- Title
-
Zebrafish myo7aa affects congenital hearing by regulating Rho-GTPase signaling
- Authors
- Xie, B., Liang, J., Jiang, J., Zeng, T., Liu, L., Xie, D., Zhu, G., Xiong, L., Zhang, K., Liu, D., Gong, J., Chen, X., Lai, R., Xie, H.
- Source
- Full text @ Front. Mol. Neurosci.
|
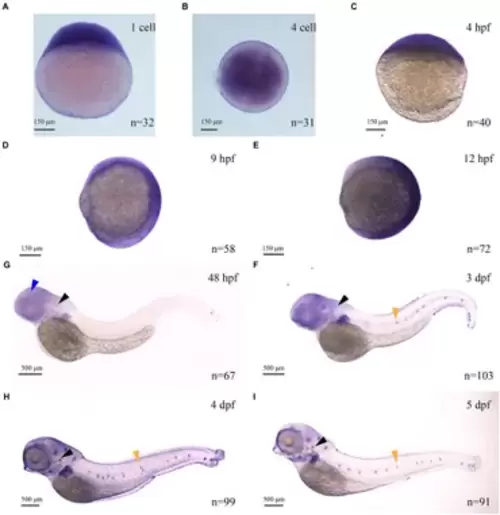
The expression of myo7aa at different stages (A?I), arrowheads indicate zebrafish retina (blue), inner ear (black) and lateral line hair cells (yellow); n: the number of embryos. |
|
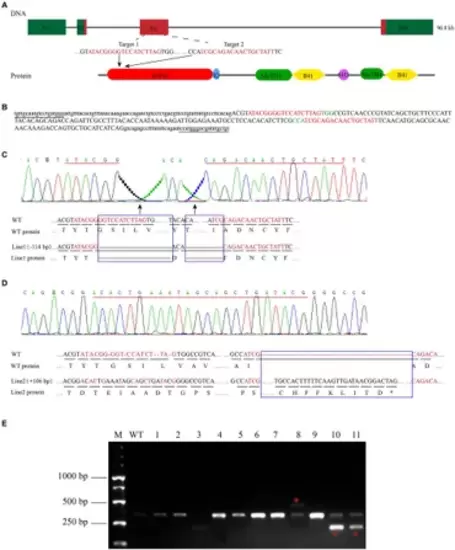
Zebrafish myo7aa gene knockout. (A) Schematic representation of the CRISPR/Cas9 target region in myo7aa gene. Green box represents the 3?UTR and 5?UTR, while the red box indicates exons. (B) Sequence of the CRSIPR/Cas9 target region in the myo7aa gene. Underlined: detection primers; red font: target site sequence; green font: PAM sequence; capital letters: exon sequence; lowercase letters: intron sequences. (C,D) Sequencing peak map, genomic DNA sequence, and amino acid sequence between two independent mutant alleles. Compared with the wild type, the myo7aa line1 mutation had a 114 bp deletion and the line2 mutation had a 106 bp insertion. The sequence of the target site is shown in red. Rectangular boxes indicate deletion or insertion sites in the mutant. *Indicates termination of protein translation. (E) The screening results of the F1 generation adult fish showed the presence of DNA marker, wild type fish, and mutant fish. |
|
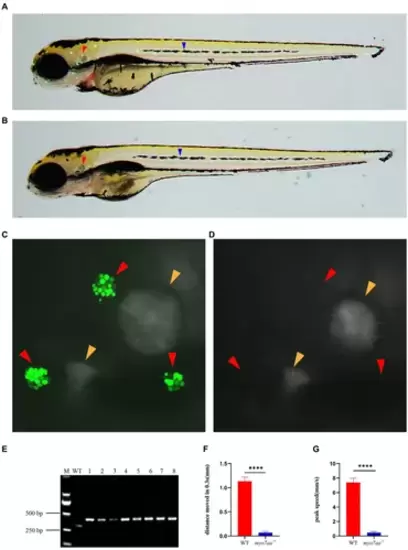
Loss of myo7aa causes hearing impairment. (A,B) YO-PRO-1 fluorescence staining results of wild-type and myo7aa mutant hair cells at 5 dpf, arrowheads indicate zebrafish inner ear (red) and lateral line hair cells (blue); (C,D) YO-PRO-1 fluorescent staining results of ear hair cells in wild-type and myo7aa mutant at 5 dpf, arrowheads indicate zebrafish inner ear hair cells (red) and otoliths (yellow). These results demonstrate the impact of myo7aa loss on the function of hair cells in the ear, leading to hearing impairment. Additionally, the results of genotype identification of embryos shown in (B,D) are presented. (E) Genotyping results of line2. M is DNA marker, WT indicates wild type, 1?8 are embryos shown in (B,D). (F,G) The movement distance (F) and reaction speed (G) of wild type and myo7aa mutant within 0.3 s after acoustic stimulation at 5 dpf are measured; n = 20; mean with SEM; with t-test, **** indicates a p-value <0.0001. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
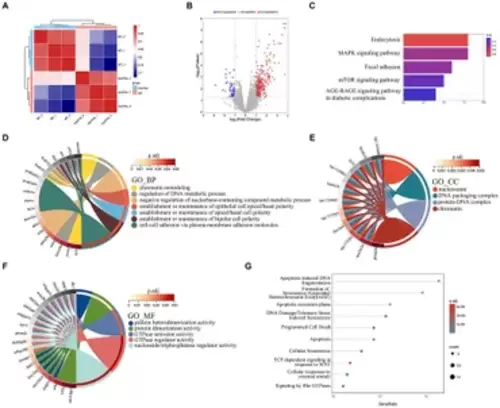
