- Title
-
Collective Cell Migration Drives Morphogenesis of the Kidney Nephron
- Authors
- Vasilyev, A., Liu, Y., Mudumana, S., Mangos, S., Lam, P.Y., Majumdar, A., Zhao, J., Poon, K.L., Kondrychyn, I., Korzh, V., and Drummond, I.A.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS Biol.
|
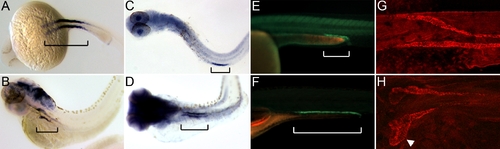
Proximal Displacement of Nephron Segment Boundaries and Convolution of the Proximal Nephron (A and B) nbc1 in situ hybridization at 24 hpf (A) and at 72 hpf (B). (C and D) trpM7 in situ staining at 24 hpf (C, yolk is stripped) and at 72 hpf (D). (E and F) ret:GFP-positive domain in live zebrafish at 30 hpf (E) and at 6 dpf (F). In (A?F), brackets show the pronephric nbc1-, trpM7-, and ret-positive segments. (G and H) Immunofluorescence staining for alpha1A4 subunit of the NaK ATPase at 24 hpf (G) and at 72 hpf (H). |
|
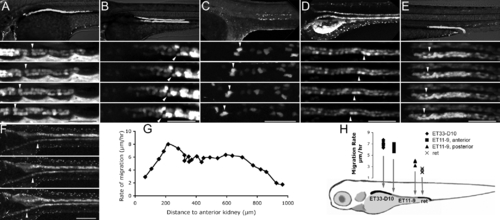
Pronephric Epithelial Cells Migrate toward the Glomerulus Individual frames of confocal fluorescent time-lapse videos at 2.5-h intervals are presented for five different kidney GFP transgenics. White arrowheads in (A?F) mark individual cells at different time points in migration. (A) ET33-D10 GFP transgenic (proximal segment).(B) ET11?9 GFP transgenic (mid segment). (C) CD41:GFP transgenic, multiciliated cells, mid kidney. (D) NaK ATPase:GFP transgenic, all transporting epithelia. (E) ret1:GFP transgenic, distal collecting segment. (F) NaK ATPase:GFP transgenic. Small arrows mark the convolutions forming in the proximal tubules. (G) The rate of migration in (F) is plotted as a function of the distance from proximal-most kidney. (H) Rates of migration determined for various segments of the kidney. The upper panels in (A), (B), (D), and (E) show live GFP transgenics. The upper panel in (C) shows immunofluorescent image using anti-GFP tagged antibody. The scale bar lengths are as follows: (A), (B), (D), (E): 80 μm, (C): 60 μm, (F): 200 μm. Inter-frame time interval is 2.5 h in (A?E) and 10 h in (F). The rate of migration is measured between 2 and 2.5 dpf in (G) and between 2.5 and 3 dpf in (H). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
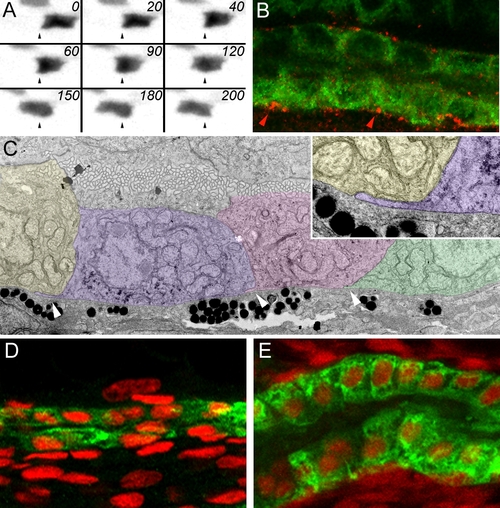
Pronephric Epithelial Cell Migration (A) Time-lapse images of an individual pronephric multiciliated cell in a 2.5 dpf CD41:GFP transgenic fish at 20-min intervals. Dynamic transient cytoplasmic projections are seen from the basal cell surface, most visible in frames 0 min, 60 min, and 120 min. (B) Double immunofluorescence staining of the pronephros in 3-dpf fish with anti-phospho-FAK antibody (red) and