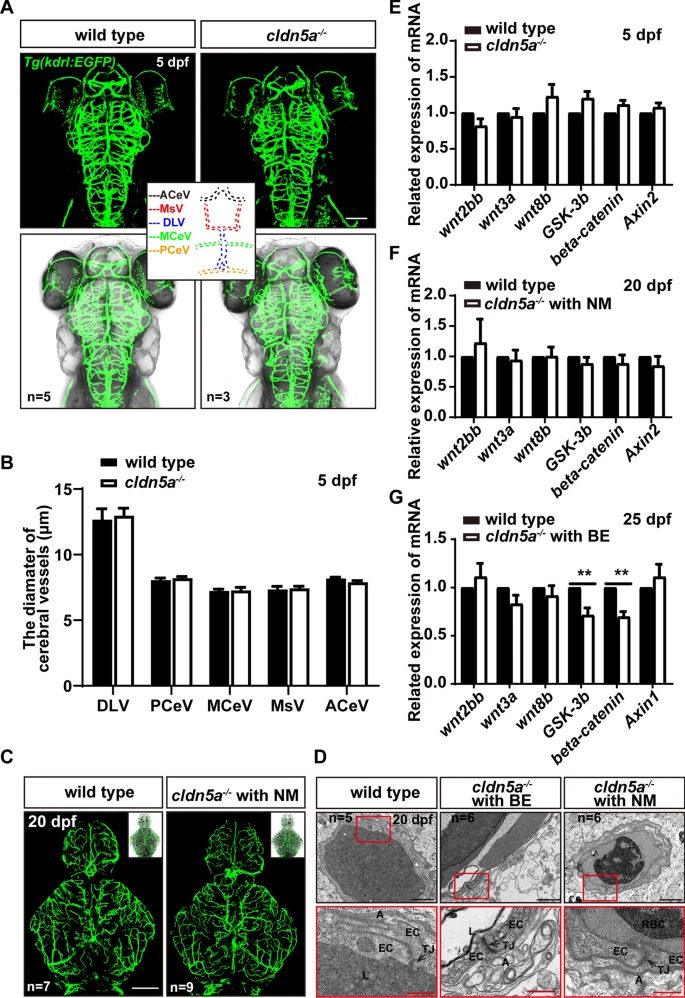
Fig. 7
The formation of cerebral vessels was not affected in cldn5a-/-. A-C The endothelial transgenic line of Tg(kdrl:EGFP) was applied to assess the vasculogenesis and angiogenesis of cerebral vessels in cldn5a-/-. The patterns and the vascular density of cerebral vessels were not altered in cldn5a at 5 dpf (A) or 20 dpf (C). The diameters of several main cerebral vessels including anterior cerebral vein (ACeV), mesencephalic vein (MsV), dorsal longitudinal vein (DLV), middle cerebral vein (MCeV), and posterior cerebral vein (PCeV) show no discrepancy between wild types and cldn5a-/- (B). D Ultrastructure of cerebral vascular ECs and TJ strands in cldn5a-/- and wild types at 20 dpf. The morphology of cerebral vascular ECs and the integrity of TJs in cldn5a mutants is normal as in wild types. The regions labeled by red rectangles show EC junctions which are presented in the lower panel with high magnification. Black arrows indicate paracellular TJs. EC, endothelial cell; L, vascular lumen; A, abluminal side; RBC, red blood cell. n?>?5 fishes analyzed per group. Scale bars: 1 ?m in black and 500 nm in red. E-G The expression level of genes coding Wnt pathway factors related to vasculogenesis or angiogenesis. No significant discrepancy was detected in the expression of genes related to the Wnt pathway at 5 dpf embryos or 20 dpf larvae between wild type and cldn5a-/-. A decrease of gsk3b and beta-catenin was detected in cldn5a-/- with BE to that in wild types at 25 dpf larvae. Each experiment was repeated more than three times. Data are shown as mean?±?SEM. *P?<?0.05, **P?<?0.01