Fig. 1
|
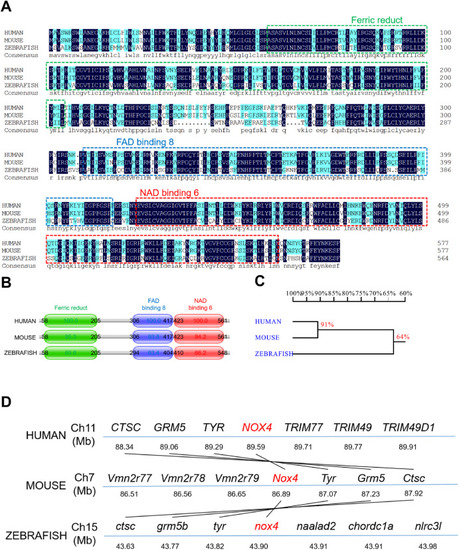
Fig. 1. Zebrafish nox4 is highly conserved. (A) Alignment of the NOX4 amino acid sequences in human, mice, and zebrafish. The same amino acids are highlighted in dark blue. Ferric reductase-like transmembrane components (Ferric Reduct), FAD-binding domains (FAD-binding 8), and NAD-binding domains (NAD-binding 6) are marked with green, blue, and red boxes, respectively. (B) NOX4 protein sequence and position in human, mice, and zebrafish. (C) Homology analysis of nox4 in humans, mice, and zebrafish. The values represent the degree of genetic similarity between different species. (D) Conservative synteny analysis of nox4 in humans, mice, and zebrafish. The number next to the gene name represents the megabase pair (MBP) of the gene position on the chromosome. Chromosomes are represented by blue lines. Homologous fragments are connected by black lines. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.) |
Reprinted from Free radical biology & medicine, 193(Pt 2), Cao, Z., Liu, G., Zhang, H., Wang, M., Xu, Y., Nox4 promotes osteoblast differentiation through TGF-beta signal pathway, 595-609, Copyright (2022) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Free Radic. Biol. Med.