Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-111128-37
- Publication
- Gallagher et al., 2011 - Rbfox-regulated alternative splicing is critical for zebrafish cardiac and skeletal muscle functions
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
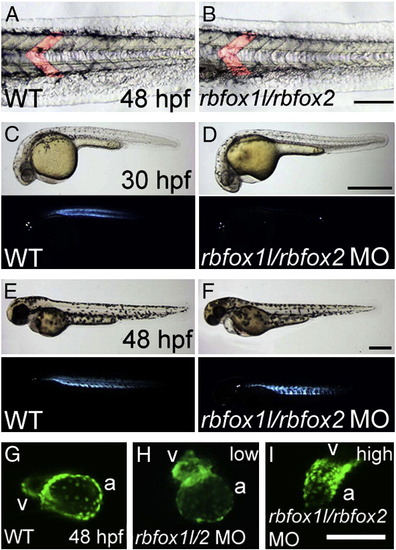
Rbfox1l/Rbfox2 knockdown results in cardiac and skeletal muscle defects. (A, B) In Rbfox double morphants, myotomes are chevron-shaped as in control embryos (lateral view, one myotome is false-colored in each panel). (C?H) Polarized light microscopy reveals that rbfox1l/rbfox2 morphant muscle has delayed birefringence at 30 hpf (compare C with D) that partially recovers by 48 hpf (compare E with F). (G?I) Rbfox1l/Rbfox2 knockdown in myl7-GFP embryos that have GFP + myocardial cells, reveals cardiac muscle defects, with low rbfox1l/rbfox2 MO doses (1.5 ng each) causing ventricular defects and high doses (9 ng each) affecting the morphology of the entire heart. WT = mock-injected; MO = morpholino; a = atrium; v = ventricle. Scale bars = 100 μm (A?B; G?I), 500 μm (C?F). |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage Range: | Prim-15 to Long-pec |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 359(2), Gallagher, T.L., Arribere, J.A., Geurts, P.A., Exner, C.R., McDonald, K.L., Dill, K.K., Marr, H.L., Adkar, S.S., Garnett, A.T., Amacher, S.L., and Conboy, J.G., Rbfox-regulated alternative splicing is critical for zebrafish cardiac and skeletal muscle functions, 251-61, Copyright (2011) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.