- Title
-
her5 expression reveals a pool of neural stem cells in the adult zebrafish midbrain
- Authors
- Chapouton, P., Adolf, B., Leucht, C., Tannhauser, B., Ryu, S., Driever, W., Bally-Cuif, L.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
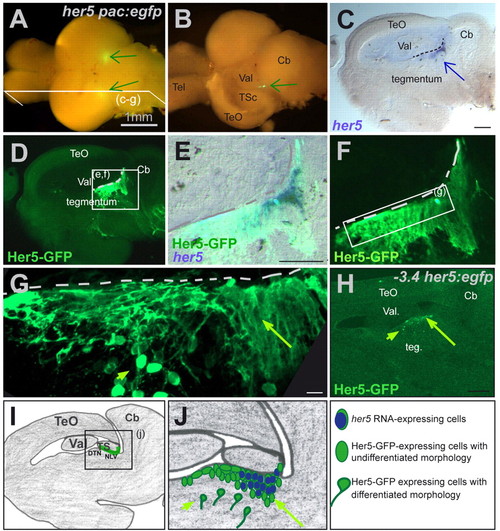
her5 expression defines an MHB cluster in the adult brain. (A) Whole brain from a 4-month-old her5pac:egfp transgenic fish viewed from the top. Two spots of GFP expression (green arrows) are visible between the hindbrain and the midbrain hemispheres. (B) Same brain following unilateral removal of the tectum. On the dissected side, the cluster of GFP-positive cells (arrow) is visible between the valvula cerebelli and torus semicircularis. (C-F) Sagittal section of a 2.5-month-old her5pac:egfp fish depicting the expression of endogenous her5 RNA (blue staining) in a group of cells included within the cluster of Her5-GFP-expressing cells (green staining). (C) Brightfield view: her5 is expressed in a cluster of cells lining the ventricle (dotted line) between tegmentum, torus semicircularis and valvula cerebelli (arrow), like Her5-GFP (D,F, fluorescence view). (E) her5-expressing cells are indeed located within the Her5-GFP-positive domain (concomitant bright and fluorescence fields). Note also, in E, that GFP-positive cells are located ventrally outside the her5-positive zone. (G) High magnification of the Her5-GFP-positive area (dotted line to the ventricle), highlighting the neuroepithelial morphology of ventricular her5 RNA- and Her5-GFP-positive cells (long arrow), contrasting with the differentiated morphology of their more ventrally located her5-negative, Her5-GFP-positive descendants (short arrow). (H) Her5-GFP expression in a sagittal section of a 2.5-month-old -3,4her5:egfp transgenic brain. Her5-GFP expression highlights the same territory as in her5pac:egfp transgenics. In particular, positive cells of neuroepithelial morphology lie at the ventricle (long arrow), while cells of differentiated morphology are found deeper within the tegmentum (short arrow). (I,J) Schematic representation of a sagittal section at the same medio-lateral position as the sections shown in C-H. The green line in I depicts the her5-expressing area, and her5- or Her5-GFP-positive cells are colour-coded in J (long arrow to the her5- and Her5-GFP-positive domain, short arrow to the her5-negative, Her5-GFP-positive domain, as in G,H). Scale bars: 1 mm in A,B; 100 μm in C,D,H; 10 μm in G. Cb, cerebellum; DTN, dorsal thalamic nucleus; NLV, nucleus lateralis valvulae; Teg, tegmentum; Tel, telencephalon; TeO, optic tectum; TSc, torus semi-circularis; Val, valvula cerebelli lateralis. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
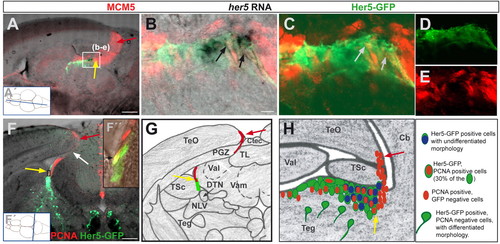
her5-positive cells proliferate and demarcate a new proliferation zone within the adult midbrain. (A-E) Saggital section through a 3-month-old her5:gfp transgenic brain (at the medio-lateral level indicated in A', anterior left), displaying the tectal proliferation zone (red arrow) and the IPZ (yellow arrow) labelled by the cell cycle marker MCM5 (red). her5 RNA-expressing cells (black) and Her5-GFP cells (green) are located in the IPZ. B-E show a higher magnification (single confocal plane) of the section in A showing the expression of the proliferation marker MCM5 (red) in her5-RNA- and Her5-GFP-expressing cells, as pointed by the arrows (B: overlay of bright field and fluorescence views, C: overlay of green and red fluorescence channels; single channels are shown in D and E, respectively). (F) Cross-section through a 3-month-old her5:egfp transgenic brain, at the rostro-caudal level indicated in