- Title
-
Modulation of p53 and met expression by krüppel-like factor 8 regulates zebrafish cerebellar development
- Authors
- Tsai, M., Lu, Y., Liu, Y., Lien, H., Huang, C., Wu, J., Hwang, S.L.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Neurobiol.
|
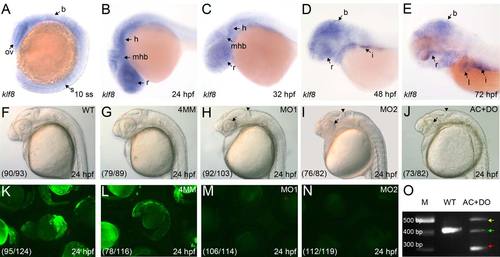
Developmental expression of zebrafish klf8, and abnormal morphology in klf8 knockdown embryos. (A?E) Spatiotemporal expression profile of klf8 in wild type (WT) embryos (lateral view). (A) At the 10 somite stage (10 ss), klf8 is expressed in the brain, optic vesicle, and somite. (B, C) klf8 is detected in the retinae, forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain from 24 to 32 hpf. (D) At 48 hpf, klf8 is also expressed in the intestine. (E) At 72 hpf, klf8 is also expressed in the liver and intestine. (F?J) At 24 hpf, klf8 knockdown embryos exhibited abnormal cerebellar primordium morphology (arrow heads) and smaller eyes (arrows). Lateral views of un-injected WT embryos (F), and embryos injected with klf8-4mmMO1 (G), klf8-MO1atg (H), klf8-MO2atg (I), or co-injected with klf8-MOAC and klf8-MODO (J). (K?N) Analysis of the specificity of klf8-MO1atg and klf8-MO2atg. EGFP is expressed in embryos injected with CMV-klf8-mo-GFP expression plasmid alone (K) or co-injected with klf8-4mmMO1 and CMV-klf8-mo-GFP plasmid (L). Green fluorescence is not observed in embryos co-injected with CMV-klf8-mo-GFP and klf8-MO1atg (M) or klf8-MO2atg (N). (O) Evaluation of the efficiency of klf8-MOAC and klf8-MODO by RT-PCR; three aberrant transcripts (arrows) were detected in embryos co-injected with klf8-MOAC and klf8-MODO. Sequencing revealed that the large (yellow arrow) and small (red arrow) transcripts contain premature stop codons, while the medium (green arrow) transcripts are comprised of wild type klf8 mRNA and a transcript with a premature stop codon. The percentage of embryos showing the indicated morphology or pattern of expression is shown in the respective panels (F?N). B, brain; h, hindbrain; i, intestine; l, liver; mhb, midbrain/hindbrain boundary; ov, optic vesicle; r, retina; s, somite. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
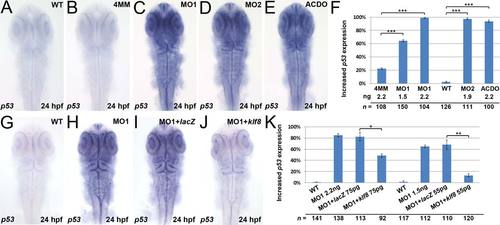
Up-regulation of p53 in the retinae and brain of klf8 morphants can be rescued by co-injection with klf8 mRNA. (A?E, G?J) Dorsal views of embryos. Enhanced p53 expression was detected in embryos injected with klf8-MO1atg (C) or klf8-MO2atg (D), or co-injected with klf8-MOAC and klf8-MODO (E), but not in WT (A) or klf8-4mmMO1-injected (B) embryos at 24 hpf. (F) Percentage of klf8 morphants and control embryos displaying enhanced p53 expression. The increase in p53 expression in klf8 morphants (H) as compared to WT (G) was rescued by co-injection with different amounts of klf8 mRNA (J), but not with LacZ mRNA (I). (K) Percentage of klf8 morphants co-injected with klf8 mRNA or LacZ mRNA displaying enhanced p53 expression. Significance was determined using Student′s t-test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Error bars indicate standard errors. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Knockdown of klf8 reduces cell proliferation and increases apoptosis in the cerebellar anlage. (A?G) Dorsal views of embryos. The number of pH3-expressing M phase cells in the cerebellar primordia at 24 hpf is decreased in embryos injected with klf8-MO1atg (C), klf8-MO2atg (D), or co-injected with klf8-MOAC and klf8-MODO (E), as compared with WT (A) or embryos injected with klf8-4mmMO1 (B) or p53 MOsp (G). Co-injection of p53 MOsp with klf8-MO1atg rescues the cell proliferation defect (F). (H) Mitotic indices of embryos of the indicated backgrounds. (I?O) Dorsal views of embryos. Increased apoptosis in the cerebellar primordium at 24 hpf is observed in embryos injected with klf8-MO1atg (K), klf8-MO2atg (L), or co-injected with klf8-MOAC and klf8-MODO (M), as compared with WT (I), or embryos injected with klf8-4mmMO1 (J) or p53 MOsp (O). Co-injection of p53 MOsp with klf8-MO1atg rescues the apoptosis defect (N). (P) Percentage of TUNEL-positive cells in embryos of the indicated backgrounds. Significance was determined using Student′s t-test. ***p < 0.001. Error bars indicate standard errors. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
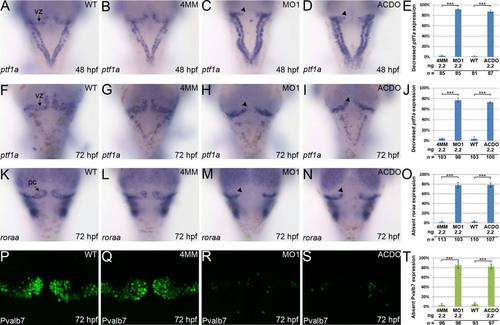
Knockdown of klf8 eliminates ptf1a expression in the VZ and affects the development of Purkinje cells. (A?D) Expression of ptf1a in the VZ at 48 hpf is decreased in embryos injected with klf8-MO1atg (C, arrowhead) or co-injected with klf8-MOAC and klf8-MODO (D, arrowhead), but expression is observed in the VZ of WT embryos (A) or embryos injected with klf8-4mmMO1 (B). (E) Percentage of embryos of the indicated backgrounds showing decreased ptf1a expression in the VZ at 48 hpf. (F-I) Expression of ptf1a in the VZ at 72 hpf is decreased in embryos injected with klf8-MO1atg (H, arrowhead) or co-injected with klf8-MOAC and klf8-MODO (I, arrowhead), but expression is observed in the VZ of WT embryos (F) or embryos injected with klf8-4mmMO1 (G). (J) Percentage of embryos of the indicated backgrounds showing decreased ptf1a expression in the VZ at 72 hpf. (K-N) Expression of roraa in the VZ at 72 hpf is not detected in embryos injected with klf8-MO1atg (M, arrowhead) or co-injected with klf8-MOAC and klf8-MODO (N, arrowhead), but expression is observed in the VZ of WT embryos (K) or embryos injected with klf8-4mmMO1 (L). (O) Percentage of embryos of the indicated backgrounds lacking roraa expression in the VZ at 72 hpf. (P?S) Expression of Pvalb7 in the VZ at 72 hpf is not detected in embryos injected with klf8-MO1atg (R) or co-injected with klf8-MOAC and klf8-MODO (S), but expression is observed in the VZ of WT embryos (P) or embryos injected with klf8-4mmMO1 (Q). (T) Percentage of embryos of the indicated backgrounds lacking Pvalb7 expression at 72 hpf. Dorsal views of embryos are shown. Significance was determined using Student′s t-test. ***p < 0.001. Error bars indicate standard errors. Pc, Purkinje cells; VZ, ventricular zone. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
