Fig. S6
|
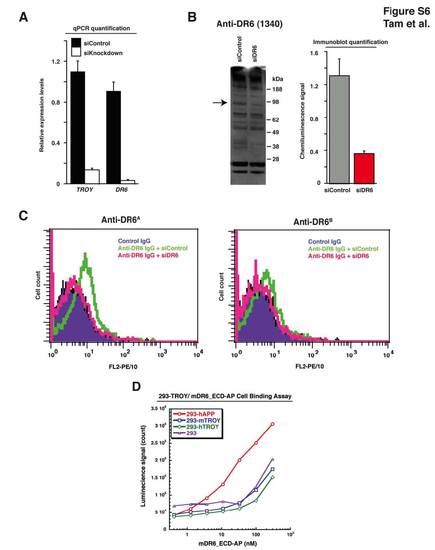
DR6 and TROY Levels Decrease in Response to siRNA-Mediated Knockdown, Anti-DR6 Function-Blocking Antibodies are Specific for DR6 Protein in HBMECs, and DR6/TROY Ectodomains Do Not Directly Interact, Related to Figure 6 (A) qPCR analysis detects knockdown of DR6 and TROY transcript levels upon DR6- and TROY-targeting siRNA transfection in HBMECs. (B) Immunoblot analysis detects knockdown of DR6 protein levels upon DR6-targeting siRNA transfection in HBMECs. Using anti-DR6 antibody 1340, we detect reduction of an approximately 90 kDa band specific to full length DR6 protein. Densitometry quantification of DR6 protein was carried out as described in experimental procedures. (C) Anti-DR6 function-blocking antibodies are DR6-specific in HBMECs. siRNA-mediated knockdown of DR6 abolishes both anti-DR6A and anti-DR6B FACS signal shift. (D) Purified DR6-ectodomain does not directly bind TROY. While hAPP-expressing 293 cells modestly bind DR6 ectodomain, TROY expression does not induce DR6 ectodomain cell binding above background levels. |
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 22(2), Tam, S.J., Richmond, D.L., Kaminker, J.S., Modrusan, Z., Martin-McNulty, B., Cao, T.C., Weimer, R.M., Carano, R.A., van Bruggen, N., and Watts, R.J., Death Receptors DR6 and TROY Regulate Brain Vascular Development, 403-417, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell