Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-111128-34
- Publication
- Gallagher et al., 2011 - Rbfox-regulated alternative splicing is critical for zebrafish cardiac and skeletal muscle functions
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
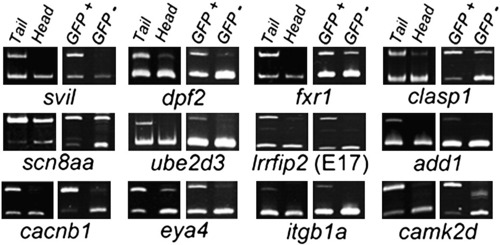
Muscle-enriched splicing of predicted Rbfox-regulated target exons. Semi-quantitative RT-PCR splicing analysis reveals 12 representative alternative exons that are better included in trunk/tail (largely muscle) than head (muscle-poor) fractions at 24 h post fertilization (hpf), as well as in FACS-purified GFP+ muscle versus GFP- cells from actc1b:GFP embryos at 24 hpf. Subsequent analyses show that splicing of 8 of the 12 exons (the top two rows) shown is regulated by rbfox1l and/or rbfox2. Upper product = inclusion isoform; lower product = exclusion isoform. PCR primers and expected band sizes for inclusion and exclusion isoforms are listed in Supplementary Table S1. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 359(2), Gallagher, T.L., Arribere, J.A., Geurts, P.A., Exner, C.R., McDonald, K.L., Dill, K.K., Marr, H.L., Adkar, S.S., Garnett, A.T., Amacher, S.L., and Conboy, J.G., Rbfox-regulated alternative splicing is critical for zebrafish cardiac and skeletal muscle functions, 251-61, Copyright (2011) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.