- Title
-
Claudin-5a is essential for the functional formation of both zebrafish blood-brain barrier and blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier
- Authors
- Li, Y., Wang, C., Zhang, L., Chen, B., Mo, Y., Zhang, J.
- Source
- Full text @ Fluids Barriers CNS
|
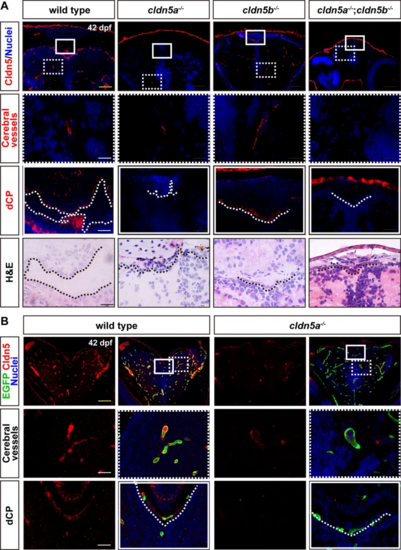
Expression patterns of Cldn5a and Cldn5b in zebrafish brain. The brain sections of 42 dpf-old zebrafish were stained by an anti-pan Cldn5 antibody. A In wild types, Cldn5s are not only expressed in cerebrovascular ECs but also the dCP epithelium. In cldn5a-/-, Cldn5b expresses only in a few cerebrovascular ECs but not in dCP. In cldn5b-/-, Cldn5a is strongly expressed in both cerebrovascular ECs and dCP. In cldn5a-/-;cldn5b-/-, no specific signals could be detected in the brain. Serial sections were stained with HE to show the histology of dCP. B Tg(kdrl:EGFP) zebrafish was introduced to help to determine the endothelial Cldn5 expression. In cldn5a-/-, Cldn5b is only expressed within a few cerebral vessels but not in dCP epithelium. White rectangles or dashed rectangles indicate the enlarged regions of dCP, or cerebral vessels respectively which are shown in the lower panels with high magnification. White dotted lines or black dotted lines show the continuous CP epithelium. n?=?3 fishes analyzed per group. Scale bars, 100 ?m in yellow or 20 ?m in black or white |
|
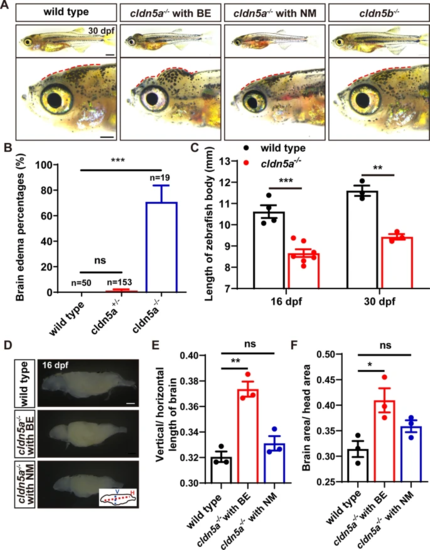
Fetal brain edema (BE) in cldn5a-/- zebrafish. A, B Around 70% of cldn5a-/- mutated zebrafish larvae show an obvious morphology with a tiny body and serious swollen head (BE), and the rest of the homozygous mutants have normal morphology (NM) but a tiny body. cldn5b-/- shows normal and healthy morphology as wild types. Enlarged figures of the head regions are shown in the lower panel. Red dotted lines figure out the profile of the skull. C cldn5a-/- larvae showed a tiny body at both 16 and 30 dpf. D-F Dissected brain tissues of 16 dpf-old larvae from wild types, cldn5a-/- with BE, and cldn5a-/- with NM brains. The ratio of vertical/horizontal length of the whole-brain was analyzed. The ratios of the brain area to head area was calculated and compared. V, vertical. H, horizontal. n?>?3 brains analyzed per group. Scale bars: 1 mm. Data are presented as mean?±?SEM. *P?<?0.05, ***P?<?0.005, ns means no significance |
|
Whole-brain oedema, ventricular dilatation, and cerebral hernia in cldn5a-/- with brain edema (BE). Histology of and HE staining on zebrafish brain sections at 22 dpf. In the forebrain and midbrain, cldn5a-/- with BE had a round outline and exhibited serious brain parenchymal edema and exaggerated ventricular dilatation. A yellow dot line labels the brain hernia in cldn5a-/- with BE. Black dot lines describe the brain ventricles. n?>?3 brains analyzed per group. Scale bars: 100 ?m |
|
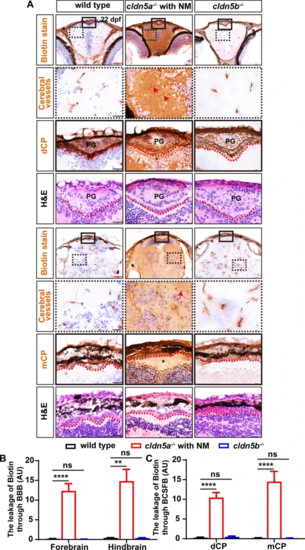