F′, displaying Her5-GFP (green) and proliferating cells stained by PCNA (red). Yellow arrow to the IPZ, red arrow to the tectal proliferation zone, the location of the connecting ribbon of proliferating cells is indicated by the white arrow. (F″) confocal plane of the area boxed in F showing two Her5-GFP cells that are PCNA-positive (black arrow). (G) Schematic representation of the cross-section shown in F (same colour code for arrows and stainings). (H) Same schematic representation of the IPZ area as in Fig. 1J (sagittal view) depicting the location of PCNA-(or MCM5)-positive cells (red) within the Her5-GFP population. Scale bars: 100 μm in A,F; 10 μm in B. Cb, cerebellum; Ctec, tectal commissure; DTN, dorsal thalamic nucleus; NLV, nucleus lateralis valvulae; PGZ, periventricular grey zone; Teg, tegmentum; TL, torus longitudinalis; TeO, optic tectum; TPZ, tectal proliferation zone; TSc, torus semi-circularis; Val, valvula cerebelli lateralis; Vam, valvula cerebelli medialis. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
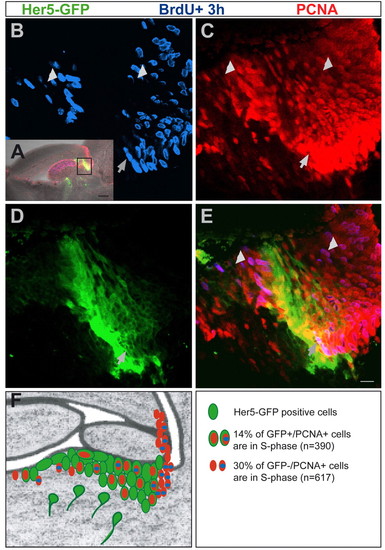
Her5-GFP-positive cells are slow proliferating. Sagittal section (anterior left) through a 3-month-old her5pac:egfp transgenic brain 4 hours after BrdU incorporation. BrdU, PCNA and Her5-GFP are co-detected by immunocytochemistry (BrdU, blue; PCNA, red; Her5-GFP, green). (A) Overview of the midbrain-hindbrain area (anterior left), showing the area analysed in B-E (boxed). (B-E) Close up on the IPZ, single confocal plane. Her5-GFP-positive cells express PCNA (compare C with D) but few are BrdU-positive. One of these triple-labelled cells is shown by the arrow. This indicates the long cell cycle of Her5-GFP-positive cells. By contrast, a high proportion of the neighbouring Her5-GFP-negative, PCNA-positive population incorporated BrdU (short arrows point to such cells), indicating their short cell cycle. (F) Summary drawing of the IPZ area (as in Fig. 1J, Fig. 2H), depicting BrdU labelling (blue) within the Her5-GFP ventricular population and within the neighbouring PCNA-positive, Her5-GFP-negative population. The slow-proliferating Her5-GFP-positive population is juxtaposed along the AP to fast-proliferating domains, which are Her5-GFP-negative. The labelling indexes of her5-positive versus her5-negative domains are indicated on the bottom right. Scale bars: 100 μm in A; 10 μm in B-E. |
|
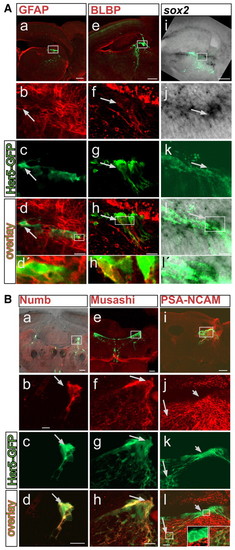
Her5-GFP-positive cells lining the tectal ventricle express stem cell markers. (A) Co-localization of Her5-GFP (green) with GFAP (a-d'), BLBP (e-h'), sox2 (i-l'). (B) Co-localization of Her5-GFP (green) with Numb (a-d), Musashi (e-h) and PSA-NCAM (i-l). Sagittal (GFAP, BLBP, sox2, PSA-NCAM) or cross-sections (Numb and Musashi) are shown. sox2 is detected by in situ hybridization (black signal), while all other markers are detected by immunohistochemistry (red signal). (A, parts i-l'; B, part a) An overlay with the brightfield view in addition to fluorescence. All long arrows point to cells that co-express Her5-GFP and the respective markers. (B, parts j-l) Her5-GFP-positive cells located close to the ventricle, which also express her5 RNA (Fig. 1C,E), are PSA-NCAM-negative (short arrow, left inset) while Her5-GFP-positive cells located further ventrally do express PSA-NCAM (long arrow, right inset), indicating their differentiation into a neuronal fate. Scale bars: 100 μm in a,e,i; 10 μm in b-d,f-h,j-l. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
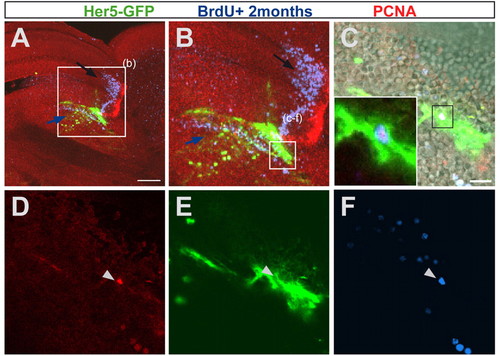
