISV and dorsal longitudinal anastomotic vessel (DLAV) at 31 hpf. Cortical F-actin (black arrowhead) is present at the neck of the cell. Arrows indicate filopodia. White arrowhead points to enrichment of F-actin at the ventral end of the cell. (C) During anastomosis of ECs at the DLAV, there is enrichment of F-actin at points of contact (white arrow). F-actin is also found at cell junctions (white arrowheads), filopodia (black arrows) and in punctate structures (black arrowheads). (D) Still images of a time-lapse movie of ISV from a 31 hpf Tg(Fli1ep:Lifeact-EGFP) embryo undergoing cell division. Arrows point to F-actin-rich membrane blebs prior to cell division (-10 and -5 minutes). Arrowheads indicate accumulation of cortical actin. Strong accumulation of F-actin is observed at the contractile ring (white arrow) during cytokinesis. (E,F) Normalised cortical F-actin intensity (E) and filopodia number (F) before, during and after cell division. Raw values were normalised to the value at 0 minutes, at which two daughter cells are observed. Mean ± s.d. n=5 cells. Scale bars: 10 μm.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development