The leakage of sulfo-NHS-biotin through BBB and BCSFB in cldn5a-/-. A Sulfo-NHS-biotin (443 Da) was injected into the circulation system to assess the tightness of BBB and BCSFB in 22 dpf-old zebrafish larvae. In wild-type biotin signals are distributed in cerebral vessels, pineal gland (PG), and inside the CPs (both dCP and mCP), but not in brain parenchyma and ventricle. In cldn5a-/- with NM, biotin was permeated through the cerebrovasculatures (red arrows) into the whole brain. In the brains of cldn5b-/-, biotin stays in the cerebral vessels, PG, and inside the CPs. Serial sections were stained with HE to show the histology of CPs. Black dashed rectangles and solid rectangles indicate the enlarged regions of cerebral vessels and CPs respectively which are shown in the lower panels with high magnification. Red dot lines describe the linear CP epithelial cells. Black asterisks indicated the brain ventricles beneath the CPs with leaky biotin. Scale bars: 100 ?m in red and 20 ?m in black. B Quantification of the biotin signal strength of the biotin leaks through BBB into brain parenchyma. C Quantification of the signal strength of the leaked biotin through BCSFB. n?>?3 fishes analyzed per group. Data are represented as mean?±?SEM; **P?<?0.01, ****P?<?0.001. ns means no significance |
|
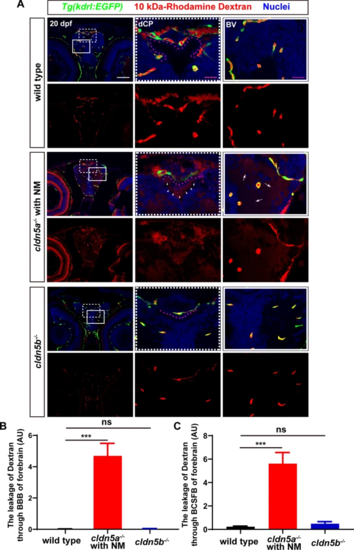
The leakage of 10 kDa-rhodamine dextran through BBB and BCSFB in the forebrain of cldn5a-/-. A In the forebrain sections of cldn5a-/- with NM, rhodamine dextran penetrates through brain capillaries and strongly accumulated in brain parenchyma (white arrows). Meanwhile, rhodamine dextran was found to leak through the paracellular space of the dCP epithelium (pink dashline) and fullfill the forebrain ventricle (white arrowheads). White dashed rectangles and solid rectangles indicate the enlarged regions of dCP and cerebral vessels respectively which are shown on the right side with high magnification. Pink dot lines label the position of the dCP epithelial cells. Scale bars: 100 ?m in white and 20 ?m in pink. B Quantification of the signal strength of the dye leaked through BBB into the forebrain parenchyma. C Quantification of the signal strength of the dye leaked through BCSFB into the forebrain ventricle. Tg(kdrl:EGFP) line was applied to label the cerebral vessels. BV, blood vessel. n?>?3 fishes analyzed per group. Data are represented as mean?±?SEM; ***P?<?0.005. ns means no significance |
|
The leakage of 10 kDa-rhodamine dextran through BBB and BCSFB in the hindbrain of cldn5a-/-. A In the hindbrain sections of cldn5a-/- with NM, rhodamine dextran penetrates through brain capillaries and strongly accumulated in brain parenchyma (white arrows). Meanwhile, rhodamine dextran was found to leak through the paracellular space of the mCP epithelium (pink dashline) and fullfill the hindbrain ventricle (white arrowheads). White dashed rectangles