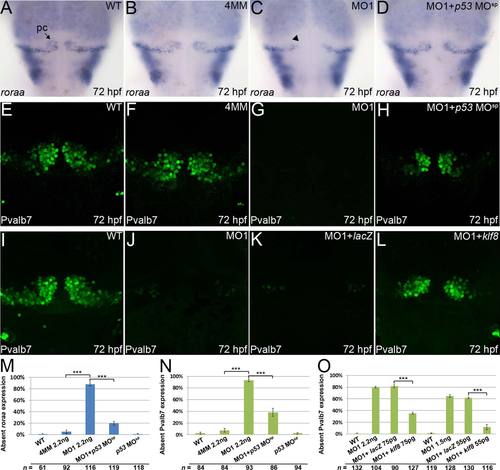
Development of Purkinje cells can be rescued in klf8 morphants by co-injection of p53 MOsp or klf8 mRNA. (A?D) Expression of roraa at 72 hpf is observed in WT embryos (A) and embryos injected with klf8-4mmMO1 (B), but not in embryos injected with klf8-MO1atg (C, arrowhead); however, expression can be rescued by co-injection of p53 MOsp (D). (E?H) Expression of Pvalb7 at 72 hpf is observed in WT embryos (E) or embryos injected with klf8-4mmMO1 (F), but not in embryos injected with klf8-MO1atg (G); however, expression can be rescued by co-injection of p53 MOsp (H). (I?L) Expression of Pvalb7 at 72 hpf is observed in WT embryos (I), but is lost in embryos injected with klf8-MO1atg (J); expression can be rescued by co-injection with different amounts of klf8 mRNA (L), but not with LacZ mRNA (K). (M) Percentage of embryos of the indicated backgrounds lacking roraa expression. (N?O) Percentage of embryos of the indicated backgrounds lacking Pvalb7 expression. Dorsal views of embryos are shown. Significance was determined using Student′s t-test. ***p < 0.001. Error bars indicate standard errors. Pc, Purkinje cells. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
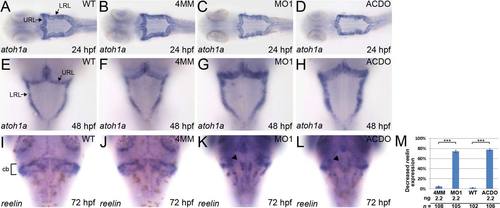
Knockdown of klf8 results in reduced expression of reelin, but not atoh1a, in the cerebellum. (A?D) Similar expression patterns of atoh1a were observed in WT embryos (A), and embryos injected with klf8-4mmMO1 (B), klf8-MO1atg (C), or both klf8-MOAC and klf8-MODO (D) at 24 hpf. (E?H) Similar expression patterns of atoh1a were observed in WT embryos (E), and embryos injected with klf8-4mmMO1 (F), klf8-MO1atg (G), or both klf8-MOAC and klf8-MODO (H) at 48 hpf. (I-L) Expression of reelin in the cerebella at 72 hpf is decreased in embryos injected with klf8-MO1atg (K, arrowhead) or co-injected with klf8-MOAC and klf8-MODO (L, arrowhead) as compared with WT embryos (I) or embryos injected with klf8-4mmMO1 (J). (M) Percentage of embryos of the indicated backgrounds exhibiting decreased reelin expression as compared to control embryos. Dorsal views of embryos are shown. Significance was determined using Student′s t-test. ***p < 0.001. Error bars indicate standard errors. Cb, cerebellum; LRL, lower rhombic lip; URL, upper rhombic lip. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
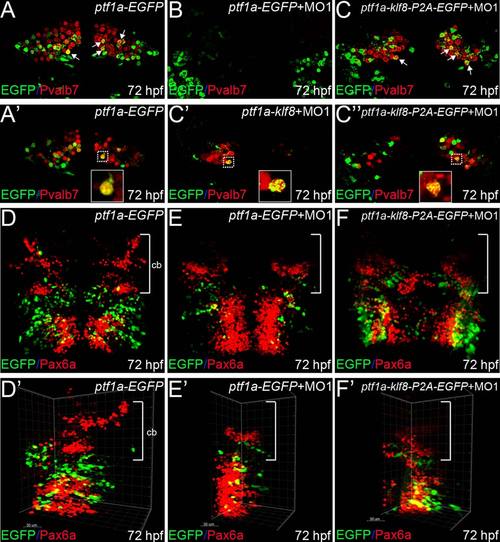
Klf8 controls formation of cerebellar Purkinje cells in a cell-autonomous manner. (A?C′′) Examination of wild type embryos injected with ptf1a-EGFP at 72 hpf revealed that differentiated Purkinje cells express Pvalb7 (red), and that some Purkinje cells (derived from ptf1a:EGFP cells) express both EGFP and Pvalb7 (yellow, arrows) (A, A′). Examination of embryos co-injected with klf8-MO1atg and ptf1a-EGFP revealed that no Purkinje cells had formed by 72 hpf (B). In embryos co-injected with klf8-MO1atg and ptf1a-klf8-P2A-EGFP, some ptf1a:klf8-P2A-EGFP+ cells differentiated into Purkinje cells expressing Pvalb7 and EGFP (yellow, arrows), while ptf1a promoter activity was switched off in the majority of Pvalb7+ Purkinje cells (red) derived from ptf1a: klf8-P2A-EGFP+ cells, so that these cells no longer expressed EGFP at 72 hpf (C; C′, n = 5; C′′, n = 5). (D?F′) In wild type embryos injected with ptf1a-EGFP, granule cells expressing Pax6a (red, bracket) are observed in the cerebella of embryos at 72 hpf (D, D′). Examination of embryos co-injected with klf8-MO1atg and ptf1a-EGFP revealed reduced numbers of granule cells expressing Pax6a (red) in the cerebella of 72 hpf embryos (E, E′). Examination of embryos co-injected with klf8-MO1atg and ptf1a-klf8-P2A-EGFP revealed a similar reduction in the number of granule cells expressing Pax6a (red) in the cerebella of embryos at 72 hpf (F, F′). Dorsal views of embryos are shown. Z-axis merged images are shown in panels A?C and D?F′. Single confocal images are shown in panels A′, C′, and C′′. Panels D′?F′ are the same images as shown in D?F, but rotated clockwise by ~30?45°. Cb, cerebellum. |
|
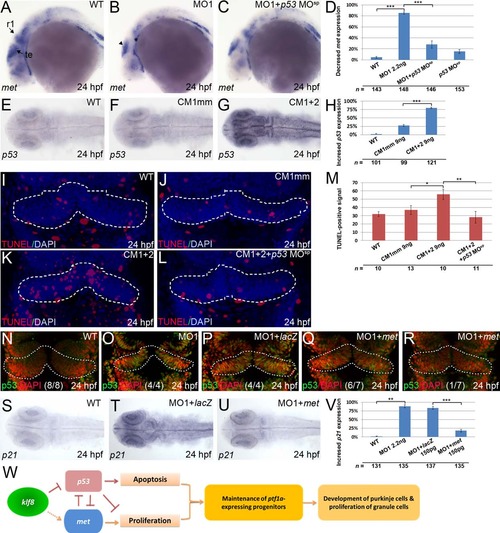
Knockdown of klf8 results in decreased met expression in the rhombomere 1 (R1) and tectum, and co-injection of met mRNA rescues development of Purkinje cells in klf8 morphants. (A?D) Reduced met expression in the tectum (arrowhead) and R1 (asterisk) is observed at 24 hpf in embryos injected with klf8-MO1atg (C) or co-injected with klf8-MOAC and klf8-MODO (D), as compared to WT embryos (A) or embryos injected with klf8-4mmMO1 (B). (E) Percentage of embryos of the indicated backgrounds with decreased met expression relative to WT embryos. (F?I) Decreased met expression in the tectum (arrowhead) and R1 (asterisk) of klf8 morphants (G) relative to WT (F) is rescued by co-injection with klf8 mRNA (I), but not LacZ mRNA (H). (J) Percentage of embryos of the indicated backgrounds with decreased met expression relative to WT embryos. (K?N) Perturbed Purkinje cell development in klf8 morphants (L) as compared to WT embryos (K) can be rescued by co-injection of met mRNA (N), but not LacZ mRNA (M). (O) Percentage of embryos of the indicated backgrounds with aberrant Purkinje cell development as compared to WT embryos. (A?D) lateral views; (F?I, K?N) dorsal views. Significance was determined using Student′s t-test. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Error bars indicate standard errors. R1, rhombomere 1; te, tectum. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Interaction between klf8, p53, and met regulates apoptosis in zebrafish embryos. (A?C) Decreased met expression in the tectum (arrowhead) and rhombomere 1 (asterisk) of klf8 morphants (B) relative to WT (A) can be rescued by co-injection of p53 MOsp (C). (D) Percentage of embryos of the indicated backgrounds with decreased met expression relative to WT embryos. (E?G) Expression of p53 in the various brain regions at 24 hpf is detected in embryos co-injected with CM1 and CM2 (G), but not in WT (E) or in embryos injected with CM1mm (F). (H) Percentage of embryos of the indicated backgrounds with increased p53 expression relative to WT embryos. (I?L) Increased apoptosis in the cerebellar primordium at 24 hpf is observed in embryos co-injected with CM1 and CM2 (K) as compared with WT (I), or embryos injected with CM1mm (J). Co-injection of p53 MOsp with CM1 and CM2 rescues the apoptosis defect (L). (M) Percentage of TUNEL-positive cells in the embryos of the indicated backgrounds relative to WT embryos. (N?R) Increased nuclear distribution of p53 in the cerebellar primordium of klf8 morphants (O) relative to WT (N) is reduced by co-injection with met mRNA (Q, R), but not with LacZ mRNA (P). (S?U) Increased p21 expression in the retinae and brain regions of klf8 morphants relative to WT (S) is rescued by co-injection with met mRNA (U), but not with LacZ mRNA (T). (V) Percentage of embryos of the indicated backgrounds with increased p21 expression relative to WT embryos. (W) A model describing how Klf8 regulates the maintenance of ptf1a-expressing neuronal progenitors by modulating expression of p53 and met. (A?C) lateral views; (E?G, I?L, N?U) dorsal views. Significance was determined using Student′s t-test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Error bars indicate standard errors. R1, rhombomere 1; te, tectum. |
|
Co-expression of klf8 and pax6a is detected in the retinae, thalamus, and hindbrain, and co-expression of klf8 and otx2 is observed in the midbrain. (A-F) Lateral views of embryos are shown. Expression of klf8 (red; A, D) and pax6a (green; B, E) in embryos at 24 hpf; merged images are shown in (C) and (F). (G-L) Dorsal views of embryos are shown. Expression of klf8 (red; G) and otx2 (green; H) in embryos at 24 hpf; merged images are shown in (I). Expression of klf8 (red, J) and nkx6.1 (green, K) in embryos at 24 hpf; merged images are shown in (L). H, hindbrain; mb, midbrain; r, retina; th, thalamus; vh, ventral hindbrain; vmb, ventral midbrain. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
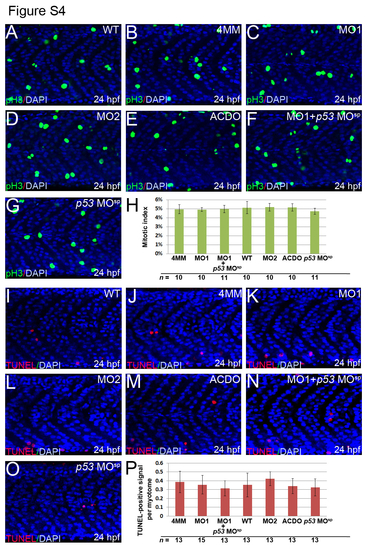