anti-alpha6 NaK ATPase (green). Phospho-FAK staining is positive at the epithelial cell interfaces along the basement membrane. (C) Transmission electron microscope images show that migrating epithelial cells send cryptic lamellipodia along the basement membrane in the direction of migration (arrowheads). Here three migrating cells are false colored to distinguish individual cells. Inset shows a single basal cytoplasmic projection. (D and E) The change in epithelial morphology of the proximal kidney (ET33-D10 GFP segment) between 36 hpf (D) and 96 hpf (E). At 36 hpf, the proximal epithelial cells are low cuboidal and the tubular diameter is small. At 96 hpf, the proximal tubule has much larger diameter and the epithelial cells become columnar. The ET33-D10 transgenic embryos were stained with anti-GFP antibody (green Alexa 488 secondary) and DAPI (red pseudocolor). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
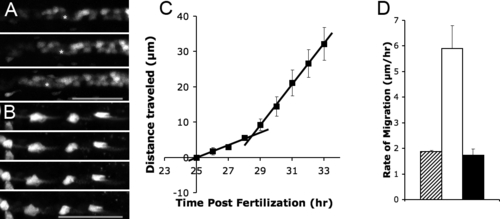
Timing of Pronephric Cell Migration (A) NaK ATPase:GFP transgenic showing initiation of cell migration after 29 hpf. Frame interval: 4.5 hr, scale bar: 70 μm. (B) Time-lapse of the CD41:GFP transgenic 5-dpf embryo showing cessation of migration. Frame interval: 2.5 hr, scale bar: 60μm. (C) A sharp increase in the distance traveled occurs at 28.5 hpf. The two regression lines intersect at 28.5 hpf. Each point represents distance traveled by epithelial cells between 25 hpf and a given time point. The data plotted represent averages from three different embryos (D) Comparative rates of epithelial migration before 28.5 hpf (striped bar), after 28.5hpf (white bar), and after 5 dpf (black bar). |
|
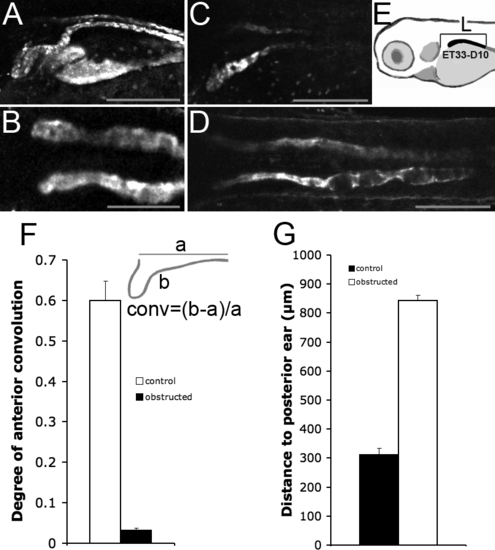
Pronephric Obstruction Prevents Convolution and Proximal Progression of the Proximal Tubule Segment (A) The proximal tubule in NaK ATPase:GFP transgenic larvae is folded into a hairpin structure at 4 dpf. This anterior convolution is abolished in kidneys obstructed at 24 hpf (B). (C and D) The ET33-D10 GFP positive nephron segment (C) fails to progress anteriorly in 84hpf obstructed kidneys (D). (E) method of measurement. (F) Convolution was defined as the ratio of the length of the anterior portion of the pronephros in NaK ATPase:GFP transgenics minus the length of a straight line connecting the ends of this segment divided by the length of this straight line. The anterior segment was arbitrarily defined as that anterior to yolk extension (conv = (b ? a)/a, as shown in the inset). The white bar is the control condition (n = 10). The black bar indicates the obstructed kidney (n = 19). Obstruction was induced at 24 hpf, measurements were performed at 96 hpf. (G) Measurement of the proximal segment progression. The black bar indicates the control nephrons (n = 13). The white bar indicates obstructed nephrons (n = 17). Obstruction was induced at 24 hpf. The measurement was performed at 84 hpf. |
