Fig. S5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-170828-2
- Publication
- Wehner et al., 2017 - Wnt signaling controls pro-regenerative Collagen XII in functional spinal cord regeneration in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
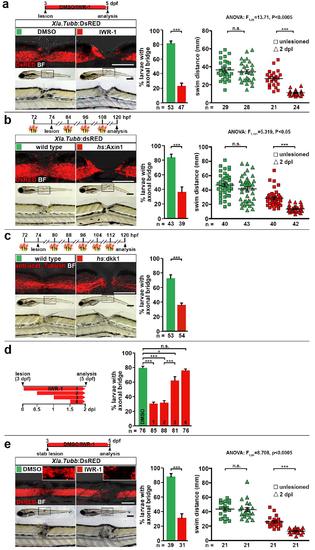
Different lesion and manipulation paradigms support that Wnt/?-catenin signaling is required for axon regeneration and functional recovery after spinal cord lesion. (a) Pharmacological interference (IWR-1) with Wnt/?-catenin signaling inhibits axon regeneration (Fischer?s exact test: ***P<0.001) and functional recovery (two-way ANOVA: F1,98=13.71, P<0.0005; t-test: ***P<0.001) in lesioned animals. (b) Heat shock-induced ubiquitous overexpression of the Wnt/?-catenin pathway antagonist axin1 inhibits axon regeneration (Fischer?s exact test: ***P<0.001) and functional recovery (two-way ANOVA: F1,161=5.319, P<0.05; t-test: ***P<0.001) in lesioned hs:Axin1 transgenic animals. (c) Heat shock-induced ubiquitous overexpression of the Wnt/?-catenin pathway antagonist dkk1 inhibits axon regeneration (Fischer?s exact test: ***P<0.001) in lesioned hs:dkk1 transgenic animals. (d) Pharmacological interference (IWR-1) with Wnt/?-catenin signaling starting at different time points post-lesion indicates that pathway activity is required between 0.5 dpl (12 hpl) and 1 dpl for axon regeneration (Fischer?s exact test: *P<0.05, ***P<0.001, n.s. indicates not significant). (e) Pharmacological (IWR-1) interference with Wnt/?-catenin signaling inhibits axon regeneration (Fischer?s exact test: ***P<0.001) and functional recovery (two-way ANOVA: F1,80=8.708, P<0.0005) in stab-lesioned animals. (a-e) Views are lateral (dorsal is up, rostral is left. BF: brightfield. Scale bars: whole mounts, 200 ?m and 100 ?m. Error bars indicate s.e.m. |