Fig. 3
|
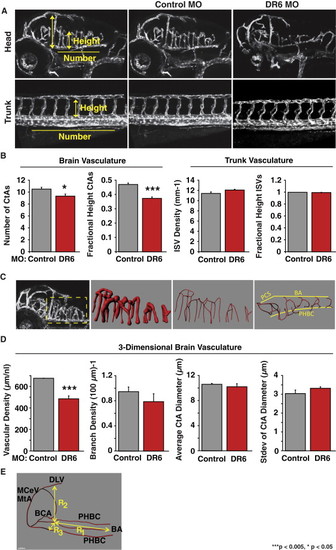
Zebrafish Blood-Brain Barrier Requires DR6 for CNS Angiogenesis (A) Translation-blocking morpholino-mediated DR6 knockdown leads to CNS-specific angiogenic defects in Tg(kdrl:egfp) embryos. Each embryo was treated with 4 ng morpholino. Results representative of at least three independent experiments are shown. MO, morpholino; CtA, central artery; ISV, intersegmental vessels. (B) 2D quantification of 3 dpf zebrafish CNS and trunk vasculature. n = 36 (control_MO), n = 15 (DR6_MO), see Experimental Procedures, Zebrafish Microangiographic Imaging and Quantification, for calculation of the fractional height of CtAs and ISVs. (C) 3D reconstructions of zebrafish hindbrain vasculature were used to create a vascular mask (second panel from the left) to determine vascular density and average CtA diameter. Filament tracing of the vessel-derived eGFP signal (first and second panels from the right) enabled branch density calculations. (D) 3D quantification of 3 dpf zebrafish hindbrain vasculature. Standard deviation of CtA diameter is a metric of irregularity in vessel lumenization. n = 4 (control_MO), n = 6 (DR6_MO). (E) Zebrafish brain volume calculation diagram. The volume of the half brain was approximated as V = R1R2R3. MtA, metencephalic artery; MCeV, middle cerebral vein; DLV, dorsal longitudinal vein; BCA, basal communicating artery; PHBC, primordial hindbrain channel; BA, basilar artery. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM (***p < 0.005; *p < 0.05). See also Figure S3 and mmc3VIDEO, mmc4VIDEO, mmc5VIDEO and mmc6VIDEO. |
| Gene: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Knockdown Reagent: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage: | Protruding-mouth |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagent: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Protruding-mouth |
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 22(2), Tam, S.J., Richmond, D.L., Kaminker, J.S., Modrusan, Z., Martin-McNulty, B., Cao, T.C., Weimer, R.M., Carano, R.A., van Bruggen, N., and Watts, R.J., Death Receptors DR6 and TROY Regulate Brain Vascular Development, 403-417, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell