- Title
-
Planar polarity pathway and Nance-Horan syndrome-like 1b have essential cell-autonomous functions in neuronal migration
- Authors
- Walsh, G.S., Grant, P.K., Morgan, J.A., and Moens, C.B.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
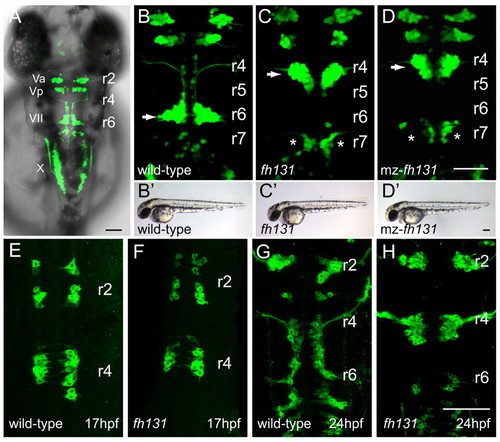
The fh131 mutant disrupts facial branchiomotor (FBM) neuron migration. Confocal images showing dorsal views of the hindbrain of Tg(isl1:GFP)rw0 transgene expression in embryos. Anterior is to the top. (A) Cranial motorneurons are easily visible in whole-mount zebrafish embryos at 48 hours post-fertilization (hpf). Va and Vp, anterior and posterior trigeminal nuclei, respectively, in hindbrain rhombomere (r)2 and r3; VII, facial branchiomotor neurons in r6 with axons exiting the hindbrain in r4; X, vagal motorneurons. (B) Wild-type embryo at 48 hpf with FBM neurons fully migrated into r6 (arrow). (C,D) Zygotic fh131 mutant (B) and maternal-zygotic (mz) fh131 mutant (C) with similarly unmigrated FBM neurons in r4 (arrows). Asterisks mark the cell bodies of the glossopharyngeal (cranial nerve IX) neurons in r7. (B2-D2) Low power transmitted light images of embryos with the genotypes shown in B-D showing otherwise normal morphology at 48 hpf. (E-H) FBM neurons in wild type (E,G) and fh131 mutants (F,H) at the onset of migration at 17 hpf (E,F) and at 24 hpf (G,H) showing that fh131 mutant FBM neurons never leave r4. Scale bars: 50 Ám. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
nhsl1b is disrupted in fh131 mutants. (A) Genetic mapping of 1444 fh131 mutant zebrafish embryos identifies a genetic interval on chromosome 20 containing nhsl1b. (B) Genomic structure of nhsl1b. Black boxes mark exons 1-8. (C) Sequence trace of a nonsense mutation in nhsl1b in fh131 mutants. (D) Phylogram of the NHS protein family. Mm, mouse; Dr, zebrafish; Hs, human; Dm, Drosophila. (E,F) Tg(isl1:GFP)rw0 expression in an embryo injected with a splice-blocking morpholino targeted to the nhsl1b exon 4-intron 4 boundary (E) or a translation-blocking morpholino targeted to the ATG of exon 1 (F). (G-I) Tg(isl1:GFP)rw0 expression in PCR-genotyped embryos heterozygous for nhsl1bfh131 (G) or for the nhs1bfh280 nonsense allele generated by TILLING (H) and in nhsl1bfh131/280 trans-heterozygotes (I). Note the strong block to FBM migration in the trans-heterozygotes indicating that fh131 and fh280 are alleles of the same gene. r4-r7, rhombomeres 4-7. Scale bar: 20 Ám. |
|
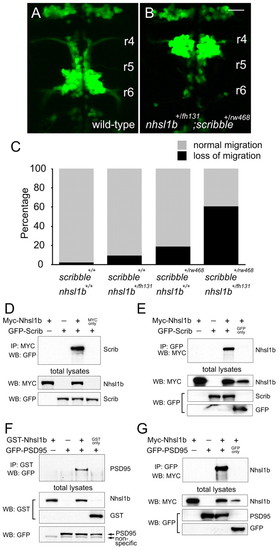