Knockdown of klf8 does not affect cell proliferation or apoptosis in the trunk muscle. (A-G, I-O) Lateral views of embryos and myotomes above the yolk extension are shown. The number of pH3-expressing M phase cells in myotomes at 24 hpf were similar between WT embryos (A), embryos injected with klf8-4mmMO1 (B), klf8-MO1atg (C), klf8-MO2atg (D), or p53 MOsp (G), and embryos co-injected with klf8-MOAC and klf8-MODO (E), or p53 MOsp and klf8-MO1atg (F). (H) Mitotic indices of embryos of the indicated backgrounds. The numbers of TUNEL-positive cells in the myotomes at 24 hpf were similar between WT embryos (I), embryos injected with klf8-4mmMO1 (J), klf8-MO1atg (K), klf8-MO2atg (L), or p53 MOsp (O), and embryos co-injected with klf8-MOAC and klf8-MODO (M), or p53 MOsp and klf8-MO1atg (N). (P) Percentage of TUNEL-positive cells in embryos of the indicated backgrounds. Error bars indicate standard errors. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
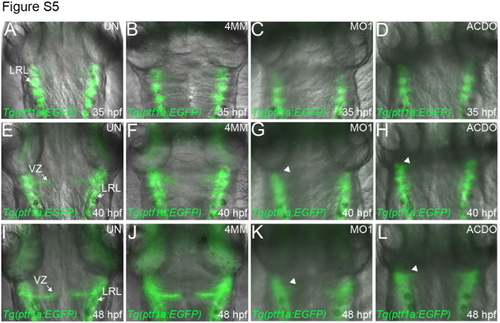
EGFP expression in the VZ of un-injected (UN) Tg(ptf1a:EGFP) embryos, or embryos of the same line injected with the indicated klf8-MOs between 35 and 48 hpf. (A-L) Dorsal views of embryos. (A-D) At 35 hpf, EGFP expression is detected in the LRL of UN embryos (A), and embryos injected with klf8-4mmMO1 (B) or klf8-MO1atg (C) or co-injected with klf8-MOAC and klf8-MODO (D). (E-L) EGFP expression is also detected in the VZ of UN embryos (E, I) and embryos injected with klf8-4mmMO1 (F, J) at both 40 and 48 hpf. However, EGFP is not detected in the VZ of embryos injected with klf8-MO1atg (G, K, arrowhead) or co-injected with klf8-MOAC and klf8-MODO (H, L, arrowhead) at either 40 or 48 hpf. LRL, lower rhombic lip; VZ, ventricular zone. |
|
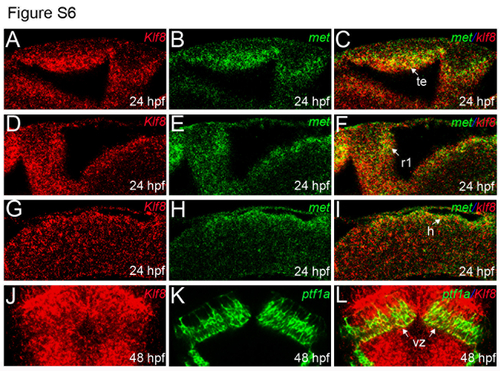
Co-expression of klf8 and met in the tectum, R1, and hindbrain, and co-expression of klf8 and ptf1a in the VZ. (A-I) Expression of klf8 (red; A, D, G) and met (green; B, E, H) in embryos at 24 hpf; merged images are shown in (C, F) and (I). Lateral views of embryos are shown. (J-L) Dorsal views of Tg(ptfla:EGFP)jh1 transgenic fish embryos following double fluorescence in situ hybridization. Expression of klf8 (red; J) and ptf1a (as visualized in green using a GFP probe; K) in embryos at 48 hpf; a merged image is shown in (L). Single confocal images are shown. H, hindbrain; r1, rhombomere 1; te, tectum; VZ, ventricular zone. |
|
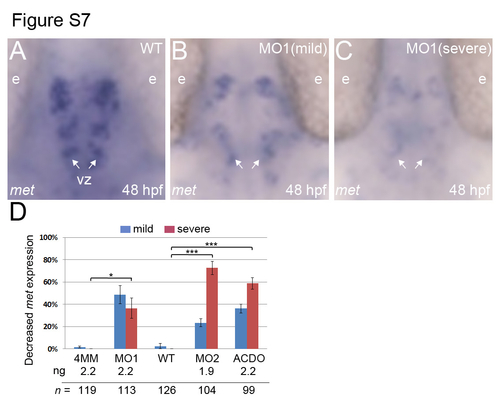
Knockdown of klf8 results in decreased met expression in the ventricular zone of embryos at 48 hpf. (A-C) Dorsal views of embryos. (A-C) Reduced met expression in the ventricular zone (arrows) is observed in 48 hpf klf8 morphants with mild (B) and severe (C) phenotypes, as compared to WT embryos (A). (D) Percentage of embryos of the indicated backgrounds with decreased met expression relative to WT embryos. Significance was determined using student?s t-test. *p<0.05, ***P<0.001. Error bars indicate standard errors. E, eye, VZ, ventricular zone. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|