|
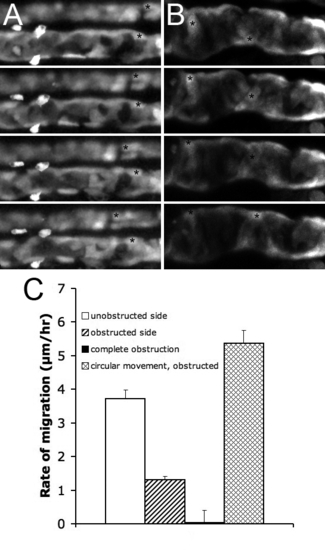
Pronephric Obstruction Blocks Proximal Cell Migration (A) Unilateral obstruction, NaK ATPase:GFP, the obstructed side is shown below the control side. (B) Complete obstruction, ET11?9 GFP transgenic. The epithelial cells move circumferentially. Frame intervals in (A, B) are 2.5 h, scale bar: 70 μm. (C) Rates of migration in various conditions, from left to right: unilateral obstruction, unobstructed side (white bar); unilateral obstruction, obstructed side (striped bar); complete obstruction, rate of anterior migration (black bar); complete obstruction, rate of circumferential movement (mesh bar). Each bar represents average over a number of cells within a single experiment. |
|
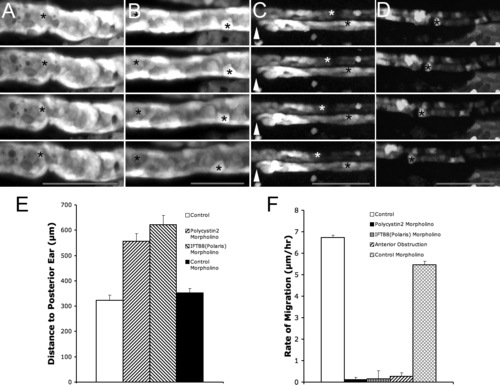
Decreasing Pronephric Fluid Flow Suppresses Anterior Migration (A?D) Time-lapse frames of ET33-D10 GFP transgenics, 2.5 dpf. Time interval between frames is 2.5 h, scale bar: 80 μm (in bottom frame). (A) polycystin2 morphant embryo; asterisk marks stationary cell in the pronephros. (B) ift88 (polaris) morphant embryo; asterisks mark stationary cells in the pronephros. (C) Anterior (proximal) obstruction; arrowhead marks position of unilateral anterior obstruction; white asterisk marks a migrating cell in the unobstructed nephron; black asterisk marks stationary cell in the obstructed nephron. (D) Control morpholino injected embryo showing normal rate of proximal cell migration (asterisk marks a migrating cell). (E) Measurement of proximal nephron segment shortening in ET33-D10 GFP transgenics (shorter lengths indicate further proximal progression as described in Figure 5E). From left to right: Control uninjected embryos (n = 36); polycystin2 morphant embryos (n = 20); ift88 (polaris) morphant embryos (n = 10); Control morpholino injected embryos (n = 17) (F) Rates of proximal cell migration, from left to right: Control; polycystin2 morphant embryo; ift88 (polaris) morphant embryo; anterior obstruction; Control morpholino. |
|
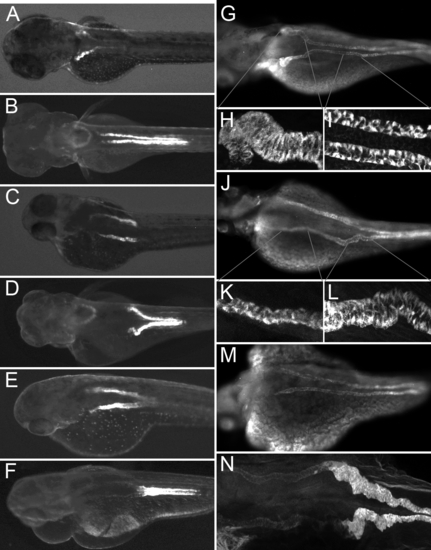