Nhsl1b interacts genetically and physically with Scrib in the regulation of facial branchiomotor (FBM) neuron migration. (A,B) Wild-type (A) and double heterozygous nhsl1bfh131/+; scribrw468/+ zebrafish embryos (B) at 48 hours post-fertilization (hpf). Double heterozygotes have unmigrated FBM neurons in rhombomere (r)4, indicative of a strong genetic interaction between the two genes. (C) Histogram of phenotypes in the genotypic classes arising from a nhsl1bfh131/+ x scribrw468/+ cross. (D-G) Nhsl1b associates with Scrib and Psd95 (Dlg4). cDNA constructs were transfected into HEK293T cells as indicated. Whole cell lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) and western-blotted (WB) with the indicated antibodies. Scale bar: 20 Ám. |
|
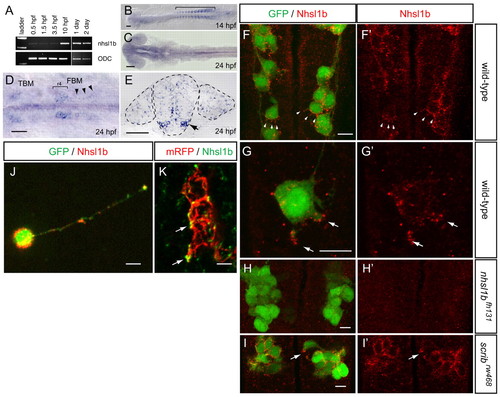
nhsl1b is expressed in facial branchiomotor (FBM) neurons and localizes to membrane protrusions. (A) RT-PCR from fertilization to 2 days old shows onset of zygotic nhsl1b expression at the end of epiboly [10 hours post-fertilization (hpf)]. ODC, ornithine decarboxylase control. (B-E) mRNA in situ hybridization with nhsl1b in whole mount (B-D) and in cross section at the level of r5 (E) showing widespread, low-level expression in somites (B) and CNS (C) and specific upregulation in cranial motorneurons (D,E). nhsl1b is expressed in FBM neurons in rhombomere (r)4 at the onset of migration (bracket in D) and in r5 and r6 during migration (arrowheads in D, arrow in E) and in trigeminal branchiomotor neurons in r2 (TBM). (F-I2) Whole-mount immunocytochemistry with anti-Nhsl1b (red). Isl1:GFP marks FBM neurons (green). Nhsl1b is localized to the membrane surface of FBM neurons, particularly to membrane protrusions (arrowheads) in wild type (F,G) but not Nhsl1b mutant embryos (H). Nhsl1b is similarly localized in FBM neurons in Scrib mutants (I). I2-J2 show Nhsl1b immunostaining alone. (J) Primary cultures of FBM neurons isolated from Tg(isl1:GFP) fish immunostained for Nhsl1b (red) and GFP (green) shows colocalization of Nhsl1b in motorneurons. (K) Anti-Nhsl1b staining in Tg(isl1CREST-hsp70l:mRFP)fh1 fish showing clear colocalization of Nhsl1b with the cell membrane (arrows). Scale bars: 50 Ám for B-E; 7 Ám for F-K. |
|
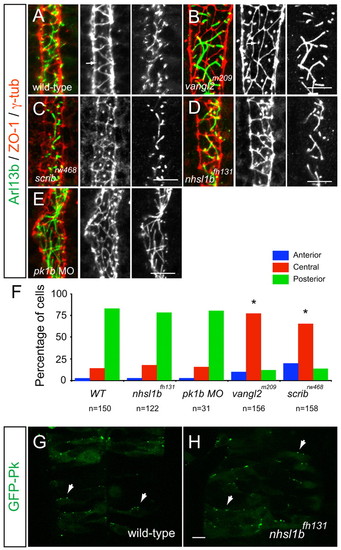
Scrib and Vangl2, but not Nhsl1b or Pk1b, are required for neuroepithelial cell polarity. (A-E) Confocal images showing floorplate planar polarity in 33 hours post-fertilization (hpf) zebrafish embryos. Anterior is to the top. ZO-1 marks subapical tight junctions (red), γ-tubulin marks basal bodies (red, indicated by arrows in A,B) and Arl13b marks the axonemes of primary cilia (green). Whereas basal bodies are localized to the posterior side of floorplate cells in wild type (A), nhsl1bfh131 mutants (D) and pk1b morphants (E) they are centrally located in zygotic vangl2m209 mutants (B) which have a widened floorplate due to defective neural tube convergence and in zygotic scribrw468 mutants (C), which have only a mild neural tube convergence defect. (F) Quantification of the percentage of cells displaying an anterior, central or posterior position of basal bodies in floorplate cells. Asterisk indicates statistically significant difference from wild type (WT) as determined by χ2 test, P<0.0001. (G,H) Live confocal imaging (dorsal view, anterior to the top) of mosaically expressed GFP-Pk marking anterior membranes (arrows) of neuroepithelial progenitors in 16 hpf wild-type (A) and nhsl1bfh131 mutant (B) embryos. Scale bars: 10 Ám. |
