- Title
-
TFG mutation induces haploinsufficiency and drives axonal Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease by causing neurite degeneration
- Authors
- Chen, X., Liu, F., Chen, K., Wang, Y., Yin, A., Kang, X., Yang, S., Zhao, H., Dong, S., Li, Y., Chen, J., Wu, Y.
- Source
- Full text @ CNS Neurosci Ther
|
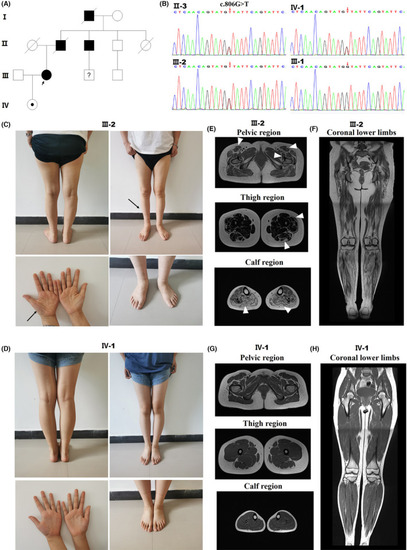
Detection of TFG p. G269V in a CMT2 family and clinical data of CMT patients with different disease durations. Pedigree of the CMT2 family. (B) DNA sequence chromatograms showing the heterozygous c.806G > T mutation in |
|
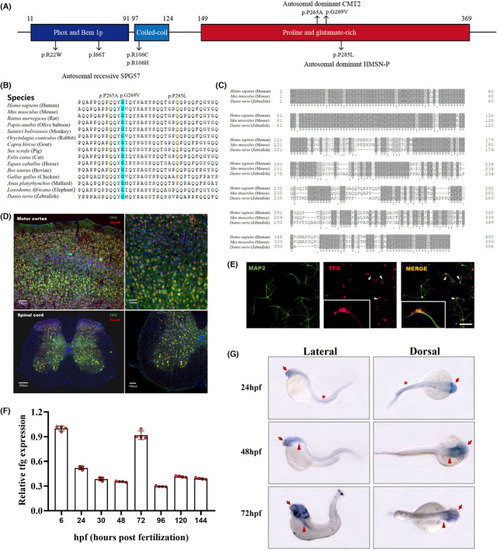
Spectrum of TFG mutations in human and characterization of |
|
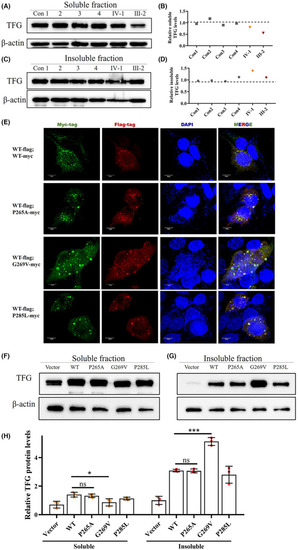
p.G269V TFG mutation induces reduced functional TFG expression level by forming insoluble cytosolic aggregates. (A and B) Western blot for soluble TFG extracted from PBMCs of four healthy controls and the two mutation carriers. Actin was used as the loading control. (C and D) Western blot for insoluble TFG extracted from PBMCs of four healthy controls and two mutation carriers. Actin was used as the loading control. (E) Immunofluorescence staining of HEK293T cells co‐transfected with plasmids encoding FLAG‐tagged wild‐type TFG (Red) and Myc‐tagged wild‐type TFG, Myc‐tagged p.P265A, Myc‐tagged p.G269V, and Myc‐tagged p.P285L TFG mutants (Green). Cell nuclei were labeled with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 10 μm. (F) Representative western blot analysis of TFG expression in HEK293T cells transfected with plasmids expressing wild‐type TFG, p.P265A, p.G269V, and p.P285L TFG mutants; empty vector was used to represent endogenous TFG as a control. β‐actin was used as the loading control. (G) Quantification of F, mean ± SD; two‐tailed unpaired |
|
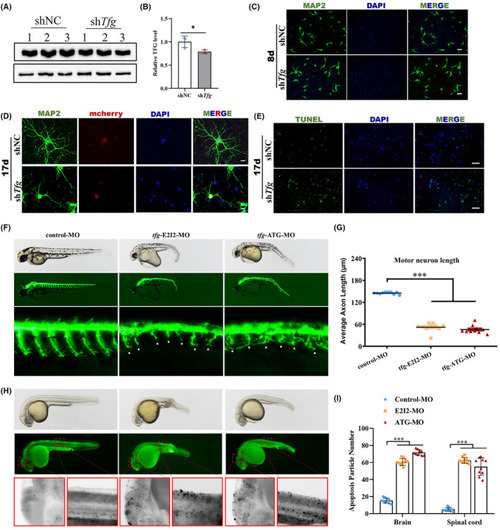
TFG deficiency impairs neurite outgrowth and causes neuronal apoptosis. (A and B) The efficiency of the small interfering RNA (siRNA) to suppress endogenous TFG expression was demonstrated by western blot. (mean ± SD; two‐tailed unpaired t‐test, * |
|
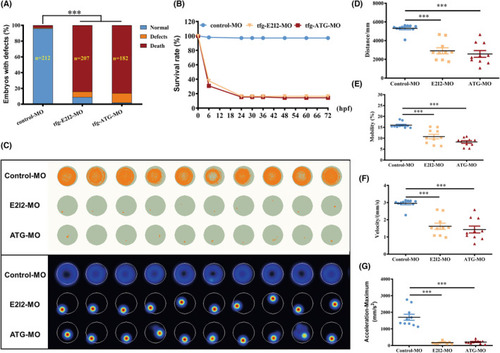
Locomotor capacity is reduced in PHENOTYPE:
|
|
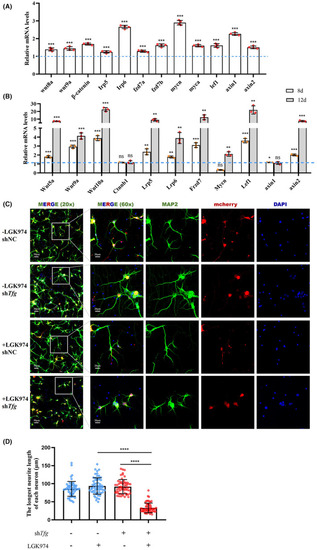
Wnt signaling is activated in response to TFG deficiency. (A) qRT‐PCR‐based validation of the key molecule in Wnt signaling in EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|