- Title
-
Impaired brain homeostasis and neurogenesis in diet-induced overweight zebrafish: a preventive role from A. borbonica extract
- Authors
- Ghaddar, B., Veeren, B., Rondeau, P., Bringart, M., Lefebvre d'Hellencourt, C., Meilhac, O., Bascands, J.L., Diotel, N.
- Source
- Full text @ Sci. Rep.
|
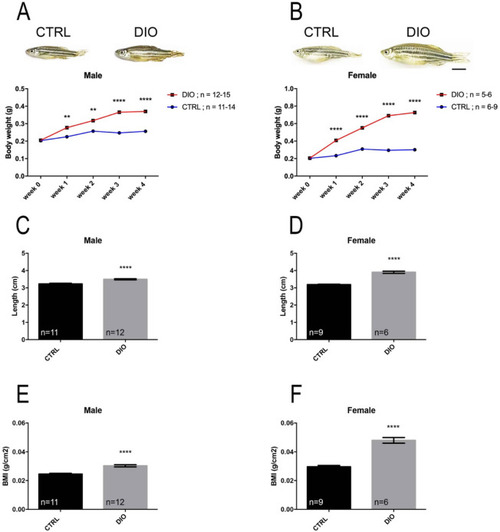
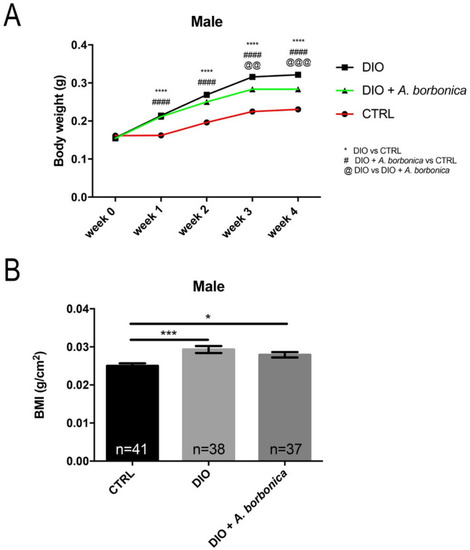
DIO results in increased body weight, length and BMI in both male and female zebrafish. ( |
|
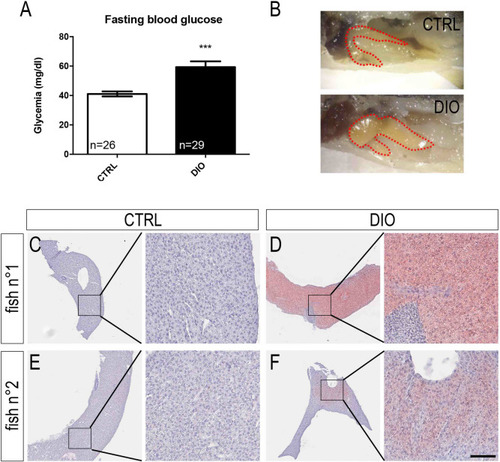
DIO leads to increased fasting blood glucose levels and to liver steatosis in zebrafish. ( |
|
DIO increases BBB leakage and neuroinflammation. ( |
|
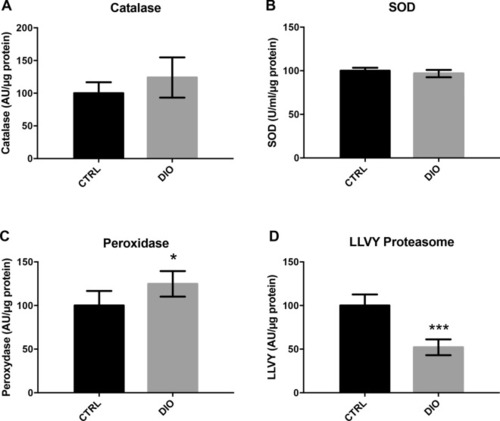
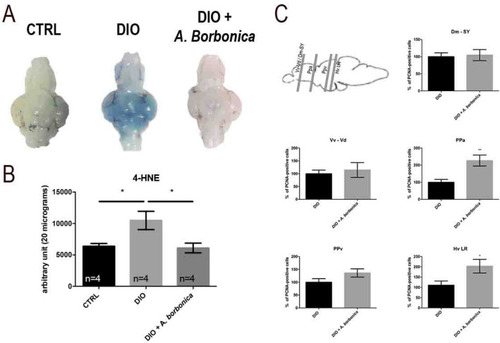
DIO disrupts antioxidant enzymes and proteasome activity in the brain of adult zebrafish. ( |
|
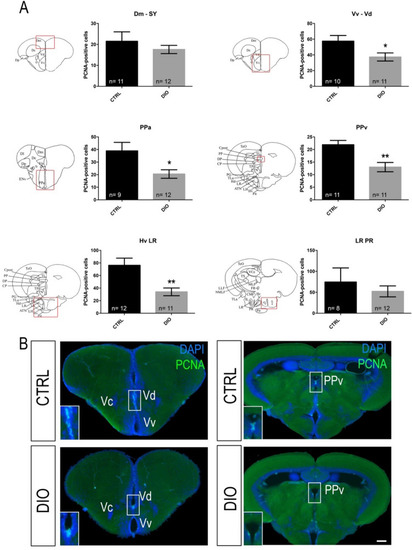
DIO impairs neurogenesis in the forebrain of adult zebrafish. ( |
|
DIO increases the occurrence of inactivity in zebrafish. ( |
|
|
|
|