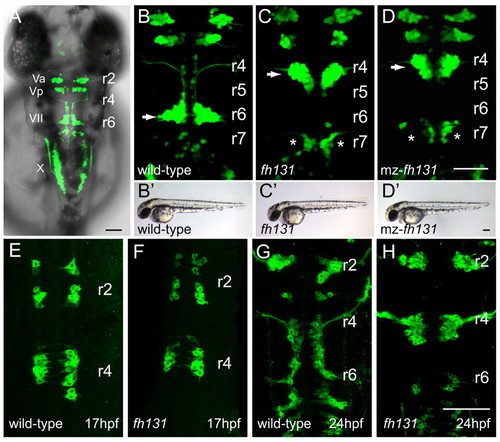
The fh131 mutant disrupts facial branchiomotor (FBM) neuron migration. Confocal images showing dorsal views of the hindbrain of Tg(isl1:GFP)rw0 transgene expression in embryos. Anterior is to the top. (A) Cranial motorneurons are easily visible in whole-mount zebrafish embryos at 48 hours post-fertilization (hpf). Va and Vp, anterior and posterior trigeminal nuclei, respectively, in hindbrain rhombomere (r)2 and r3; VII, facial branchiomotor neurons in r6 with axons exiting the hindbrain in r4; X, vagal motorneurons. (B) Wild-type embryo at 48 hpf with FBM neurons fully migrated into r6 (arrow). (C,D) Zygotic fh131 mutant (B) and maternal-zygotic (mz) fh131 mutant (C) with similarly unmigrated FBM neurons in r4 (arrows). Asterisks mark the cell bodies of the glossopharyngeal (cranial nerve IX) neurons in r7. (B2-D2) Low power transmitted light images of embryos with the genotypes shown in B-D showing otherwise normal morphology at 48 hpf. (E-H) FBM neurons in wild type (E,G) and fh131 mutants (F,H) at the onset of migration at 17 hpf (E,F) and at 24 hpf (G,H) showing that fh131 mutant FBM neurons never leave r4. Scale bars: 50 Ám.
|

