FIGURE
Fig. s8
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-110622-38
- Publication
- Waxman et al., 2011 - Zebrafish retinoic acid receptors function as context-dependent transcriptional activators
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
Fig. s8
|
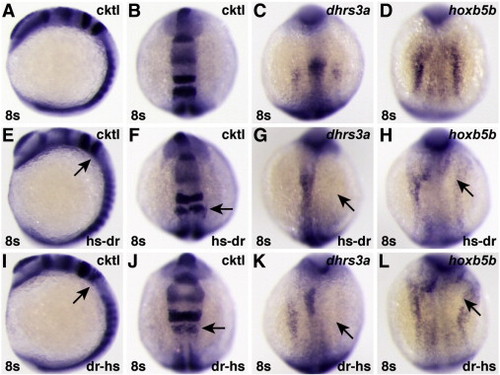
Chimeric human/zebrafish dominant negative RARs can inhibit expression of RA-responsive target genes. (A?D) Uninjected control embryos. (E?H) Embryos injected with mRNA encoding a hs-dr RAR fusion protein, in which the human A?C domains are fused to the zebrafish D?ΔF domains. (I?L) Embryos injected with mRNA encoding a dr-hs RAR fusion protein, in which the zebrafish A?C domains are fused to the human D?ΔF domains. Although neither chimeric protein was as effective as the human dnRARa (Figs. 8O?R), either can inhibit expression of RA-responsive genes. |
Expression Data
Expression Detail
Antibody Labeling
Phenotype Data
Phenotype Detail
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 352(1), Waxman, J.S., and Yelon, D., Zebrafish retinoic acid receptors function as context-dependent transcriptional activators, 128-140, Copyright (2011) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.