and solid rectangles indicate the enlarged regions of mCP and cerebral vessels respectively which are shown on the right side with high magnification. Pink dot lines label the position of the mCP epithelial cells. Scale bars: 100 ?m in white and 20 ?m in pink. B Quantification of the signal strength of the dye leaked through BBB into the hindbrain parenchyma. C Quantification of the signal strength of the dye leaked through BCSFB into the hindbrain ventricle. Tg(kdrl:EGFP) line was applied to label the cerebral vessels. BV, blood vessel. n?>?3 fishes analyzed per group. Data are represented as mean?±?SEM; ***P?<?0.005. ns means no significance |
|
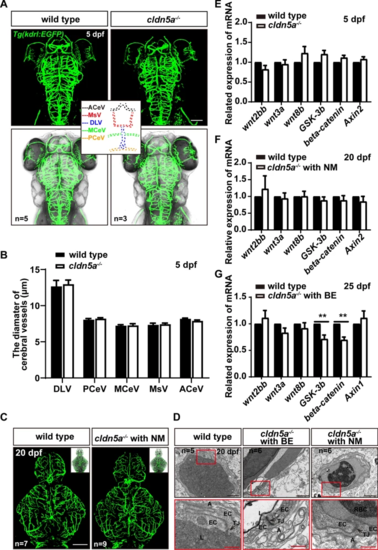
The formation of cerebral vessels was not affected in cldn5a-/-. A-C The endothelial transgenic line of Tg(kdrl:EGFP) was applied to assess the vasculogenesis and angiogenesis of cerebral vessels in cldn5a-/-. The patterns and the vascular density of cerebral vessels were not altered in cldn5a at 5 dpf (A) or 20 dpf (C). The diameters of several main cerebral vessels including anterior cerebral vein (ACeV), mesencephalic vein (MsV), dorsal longitudinal vein (DLV), middle cerebral vein (MCeV), and posterior cerebral vein (PCeV) show no discrepancy between wild types and cldn5a-/- (B). D Ultrastructure of cerebral vascular ECs and TJ strands in cldn5a-/- and wild types at 20 dpf. The morphology of cerebral vascular ECs and the integrity of TJs in cldn5a mutants is normal as in wild types. The regions labeled by red rectangles show EC junctions which are presented in the lower panel with high magnification. Black arrows indicate paracellular TJs. EC, endothelial cell; L, vascular lumen; A, abluminal side; RBC, red blood cell. n?>?5 fishes analyzed per group. Scale bars: 1 ?m in black and 500 nm in red. E-G The expression level of genes coding Wnt pathway factors related to vasculogenesis or angiogenesis. No significant discrepancy was detected in the expression of genes related to the Wnt pathway at 5 dpf embryos or 20 dpf larvae between wild type and cldn5a-/-. A decrease of gsk3b and beta-catenin was detected in cldn5a-/- with BE to that in wild types at 25 dpf larvae. Each experiment was repeated more than three times. Data are shown as mean?±?SEM. *P?<?0.05, **P?<?0.01 |
|
Development and morphology of CPs in cldn5a-/-. A WISH of clusterin reflects normal morphology of CPs in 5 dpf larvae of cldn5a-/-. White dash line squares and solid squares indicate the regions of dCPs and mCPs which are shown in high magnification in the right panels respectively. Scale bars: 200 ?m. B, C The area of dCPs and mCPs were quantified and no difference between wild types and cldn5a-/- embryos was detected. D, E The expression levels of clusterin mRNA in 5 dpf embryos and 20 dpf larvae was analyzed by RT-qPCR and no discrepancy was detected between wild type and cldn5a. Each experiment was repeated more than three times. Data are shown as mean?