|
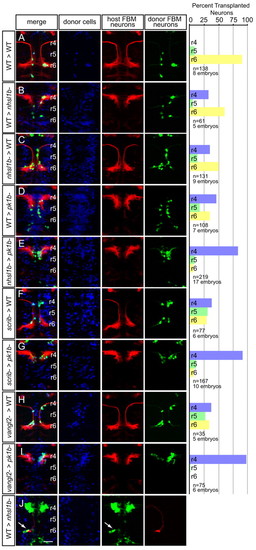
A cell-autonomous role for Nhsl1b, Scrib and Vangl2 in migration. (A-J) Live confocal images at 48 hours post-fertilization (hpf) of chimeric zebrafish embryos with anterior to the top. Cascade blue marks donor-derived cells (blue), Tg(isl1CREST-hsp70l:mRFP)fh1 marks host motorneurons (red) and Tg(isl1:GFP) marks donor-derived motorneurons (green). Histograms on the right indicate the percent of donor-derived FBM neurons in rhombomere (r)4 (unmigrated), r5 and r6 (fully migrated) under the transplantation conditions indicated on the far left, which are written as Donor>Host. n refers to the total number of FBM neurons scored in each condition. Pk1b MOs were used in D, E, G and I to prevent host FBM neurons from migrating by a cell-autonomous mechanism. J shows the rescue of host nhsl1b mutant FBM neurons expressing Tg(isl1:GFP) (green) (arrow) by wild-type donor FBM neurons expressing Tg(isl1CREST-hsp70l:mRFP)fh1 (red). Scale bar: 50 Ám. |
|
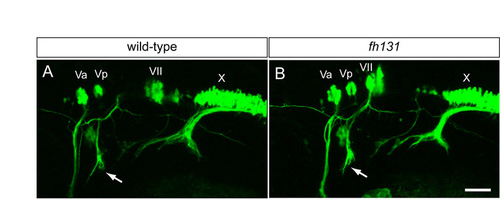
Cranial nerve architecture in nhsl1b mutants. Live confocal images of isl1:GFP transgene expression in lateral view in wild-type (A) and nhsl1bfh131 mutant (B) embryos at 48 hours post-fertilization (hpf). Va and Vp, anterior and posterior nuclei, respectively, of the fifth cranial nerve (trigeminal); VII, nucleus of the seventh cranial nerve (facial), which is migrated into r6 in wild-type and is unmigrated in mutant embryos; X, nucleus of the tenth cranial nerve (vagus). Arrows indicate the projection of the facial nerve into the second pharyngeal arch, which is unaffected in nhsl1bfh131 mutants in spite of the failure of the FBM neurons to migrate out of r4. Scale bar: 50 Ám. |
|
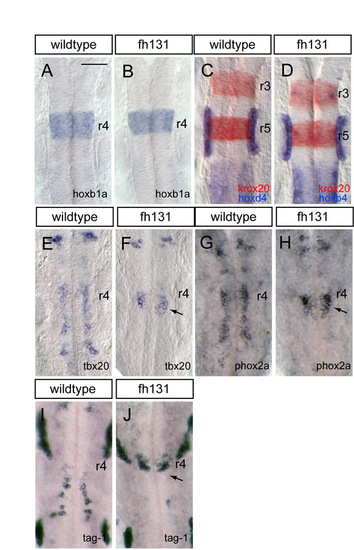
Segmental patterning and facial branchiomotor (FBM) neuron differentiation is normal in nhsl1b mutants. (A-D) RNA in situ hybridization with hindbrain markers for rhombomere (r)4 (hoxb1a, blue in A,B); r3 and r5 (krox20; red in C,D); r7 and posterior hindbrain (hoxd4; blue in C,D); and otic vesicles (pax2b, blue in C,D). All of these genes are expressed normally in nhsl1bfh131 mutants (B,D). (E-J) RNA in situ hybridization with motor neuron genes that are required to specify the migratory phenotype: tbx20 (E,F), phox2a (G,H) and tag-1 (I,J). Although FBM neurons fail to migrate caudally in nhsl1bfh131 mutants, they nevertheless express these genes, indicating that their failure to migrate is not due to failure to activate a migratory transcriptional program. Scale bar: 50 Ám. |
|
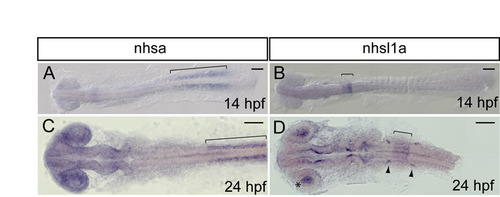