Eliminating Glomerular Filtration Results in Ectopic Tubule Convolution All embryos were imaged at 84 hpf. (A and B) Control condition, ET33-D10 transgenics (A) and ET11?9 transgenics (B). (C and D) Cardiac tnnt2 morpholino injected embryos, ET33-D10 transgenic (C) and ET11?9 transgenic (D). (E and F) Cardiac tnnt2 and ift88 (polaris) morpholino injected embryos, ET33d10 transgenic (E) and ET11?9 transgenic (F). (G?M) Anti-alpha6F NaK ATPase stained embryos. (G) Control embryo. (H and I) Close-ups of the proximal and mid segments. (J) Cardiac tnnt2 morpholino injected embryo. (K and L) Close-ups of the proximal and the mid segments. (M) Cardiac tnnt2 and ift88(polaris) morpholino-injected embryo. (N) ET11?9 GFP transgenic embryo injected with cardiac tnnt2 morpholino, stained with anti-alpha6 NaK ATPase (faint), and anti-GFP (bright). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
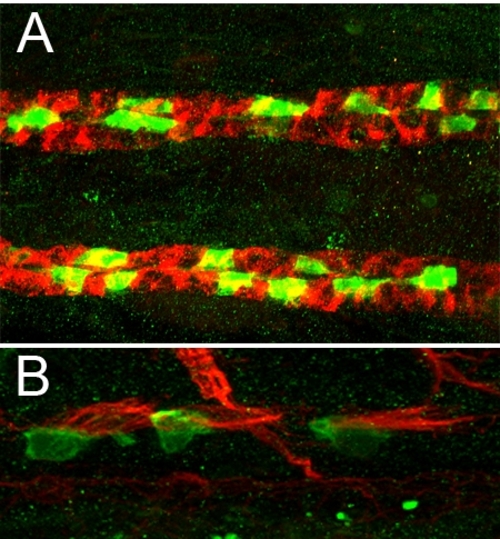
CD41:GFP Transgenics Express GFP in Multiciliated Cells of the Pronephros (A) 2-dpf CD41:GFP transgenic stained with anti-alpha6 NaK ATPase (red) and anti-GFP (green). (B) 7-dpf CD41:GFP transgenics stained with anti-acetylated tubulin (cilia, red) and anti-GFP (green). |
|
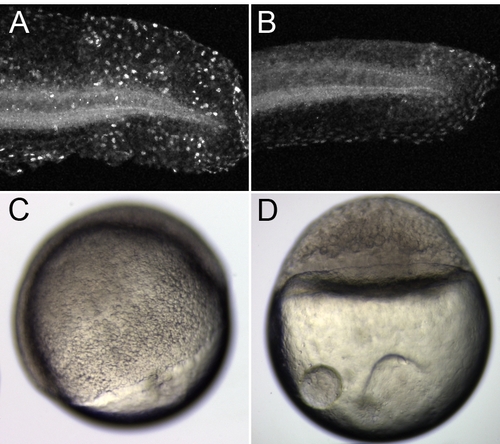
Camptothecin Treatment Blocks Embryo Development and Cell Proliferation (A and B)The difference in BrdU incorporation in the tail region between a 1% DMSO control embryo (A) and an embryo incubated in 60 μM camptothecin (B). (C and D) Camptothecin blocks early embryo development. 1% DMSO and 30 μM camptothecin were applied to dechorionated embryos at 3 hpf. The embryos were fixed at 7 hpf. While the control embryos progressed normally to about 60% epiboly, the camptothecin-treated embryos were completely arrested at the blastula stage. |
|
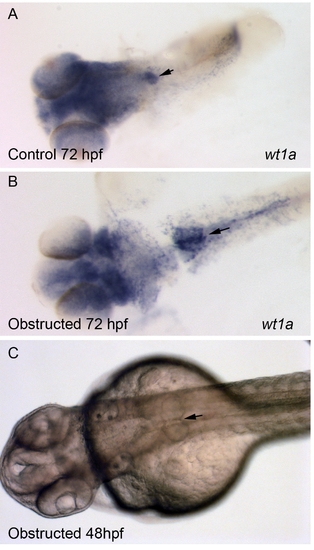
Blockade of Fluid Flow Does Not Prevent Glomerular Fusion In situ hybridization with wt1a probe was used to localize podocytes in control 72-hpf (A) and obstructed 72-hpf (B) embryos (obstruction in (B) was initiated at 24 hpf). Arrows mark the area of midline fusion of podocytes in both (A) and (B). (C) Light microscopic view of fused, cystic glomeruli in a 48-hpf obstructed embryo (obstruction was initiated at 24 hpf). |
|
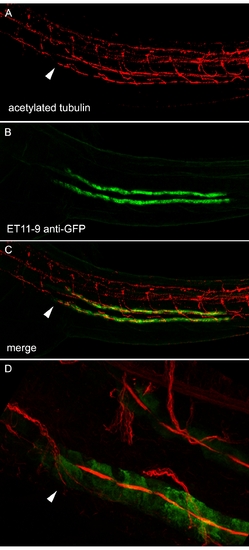
The ET11?9?Positive Segment Marks the Proximal-Most Extent of Multiciliated Cells Two-dpf ET11?9 embryos were stained with anti-acetylated tubulin (A; red) and anti-GFP (B; green). (C) Merge of (A) and (B). (D) Close-up of the anterior (proximal) end of the ET11?9 GFP-positive domain showing compressed, acetylated tubulin-positive bundles of cilia in the lumen of GFP-positive tubule cells. Dorsal acetylated tubulin-positive cells are neurons. Arrows mark the most proximal bundles of cilia originating from pronephric multiciliated cells [23]. |