The results of RNA-seq analysis, (A) the Principal Component Analysis (PCA) diagram; (B) the volcano plot of differentially expressed genes. Red dots indicate upregulated genes. Blue dots indicate genes that are down-regulated; (C) the enrichment bar chart of gene function annotation analysis in the KEGG database. The bar length in the chart represents the number of genes. The bar color represents the p corrected value; (D?F) the GO database enrichment analysis results are provided for Biological process (BP), cellular component (CC), and molecular function (MF); (G) the Reactome database enrichment analysis results. |
|
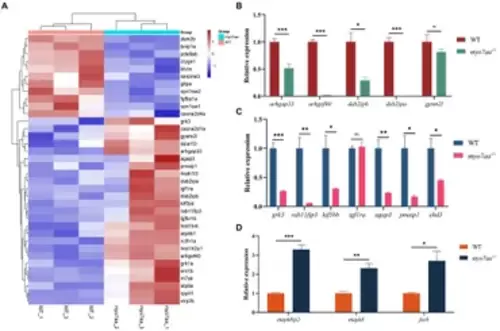
myo7aa regulates G-protein signaling. (A) The gene heatmap is depicted in (A), while (B?D) display the relative expression of genes in the Rho GTPase signaling pathway (B), cellular endocytosis pathway (C), and MAPK signaling pathway (D) between WT and myo7aa?/? at 3 dpf, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (t-test). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
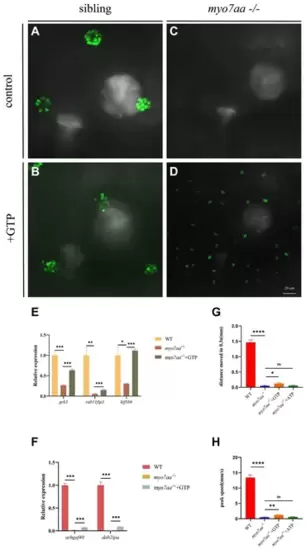
GTP compensation partially restored the hearing impairment caused by myo7aa deficiency. (A?D) YO-PRO-1 staining results of inner ear hair cells were observed in sibling (A), myo7aa?/? (B), GTP-compensated sibling (C), and myo7aa?/? (D) embryos at 5 dpf. (E,F) The relative expression of some genes in the cellular endocytic pathway (E) and G protein signaling pathway (F) is examined between WT, myo7aa?/?, and GTP-compensated myo7aa?/? embryos at 3 dpf is examined. (G,H) The movement distance (G) and reaction speed (H) of wild WT, myo7aa?/?, and GTP-compensated myo7aa?/? embryos are measured within 0.3 s after acoustic stimulation at 5 dpf are measured. n = 20; mean with SEM; with ANOVA, ****p < 0.0001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05, nsp > 0.05. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
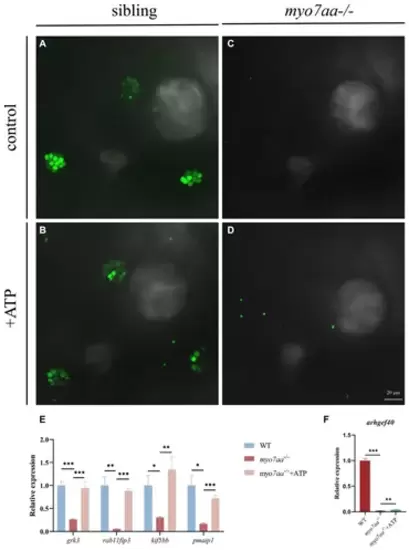
ATP compensation partially restored the hearing defects caused by myo7aa deficiency. (A?D) The YO-PRO-1 staining results of inner ear hair cells were observed in sibling (A), myo7aa?/? (B) and ATP-compensated sibling (C), myo7aa?/? (D) embryos at 5 dpf. (E,F) The relative expression of some genes in the cellular endocytic pathway (E) and G protein signaling pathway (F) was compared between WT, myo7aa?/? and ATP-compensated myo7aa?/? embryos at 3 dpf. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
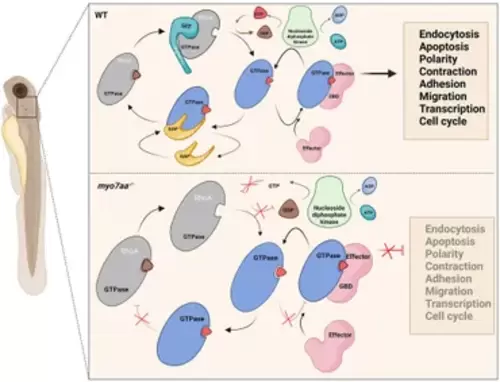
Loss of myo7aa leads to impaired Rho GTPase signaling, resulting in hearing impairment (image created at BioRender.com). |