±?SEM. ns meant no significance. F Histological analysis by HE staining was performed to show the morphology dCPs and mCPs in 22 dpf larvae. In the brains of cldn5a-/- with NM, the morphology of CP epithelium is as normal as in wild types. In cldn5a-/- with BE, the structure of the pineal gland (PG) is disorganized with irregular cell arrangement and severe cell necrosis. The epithelial cells of dCPs and mCPs were necrotic and the plexus epithelial layer is disordered. Meanwhile, the brain ventricles (V) of cldn5a-/- with BE were enlarged dramatically. Black dot lines figure out the linear CP epithelium. The necrotic CP epithelial cells are indicated by red asterisks. n?=?3 fishes analyzed per group. Scale bars: 20 ?m. G Ultrastructural analysis of dCP epithelium of wild types and cldn5a-/- with or without BE at 20 dpf. The morphology of cerebral vascular ECs and the integrity of TJs in cldn5a with NM are normal as in wild types. The morphology of dCP epithelium and paracellular TJs (black arrows) in cldn5a with NM was not altered compared to that in wild types, whereas the microvillus of the dCP epithelial cells disappeared in cldn5a-/- with BE. Moreover, there occured paracellular gaps between dCP epithelial cells (green arrow). The regions labeled by red rectangles show epithelial TJs which are presented in the lower panel with high magnification. MV, microvilli; FV, fenestrated vessel. n?>?3 fishes analyzed per group. ns means no significance. Scale bars: 5 ?m in black and 1 ?m in red |
|
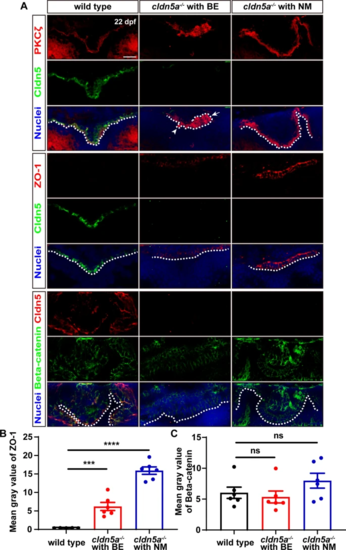
Maintenance of CP epithelial polarity and junctions in cldn5a-/- larvae. A Apical polarity marker of PKC? and epithelial junction proteins were stained to investigate the integrity of dCP epithelium. In the larval brains of wild types and cldn5a-/- with NM, PKC? colocalizes with Cldn5a and is linearly expressed in the apical side of dCP epithelium. In cldn5a-/- with BE, PKC? localizes non-apically and misexpresses on the protruded CP into the ventricle (white arrowhead) and the misfolded plexus epithelial layers (white arrow). Furthermore, compared to that in wild types, cldn5a-/- larvae show a dramatic upregulation of ZO-1. There was no discrepancy in the expression of Beta-catenin between wild types and cldn5a-/- mutated larvae. White dot lines figure out the linear dCP epithelium. n?>?3 fishes analyzed per group. Scale bars: 20 ?m. B, C The quantitative analysis of ZO-1 and Beta-catenin by measuring the mean gray values in CP epithelial cells with ImageJ software. Data are shown as mean?±?SEM. ***P?<?0.005, ****P?<?0.001 |
|
Cldn5a is essential for the development of both zebrafish BBB and BCSFB. Zebrafish Cldn5a expresses in both cerebrovascular endothelial cells and CP epithelial cells and is required for the functional maintenance of the barrier function of BBB and BCSFB |