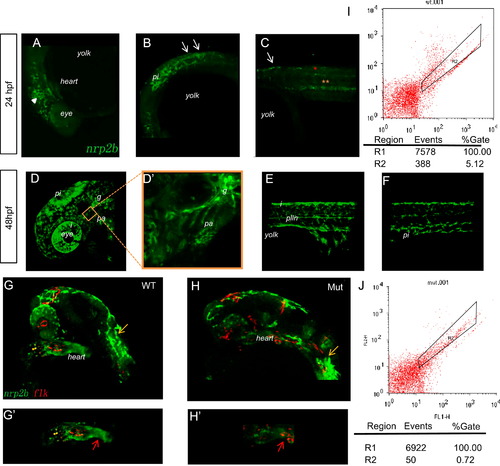
Tracing the migration of cranial NCCs in Et(gata2a:EGFP)pku418 fish line from 24 hpf to 48 hpf. (A)?(F) The dynamic EGFP expression pattern in the head (A, D, D′) and trunk (B, C, E, F) of Et(gata2a:EGFP)pku418 fish line revealed by confocal microscopy. (A)?(C) Pre-migratory and migrating NCCs in the head (white triangle) and on the medial pathway in the anterior trunk (white arrows) at 24 hpf. Gut endoderms are indicated by yellow asterisks and spinal cord neurons by red asterisks. (D)?(F) At 48 hpf, EGFP-positive cells include NCCs in the pharyngeal arches (pa), glial precursors (g), iridophores (i), pigment cells (pi), and Schwann cell precursors of the posterior lateral line nerve (plln). (D′) A higher magnification image of the pharyngeal arch region of (D). Lateral view with anterior to the left and dorsal up. (G)?(H′) Confocal images to reveal the heart region of zebrafish embryos from Et(gata2a:EGFP)pku418 crossed with the Tg(flk:mCherry) fish line. The EGFP-labeled cardiac NCCs are found at the OFT (red arrow) and also spread through the whole heart, but do not overlap with the mCherry-positive endocardial cells (G, G2). The mutant heart has reduced numbers and staining-intensity of cardiac NCCs (H, H′), while the mCherry-labeled endocardial cells and the pigment cells (yellow arrows) remain normal at 24 hpf. (G′, H′) show the heart region of the embryos from (G, H), respectively. (I?J) FACS analyses of the numbers of EGFP-positive cells in the heart from both wild-type and eif3ba mutant embryos (<70 isolated hearts for each genotype, 28 hpf) on the background of the Et(gata2a:EGFP)pku418 fish line. The numbers of EGFP-positive cells in the mutant heart are much fewer than in wild-type embryos. WT, wild type; Mut, eif3ba mutant.
|

