Fig. 4
|
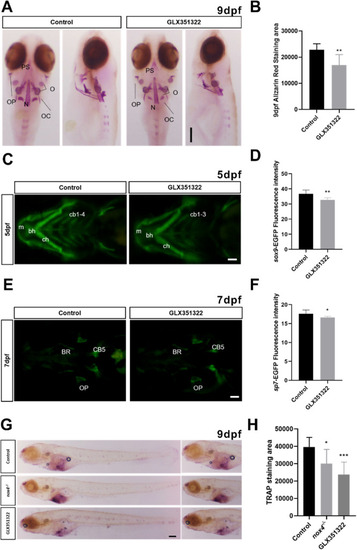
Fig. 4. Treatment with Nox4 inhibitor GLX351322 reduces bone mineralization in early development. (A) WT zebrafish were treated with GLX351322 at 8 hpf. Tissue was collected at 9 days postfertilization (dpf) and stained with alizarin red. Dorsal and lateral views of larvae are shown. (B) Quantification of alizarin red staining. (C) Tg(sox9-EGFP) zebrafish were treated with GLX351322 at 8 hpf and fluorescence intensity was assessed at 5 dpf. (D) Quantification of green fluorescence in chondrocytes. (E) Tg(sp7-EGFP) zebrafish were treated with GLX351322 at 8 hpf and fluorescence intensity was observed at 7 dpf. (F) Quantification of green fluorescence in osteoblasts. (G) WT zebrafish were treated with GLX351322 at 8 hpf. Samples were collected at 9 dpf for TRAP staining. (H) Quantification of TRAP-stained area. m: Meckel's cartilage; bh: basihyoid bone; cb: ceratobranchial bone; ch: ceratohyal bone; PS: parasphenoid bone; OC: occipital bone; N: notochord; BR: branchial ray; OP: operculum; O: otolith. The scale bars in panels A, C, E, and G indicate 200 ?m n = 10. The results were analyzed using one-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.) |
Reprinted from Free radical biology & medicine, 193(Pt 2), Cao, Z., Liu, G., Zhang, H., Wang, M., Xu, Y., Nox4 promotes osteoblast differentiation through TGF-beta signal pathway, 595-609, Copyright (2022) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Free Radic. Biol. Med.