Expression of nhsl1b homologs nhsa and nhsl1a. (A-D) RNA in situ hybridization of wild-type embryos at the stages shown. nhsa expression overlaps with nhsl1b in somites (bracket in A,C) and at low levels throughout the CNS, but is not upregulated in facial branchiomotor (FBM) neurons. nhsl1a is also expressed at low levels throughout the CNS and is upregulated in rhombomeres (r)5 and r6 (bracket in B,D), in the lens of the eye (asterisk in D) and in cranial ganglia (arrowheads in D), but is not expressed in FBM neurons. hpf, hours post-fertilization. Scale bar: 100 Ám. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
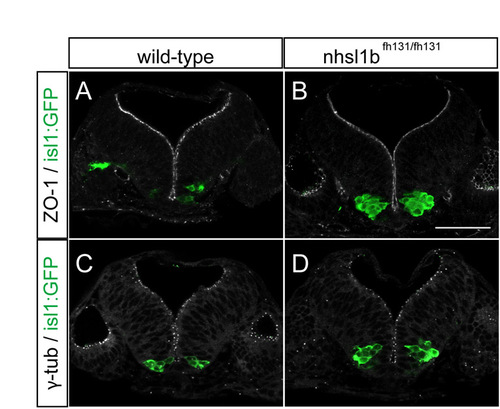
Nhsl1b is not required for neuroepithelial apico-basal polarity. (A-D) Confocal images of cross sections at the level of rhombomere (r)4 showing normal apico-basal polarity in the neuroepithelium of 24 hours post-fertilization (hpf) wild-type (A,C) and nhsl1bfh131 mutant (B,D) embryos. ZO-1 marks sub-apical tight junctions of progenitors (A,B) and γ-tubulin marks apical centrosomes (C,D). isl1:GFP marks FBM neurons which accumulate in r4 in nhsl1bfh131 mutants (B,D). Scale bar: 50 Ám. |
|
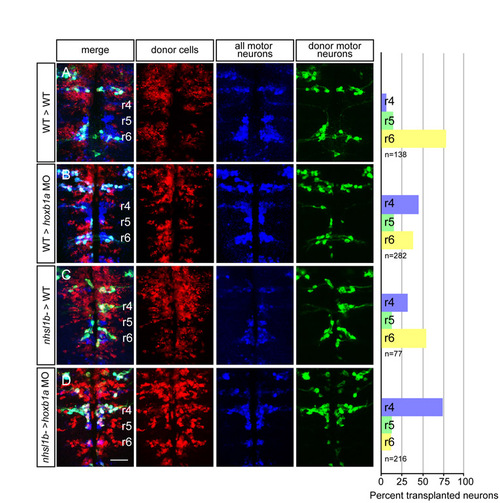
nhsl1bfh131 mutant facial branchiomotor (FBM) neurons require wild-type FBM neurons for migration. (A-D) Confocal images of fixed mosaic embryos at 48 hours post-fertilization (hpf) with anterior to the top. Lysinated rhodamine dextran marks donor-derived cells (red); anti-Isl1 antibody marks all cranial motor neurons (donor and host-derived, blue); and Tg(isl1:GFP) marks donor-derived motor neurons (green). Histograms on the right indicate the percent of donor-derived FBM neurons in rhombomere (r)4 (unmigrated), r5 and r6 (fully migrated) under the transplantation conditions indicated on the far left, which are written as Donor>Host. n refers to the total number of FBM neurons scored in each condition. hoxb1a morpholinos were used in B and D to prevent host FBM neurons from migrating by a cell-autonomous mechanism. Scale bar: 50 Ám. |
|
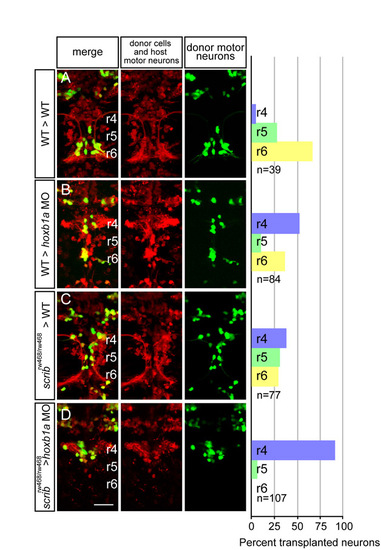
scribrw468 mutant facial branchiomotor (FBM) neurons require wild-type FBM neurons for migration. (A-D) Live confocal images of mosaic embryos at 48 hours post-fertilization (hpf) with anterior to the top. Lysinated rhodamine dextran marks donor-derived cells (red); Tg(isl1:membRFP) marks host FBM neurons (also red) and Tg(isl1:GFP) marks donor-derived motor neurons (green). Histograms on the right indicate the percent of donor-derived FBM neurons in rhombomere (r)4 (unmigrated), r5 and r6 (fully migrated) under the transplantation conditions indicated on the far left, which are written as Donor>Host. n refers to the total number of FBM neurons scored in each condition. hoxb1a morpholinos were used in B and D to prevent host FBM neurons from migrating by a cell-autonomous mechanism. Scale bar: 50 Ám. |