her5-positive cells are self-renewing. A 3-month-old her5:gfp transgenic brain was injected cumulatively over 9 days with BrdU and sacrificed 2 months later. The sagittal section is seen as an overview in A, and magnified in B-F, as single confocal planes. (C-F) Enlargement on an Her5-GFP cell (green, pointed by an arrowhead) that has incorporated BrdU 2 months earlier (blue) and is PCNA-positive (red), indicating that it has remained in a proliferative state after division, i.e. it is a self-renewing progenitor. Note that most cells of the IPZ that have incorporated BrdU 2 months earlier move towards ventral positions into the tegmentum (see in B the location of blue cells below the Her5-GFP domain, blue arrow), while cells originating from the tectal proliferation zone are displaced towards anterior into the optic tectum (B, black arrow). Scale bars: 100 μm in A; 10 μm in C. |
|
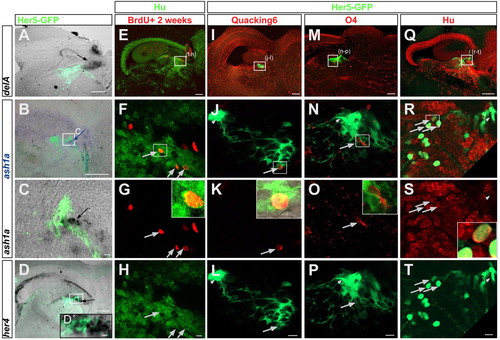
Her5-positive cells differentiate into neurons and oligodendroglia in vivo. (A-D) Expression of proneural genes within or near the IPZ, indicating an ongoing neurogenesis in that area. deltaA (A), ash1a (B,C) and her4 (D,D') are detected by in situ hybridization on sagittal sections of her5:gfp brains (anterior left) and visible as a black or blue (in B) signal (indicated by the arrows). All panels are an overlay of brightfield and fluorescence exposures, also revealing Her5-GFP protein in green. Note some overlap between Her5-GFP and ash1a (C) or her4 (D'). (E-H) Generation of neurons (Hu-positive cells in green) 2 weeks after BrdU injection (red) next to the IPZ, in a 6-month-old non-transgenic brain. Confocal planes of a sagittal section (anterior left) seen as an overview in E, and magnified in F-H. The arrows point to BrdU/Hu double-positive cells. The inset in G depicts an enlarged double-labelled cell boxed in F. (I-P) Differentiation of Her5-GFP-positive cells (green) into oligodendrocytes. Confocal planes of a sagittal section (anterior left) as an overview in I and M, and magnified in the panels below. Some Her5-GFP-positive cells pointed to by the long arrows co-express QKI-6 (J-L, enlarged in the inset in K) or O4 (N-P, inset in O). Small arrows in J,L,N,P point to the ventricular Her5-GFP-positive cells, which are negative for QKI-6 or O4. (Q-T) Differentiation of Her5-GFP-positive cells into neurons. Confocal planes of a sagittal section (anterior left) seen as an overview in Q, and magnified in R-T. All Her5-GFP-positive cells located away from the ventricular surface express the neuronal marker Hu (long arrows in R-T to some of them, enlargement of one double-labelled cell in the inset in S). The small arrows in R-T point to the ventricular Her5-GFP-positive population, which is Hu-negative. Scale bars: 100 μm in A,B,D and in the upper row; 10 μm in C,F-H,J-L,N-P,R-T. |
|
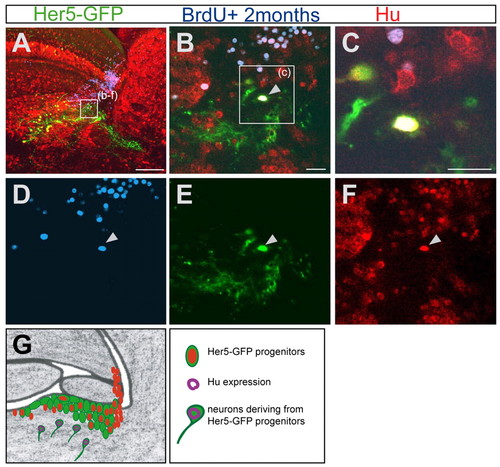
Her5-GFP-positive newborn tegmental neurons originate from cells proliferating at adulthood. (A-F) Sagittal section (anterior is to the left) of a 5-month-old brain stained for Her5-GFP (green), Hu (red) and BrdU (blue), 2 months after a cumulative BrdU labelling. (A) Overview of the tegmental region containing differentiated Her5-GFP-positive cells. (B-F) Higher magnifications of the same section. The arrow in B points to a cell in the tegmentum triply labelled for Hu, BrdU and GFP, indicating that this neuron is deriving from a Her5-expressing cell and was generated 2 months earlier. The single channels of this confocal plane are depicted in D-F. (C) Higher magnification of the same triple-labelled cell. (G) Summary scheme of the IPZ area (as in Fig. 1J, Fig. 2H, Fig. 3F), depicting the tegmental neurons (Hu staining, purple) generated by Her5-expressing progenitor cells. Scale bars: 100 μm in A; 10 μm in B,C. |

Unillustrated author statements |